Abstract
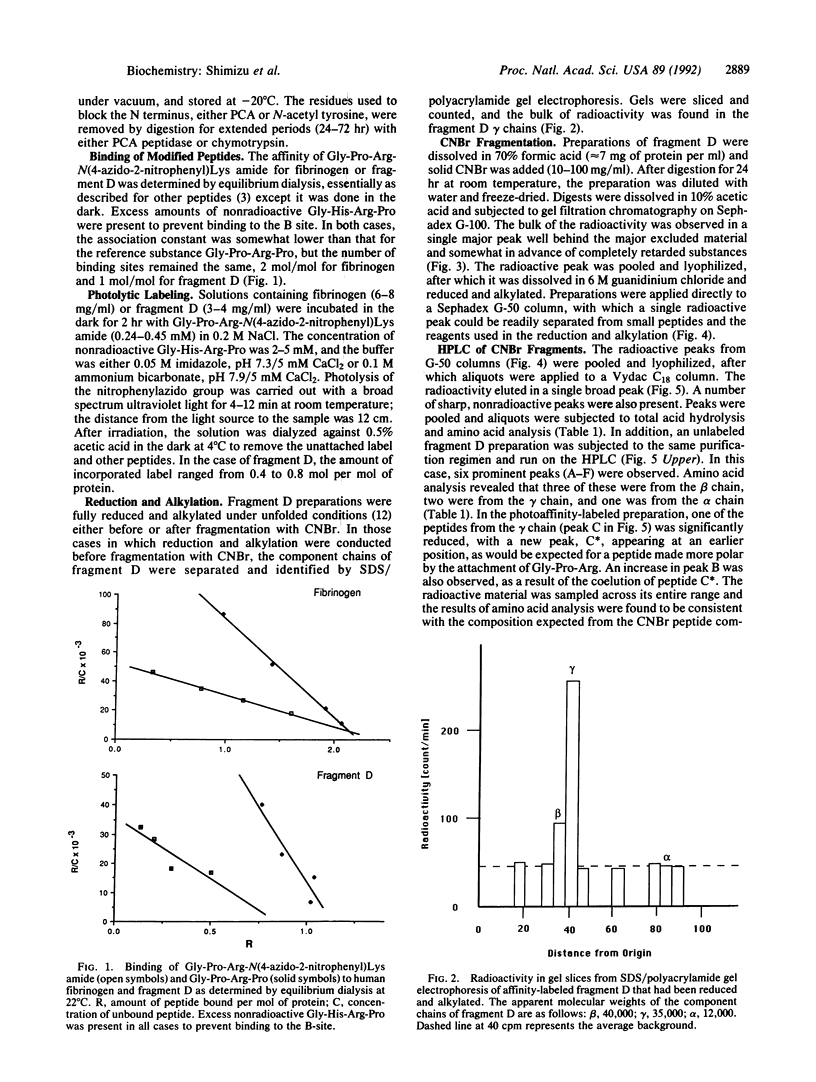
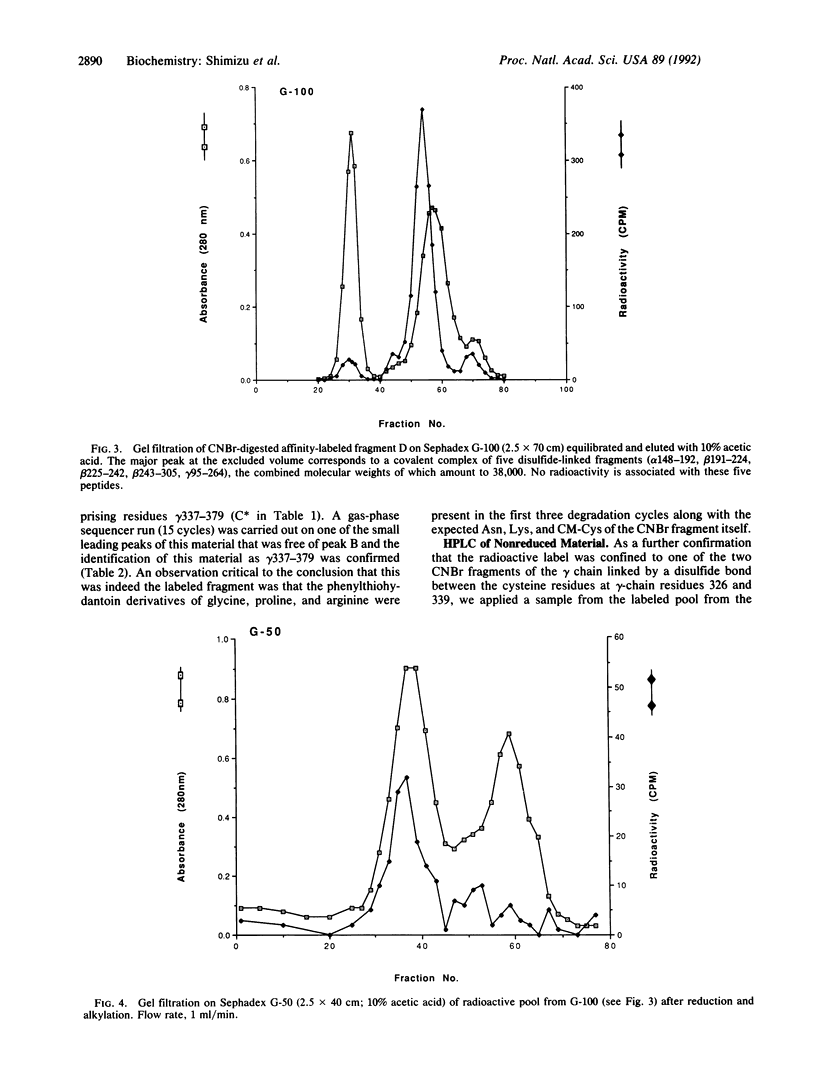
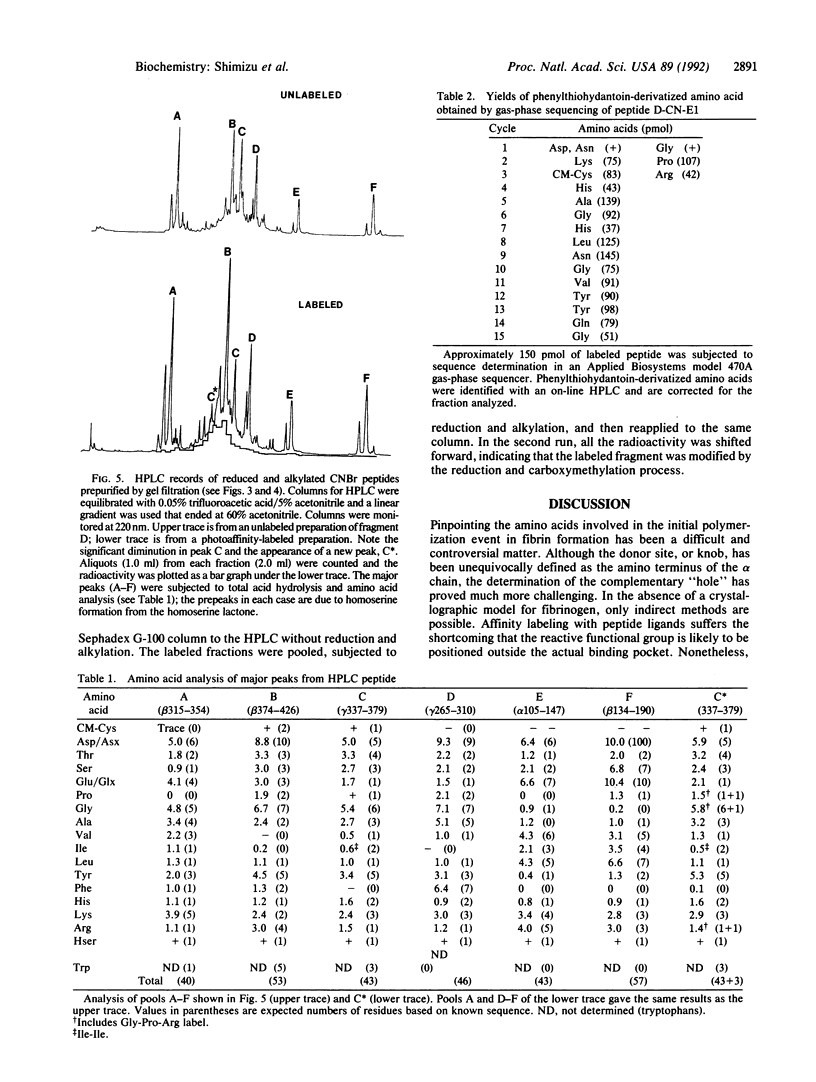
Human fibrinogen and the plasmin-generated fibrinogen fragment D were photoaffinity labeled specifically with the peptide [14C]Gly-Pro-Arg-N(4-azido-2-nitrophenyl)Lys amide. In the case of fibrinogen, greater than 85% of the incorporated radioactivity was found in the gamma chain. Similarly, when fragment D (Mr, 90,000) was labeled with the same derivatized peptide, virtually all the radioactivity was found in the gamma-chain portion. The labeled fragment D was treated with CNBr and an initial purification was achieved by two gel-filtration steps. The labeled material was purified further by HPLC and was also compared with CNBr digests of unlabeled material. Amino acid analysis and gas-phase sequencing showed the labeled fragment to be gamma-chain residues 337-379.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouma H., Takagi T., Doolittle R. F. The arrangement of disulfide bonds in fragment D from human fibrinogen. Thromb Res. 1978 Sep;13(3):557–562. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Cassman K. G., Cottrell B. A., Friezner S. J., Takagi T. Amino acid sequence studies on the alpha chain of human fibrinogen. Covalent structure of the alpha-chain portion of fragment D. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 19;16(8):1710–1715. doi: 10.1021/bi00627a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:195–229. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Schubert D., Schwartz S. A. Amino acid sequence studies on artiodactyl fibrinopeptides. I. Dromedary camel, mule deer, and cape buffalo. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Feb;118(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkate F., Timan G. Protective effect of calcium in the plasmin degradation of fibrinogen and fibrin fragments D. Thromb Res. 1977 Jun;10(6):803–812. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. H., Váradi A., Scheraga H. A. Localization of a fibrin gamma-chain polymerization site within segment Thr-374 to Glu-396 of human fibrinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5980–5984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuyas C., Haeberli A., Walder P., Straub P. W. Isolation of human fibrinogen and its derivatives by affinity chromatography on Gly-Pro-Arg-Pro-Lys-Fractogel. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Jun 28;63(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Studies on synthetic peptides that bind to fibrinogen and prevent fibrin polymerization. Structural requirements, number of binding sites, and species differences. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):1013–1019. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Synthetic peptide derivatives that bind to fibrinogen and prevent the polymerization of fibrin monomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3085–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottspeich F., Henschen A. Amino acid sequence of human fibrin. Preliminary note on the completion of the gamma-chain sequence. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Jul;358(7):935–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSENZWEIG V., SELIGMANN M., PELMONT J., GRABAR P. [The products of degradation of human fibrinogen by plasmin. I. Separation and physicochemical properties]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1961 Mar;100:377–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olexa S. A., Budzynski A. Z. Localization of a fibrin polymerization site. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3544–3549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southan C., Thompson E., Panico M., Etienne T., Morris H. R., Lane D. A. Characterization of peptides cleaved by plasmin from the C-terminal polymerization domain of human fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13095–13101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Váradi A., Scheraga H. A. Localization of segments essential for polymerization and for calcium binding in the gamma-chain of human fibrinogen. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 11;25(3):519–528. doi: 10.1021/bi00351a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazumi K., Doolittle R. F. Photoaffinity labeling of the primary fibrin polymerization site: localization of the label to gamma-chain Tyr-363. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2893–2896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



