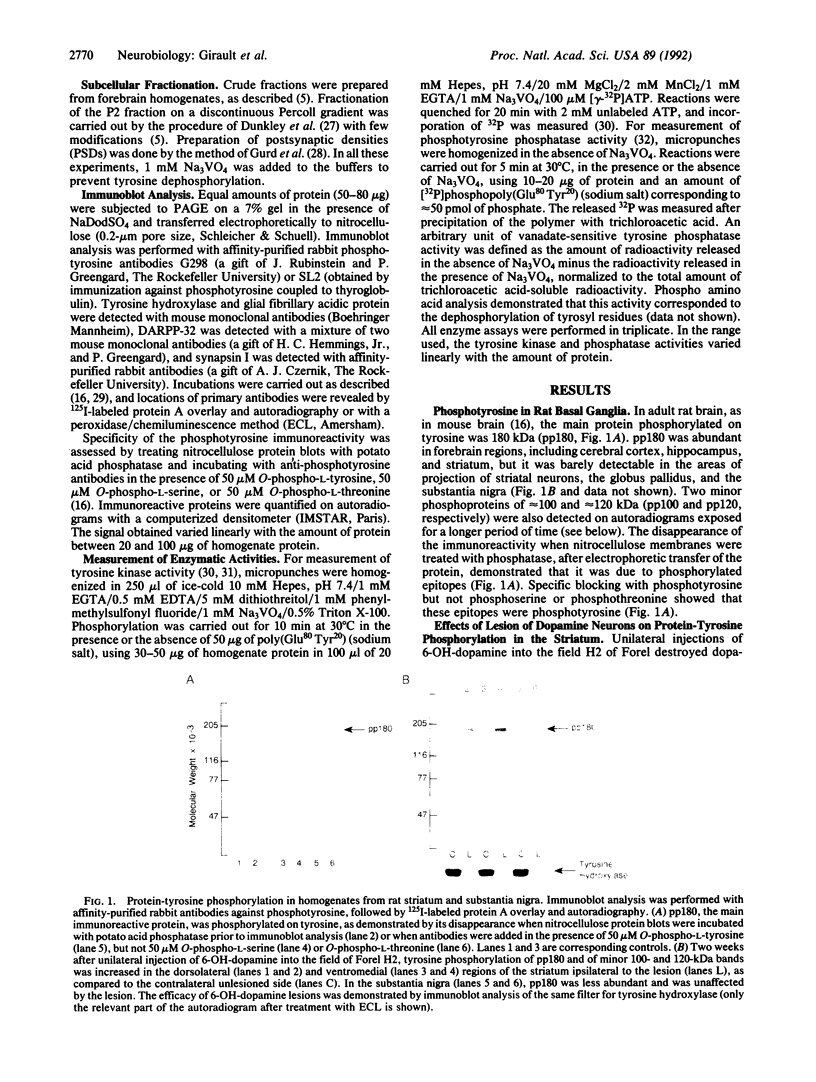
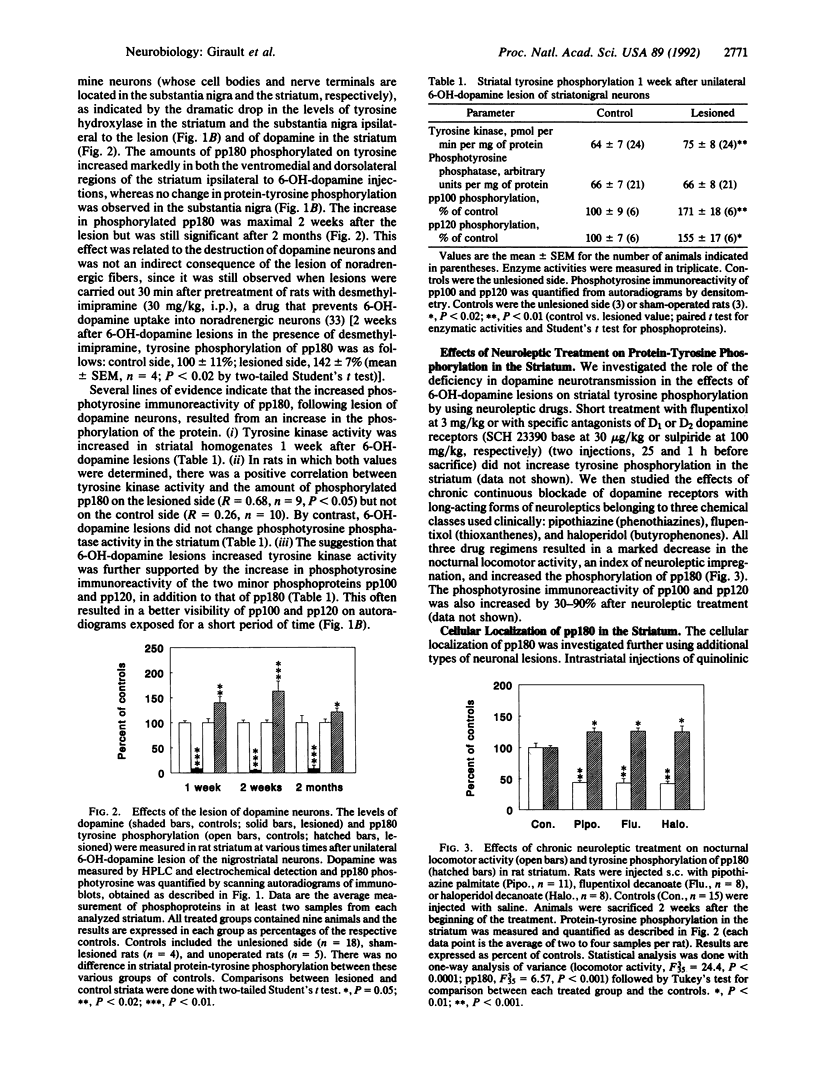
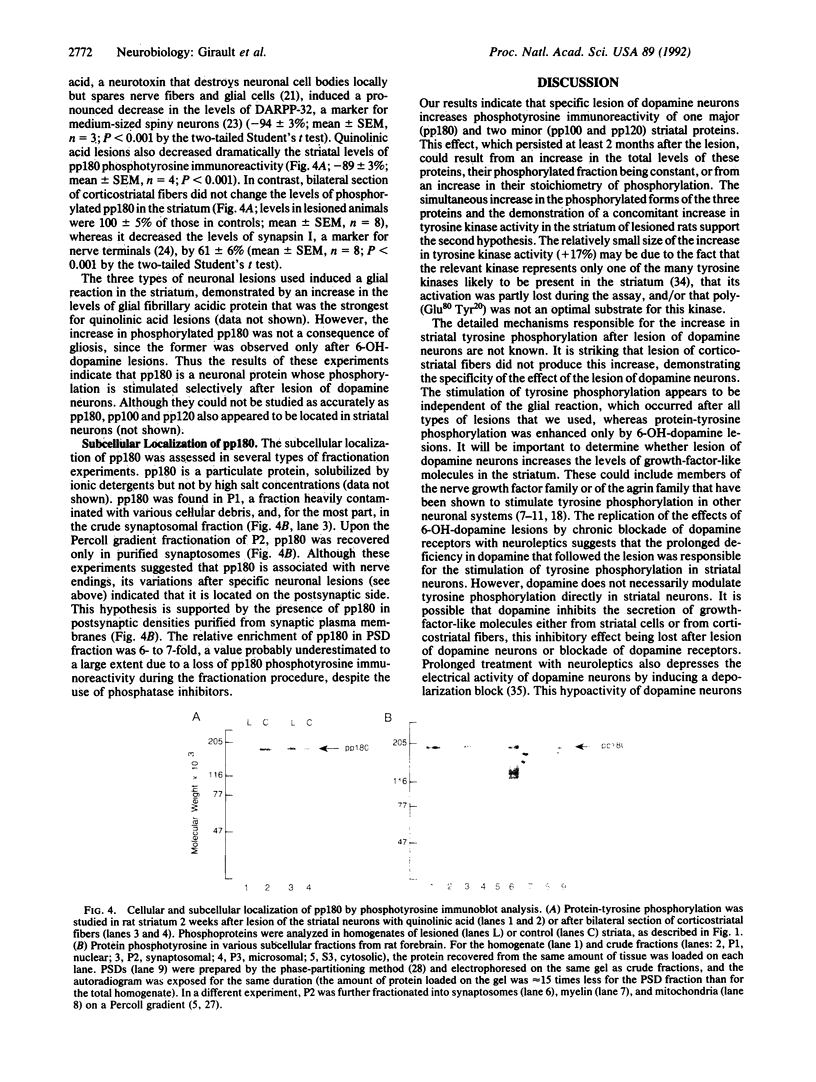
Abstract
Even though the short-term actions of dopamine on postsynaptic receptors are well-characterized, the molecular bases for long-term trophic interactions between dopamine neurons and their targets remain unclear. Since protein-tyrosine phosphorylation plays a key role in the action of trophic factors, we have investigated its possible involvement in the interactions between dopamine neurons and their striatal targets. Lesioning rat nigrostriatal dopamine neurons by using 6-hydroxydopamine increased the phosphorylation on tyrosine of several proteins, including a major 180-kDa protein (pp180) in the ipsilateral striatum. Protein-tyrosine kinase activity was also increased in the striatum ipsilateral to the lesion, whereas no change in phosphotyrosine phosphatase activity was detected. The stimulation of pp180 phosphorylation was observed 1, 2, and 8 weeks after 6-hydroxydopamine lesion, was selective for the destruction of dopamine neurons, and was mimicked by chronic blockade of dopamine receptors with neuroleptics. Additional lesion experiments and subcellular fractionation showed that pp180 is located in neuronal postsynaptic densities, suggesting that pp180 is a postsynaptic component of corticostriatal synapses. Our results indicate that lesion of specific afferent fibers can activate tyrosine phosphorylation in central neurons and suggest that tyrosine phosphorylation is involved in the long-term consequences of dopamine deficiency and may play a role in synaptic plasticity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouyer J. J., Park D. H., Joh T. H., Pickel V. M. Chemical and structural analysis of the relation between cortical inputs and tyrosine hydroxylase-containing terminals in rat neostriatum. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 8;302(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calverley R. K., Jones D. G. Contributions of dendritic spines and perforated synapses to synaptic plasticity. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990 Sep-Dec;15(3):215–249. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(90)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudmore S. B., Gurd J. W. Postnatal age and protein tyrosine phosphorylation at synapses in the developing rat brain. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1240–1248. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley P. R., Jarvie P. E., Heath J. W., Kidd G. J., Rostas J. A. A rapid method for isolation of synaptosomes on Percoll gradients. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 30;372(1):115–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Powell J. F., Smith A. D. Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive boutons in synaptic contact with identified striatonigral neurons, with particular reference to dendritic spines. Neuroscience. 1984 Dec;13(4):1189–1215. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girault J. A., Chamak B., Bertuzzi G., Tixier H., Wang J. K., Pang D. T., Greengard P. Protein phosphotyrosine in mouse brain: developmental changes and regulation by epidermal growth factor, type I insulin-like growth factor, and insulin. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):518–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girault J. A., Horiuchi A., Gustafson E. L., Rosen N. L., Greengard P. Differential expression of ARPP-16 and ARPP-19, two highly related cAMP-regulated phosphoproteins, one of which is specifically associated with dopamine-innervated brain regions. J Neurosci. 1990 Apr;10(4):1124–1133. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-04-01124.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girault J. A., Raisman-Vozari R., Agid Y., Greengard P. Striatal phosphoproteins in Parkinson disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2493–2497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girault J. A., Walaas S. I., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P. ARPP-21, a cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions: tissue distribution and regulation of phosphorylation in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1990;37(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90402-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace A. A., Bunney B. S. Induction of depolarization block in midbrain dopamine neurons by repeated administration of haloperidol: analysis using in vivo intracellular recording. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Sep;238(3):1092–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd J. W., Bissoon N. Phosphorylation of proteins of the postsynaptic density: effect of development on protein tyrosine kinase and phosphorylation of the postsynaptic density glycoprotein, PSD-GP180. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Mar;25(3):336–344. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490250310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd J. W., Gordon-Weeks P., Evans W. H. Biochemical and morphological comparison of postsynaptic densities prepared from rat, hamster, and monkey brains by phase partitioning. J Neurochem. 1982 Oct;39(4):1117–1124. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb11504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd J. W. Phosphorylation of the postsynaptic density glycoprotein gp180 by endogenous tyrosine kinase. Brain Res. 1985 May 6;333(2):385–388. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91599-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpain S., Girault J. A., Greengard P. Activation of NMDA receptors induces dephosphorylation of DARPP-32 in rat striatal slices. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):369–372. doi: 10.1038/343369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herve D., Trovero F., Blanc G., Thierry A. M., Glowinski J., Tassin J. P. Nondopaminergic prefrontocortical efferent fibers modulate D1 receptor denervation supersensitivity in specific regions of the rat striatum. J Neurosci. 1989 Nov;9(11):3699–3708. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-11-03699.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A. A., Greengard P., Huganir R. L. Protein tyrosine kinase activity and its endogenous substrates in rat brain: a subcellular and regional survey. J Neurochem. 1988 May;50(5):1447–1455. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. H., Iversen S. D. Selective 6OHDA-induced destruction of mesolimbic dopamine neurons: abolition of psychostimulant-induced locomotor activity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;40(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90352-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C., Lemke G. An extended family of protein-tyrosine kinase genes differentially expressed in the vertebrate nervous system. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):691–704. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMoal M., Stinus L., Galey D. Radiofrequency lesion of the ventral mesencephalic tegmentum: neurological and behavioral considerations. Exp Neurol. 1976 Mar;50(3):521–535. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(76)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Nerve growth factor induces protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6788–6791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Tissue-dependent regulation of protein tyrosine kinase activity during embryonic development. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):955–963. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshul C. K., Casey D. E. Regional, reversible ultrastructural changes in rat brain with chronic neuroleptic treatment. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 12;489(2):338–346. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90867-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouimet C. C., Miller P. E., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Walaas S. I., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. III. Immunocytochemical localization. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):111–124. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng H. B., Baker L. P., Chen Q. Induction of synaptic development in cultured muscle cells by basic fibroblast growth factor. Neuron. 1991 Feb;6(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90359-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu Z. C., Moritz E., Huganir R. L. Regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at the rat neuromuscular junction. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90049-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarcz R., Whetsell W. O., Jr, Mangano R. M. Quinolinic acid: an endogenous metabolite that produces axon-sparing lesions in rat brain. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):316–318. doi: 10.1126/science.6849138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppet D., Escandon E., Maragos J., Middlemas D. S., Reid S. W., Blair J., Burton L. E., Stanton B. R., Kaplan D. R., Hunter T. The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):895–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90396-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Stitt T. N., Aldrich T. H., Davis S., Bianco S. M., Radziejewski C., Glass D. J., Masiakowski P., Furth M. E., Valenzuela D. M. trkB encodes a functional receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 but not nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90395-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Subrahmanyam G. Purification and characterization of a protein-phosphotyrosine phosphatase from rat spleen which dephosphorylates and inactivates a tyrosine-specific protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7801–7808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uranova N. A., Orlovskaya D. D., Apel K., Klintsova A. J., Haselhorst U., Schenk H. Morphometric study of synaptic patterns in the rat caudate nucleus and hippocampus under haloperidol treatment. Synapse. 1991 Apr;7(4):253–259. doi: 10.1002/syn.890070402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner K. R., Mei L., Huganir R. L. Protein tyrosine kinases and phosphatases in the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Jun;1(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(91)90011-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Aswad D. W., Greengard P. A dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):69–71. doi: 10.1038/301069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Jahn R., Greengard P. Quantitation of nerve terminal populations: synaptic vesicle-associated proteins as markers for synaptic density in the rat neostriatum. Synapse. 1988;2(5):516–520. doi: 10.1002/syn.890020507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. G., Qu Z., Huganir R. L. Agrin induces phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):869–878. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90227-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]