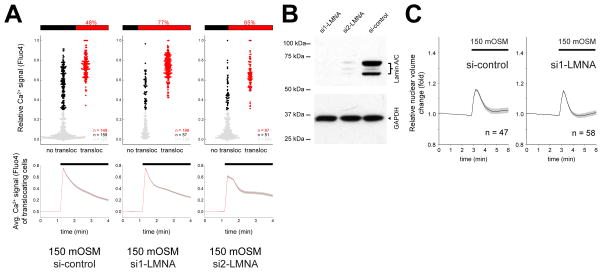
Figure 4. Lamin A/C inhibits cPla2 translocation after osmotic shock of HeLa cells.
(A) Parallel measurements of cytoplasmic Ca2+ signals and cPla2-mK2 translocation to the nuclear membrane in control (si-control) and LMNA knockdown HeLa cells (si1-LMNA and si2-LMNA). Ca2+ signals were stimulated by hypotonic swelling (150 mOSM), and the efficiency of Ca2+ signals to induce cPla2-mK2 translocation was assessed. The data representation is analogous to Fig. 2D and is explained there. n, number of cells.
(B) Western blot of Lamin A/C knockdown (si1-LMNA and si2-LMNA) and control siRNA treated HeLa cells.
(C) Average nuclear volume evolution after hypotonic shock in Lamin A/C knockdown (si1-LMNA) and control siRNA treated HeLa cells, measured by confocal imaging of nuclear targeted EGFP. Error bars, SEM. n, number of cells.