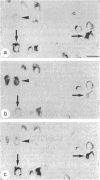
Abstract
The chromogranins A and B (CgA and CgB, respectively), originally detected in the adrenal medulla, are present in various endocrine organs. Remarkably, their immunoreactivities vary among different endocrine cell types and also within a given endocrine cell population. With densitometric techniques at the cellular level, individual gastrin cells (n = 318) from guinea pig antral mucosa were studied to measure their content of immunoreactive CgA, CgB, and gastrin. The composition of these secretory proteins in individual gastrin cells varied considerably but with predictable components. Statistical evaluation of the data showed that immunoreactivities for gastrin and CgA correlated negatively in these cells; CgA and CgB immunoreactivities also correlated inversely. On the other hand, immunoreactivities for gastrin and CgB exhibited a high positive correlation. The mutual relationships between gastrin, CgA, and CgB suggest that under physiological conditions biosynthetic pathways of these secretory constituents are linked to each other in individual gastrin cells.
Full text
PDF
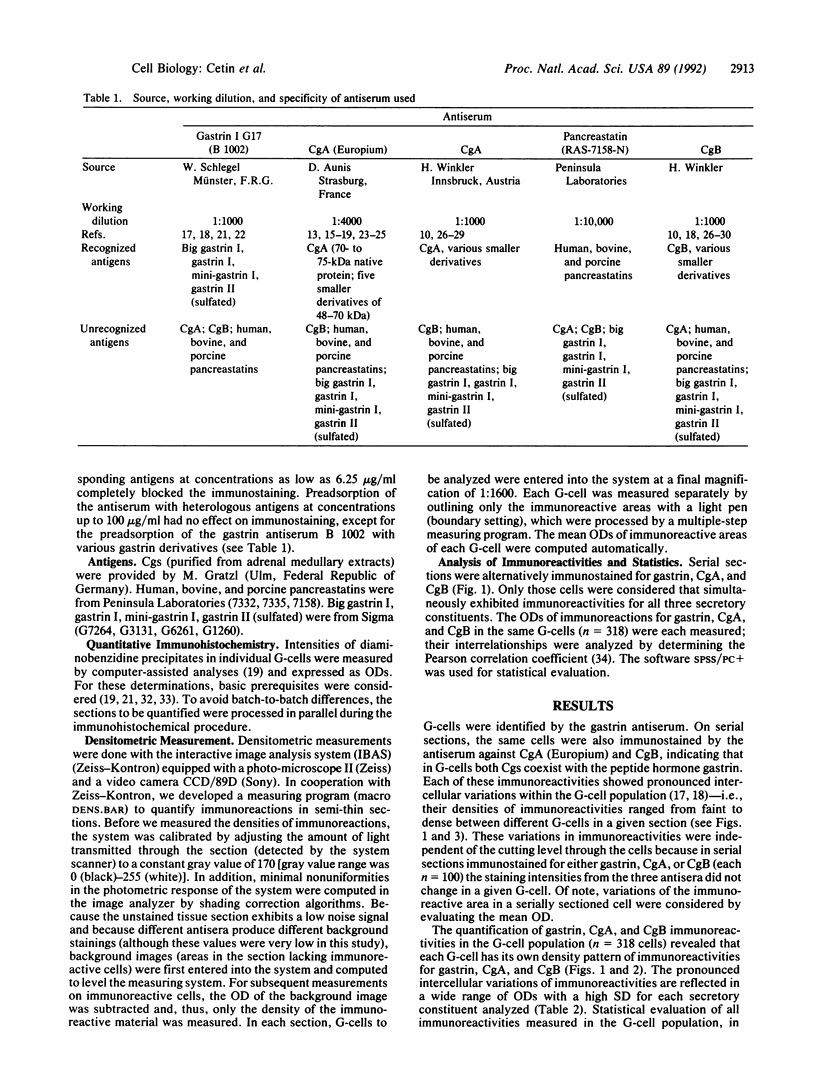
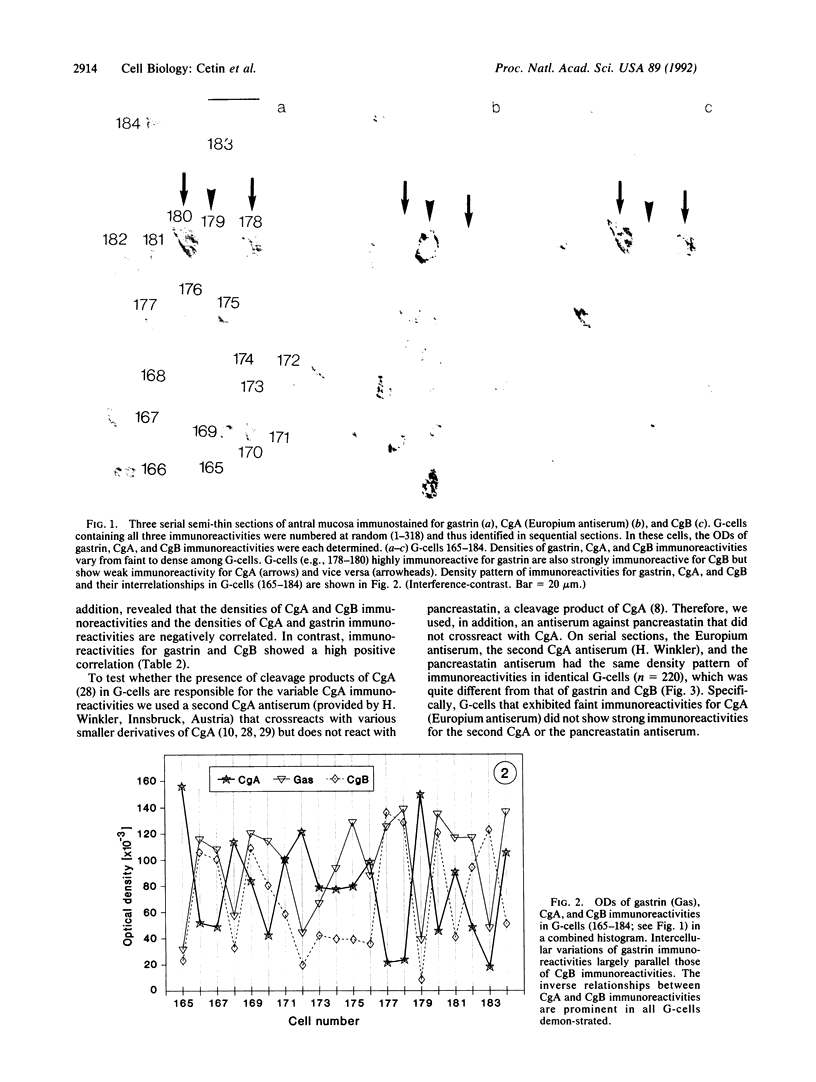


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbosa J. A., Gill B. M., Takiyyuddin M. A., O'Connor D. T. Chromogranin A: posttranslational modifications in secretory granules. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):174–190. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedum U. M., Baeuerle P. A., Konecki D. S., Frank R., Powell J., Mallet J., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of bovine chromogranin A: a representative of a class of acidic secretory proteins common to a variety of peptidergic cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1495–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetin Y., Grube D. Immunoreactivities for chromogranin A and B, and secretogranin II in the guinea pig entero-endocrine system: cellular distributions and intercellular heterogeneities. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 May;264(2):231–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00313960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cetin Y., Müller-Köppel L., Aunis D., Bader M. F., Grube D. Chromogranin A (CgA) in the gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) endocrine system. II. CgA in mammalian entero-endocrine cells. Histochemistry. 1989;92(4):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00500540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty D., Yamada T. Posttranslational processing of gastrin. Physiol Rev. 1989 Apr;69(2):482–502. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.2.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efendić S., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Quan C., Chang D., Ostenson C. G. Pancreastatin and islet hormone release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7257–7260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart M., Grube D., Bader M. F., Aunis D., Gratzl M. Chromogranin A in the pancreatic islet: cellular and subcellular distribution. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Dec;34(12):1673–1682. doi: 10.1177/34.12.2878021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart M., Jörns A., Grube D., Gratzl M. Cellular distribution and amount of chromogranin A in bovine endocrine pancreas. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 May;36(5):467–472. doi: 10.1177/36.5.3282005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Huttner W. B., Mallet J., O'Connor D. T., Winkler H., Zanini A. A nomenclature proposal for the chromogranin/secretogranin proteins. Neuroscience. 1987 Jun;21(3):1019–1021. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Iacangelo A., Hsu C. M., Hotchkiss A. J., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Chromogranin A synthesis and secretion in chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1987 Jul;49(1):65–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb03395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E. Is chromogranin a prohormone? Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):301–301. doi: 10.1038/325301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkensammer G., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Biogenesis of chromaffin granules: incorporation of sulfate into chromogranin B and into a proteoglycan. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1475–1480. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Frischenschlager I. Immunological characterization of secretory proteins of chromaffin granules: chromogranins A, chromogranins B, and enkephalin-containing peptides. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1854–1861. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Hagn C., Schober M. Chromogranins A, B, and C: widespread constituents of secretory vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:120–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Iacangelo A., Eiden L. E. Neural and humoral factors separately regulate neuropeptide Y, enkephalin, and chromogranin A and B mRNA levels in rat adrenal medulla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3240–3244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greeley G. H., Jr, Thompson J. C., Ishizuka J., Cooper C. W., Levine M. A., Gorr S. U., Cohn D. V. Inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin release in the perfused rat pancreas by parathyroid secretory protein-I (chromogranin-A). Endocrinology. 1989 Mar;124(3):1235–1238. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-3-1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grube D., Aunis D., Bader F., Cetin Y., Jörns A., Yoshie S. Chromogranin A (CGA) in the gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) endocrine system. I. CGA in the mammalian endocrine pancreas. Histochemistry. 1986;85(6):441–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00508425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grube D., Kusumoto Y. Serial semithin sections in immunohistochemistry: techniques and applications. Arch Histol Jpn. 1986 Oct;49(4):391–410. doi: 10.1679/aohc.49.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagn C., Schmid K. W., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Chromogranin A, B, and C in human adrenal medulla and endocrine tissues. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):405–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Gerdes H. H., Rosa P. The granin (chromogranin/secretogranin) family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jan;16(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90012-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutton J. C., Davidson H. W., Grimaldi K. A., Peshavaria M. Biosynthesis of betagranin in pancreatic beta-cells. Identification of a chromogranin A-like precursor and its parallel processing with proinsulin. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):449–456. doi: 10.1042/bj2440449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfle G., Weiler R., Fischer-Colbrie R., Humpel C., Laslop A., Wohlfarter T., Hogue-Angeletti R., Saria A., Fleming P. J., Winkler H. Stimulation of rat adrenal medulla can induce differential changes in the peptide and mRNA levels of chromogranins, neuropeptides and other constituents of chromaffin granules. Regul Pept. 1991 Feb 26;32(3):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90025-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A. L., Fischer-Colbrie R., Koller K. J., Brownstein M. J., Eiden L. E. The sequence of porcine chromogranin A messenger RNA demonstrates chromogranin A can serve as the precursor for the biologically active hormone, pancreastatin. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2339–2341. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Affolter H. U., Eiden L. E., Herbert E., Grimes M. Bovine chromogranin A sequence and distribution of its messenger RNA in endocrine tissues. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):82–86. doi: 10.1038/323082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYOR H. D., HAMPTON J. C., ROSARIO B. A simple method for removing the resin from epoxy-embedded tissue. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Apr;9:909–910. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.4.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mize R. R., Holdefer R. N., Nabors L. B. Quantitative immunocytochemistry using an image analyzer. I. Hardware evaluation, image processing, and data analysis. J Neurosci Methods. 1988 Nov;26(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(88)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch D. M., Iacangelo A. L., Eiden L. E. Glucocorticoid- and nerve growth factor-induced changes in chromogranin A expression define two different neuronal phenotypes in PC12 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;2(10):921–927. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-10-921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzola M., Efendic S., Ostenson C. G., Tatemoto K., Hutton J. C., Orci L. Localization of pancreastatin immunoreactivity in porcine endocrine cells. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):227–229. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfeld J. F., Bardram L., Cantor P., Hilsted L., Schwartz T. W. Cell-specific processing of pro-cholecystokinin and pro-gastrin. Biochimie. 1988 Jan;70(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieker S., Fischer-Colbrie R., Eiden L., Winkler H. Phylogenetic distribution of peptides related to chromogranins A and B. J Neurochem. 1988 Apr;50(4):1066–1073. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb10574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindi G., Buffa R., Sessa F., Tortora O., Solcia E. Chromogranin A, B and C immunoreactivities of mammalian endocrine cells. Distribution, distinction from costored hormones/prohormones and relationship with the argyrophil component of secretory granules. Histochemistry. 1986;85(1):19–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00508649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Weiss U., Pepperkok R., Ansorge W., Niehrs C., Stelzer E. H., Huttner W. B. An antibody against secretogranin I (chromogranin B) is packaged into secretory granules. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):17–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scammell J. G., Rosa P., Hille A., Huttner W. B. Regulation of chromogranin B/secretogranin I and secretogranin II storage in GH4C1 cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Jul;38(7):949–956. doi: 10.1177/38.7.2192000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Raptis S. A reliable method for generating antibodies against pancreozymin, secretin and gastrin. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Dec;73(3):439–444. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Hendy G. N., Hamelin J., Paquin J., Lazure C., Metters K. M., Rossier J., Chrétien M. Chromogranin A can act as a reversible processing enzyme inhibitor. Evidence from the inhibition of the IRCM-serine protease 1 cleavage of pro-enkephalin and ACTH at pairs of basic amino acids. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81425-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sietzen M., Schober M., Fischer-Colbrie R., Scherman D., Sperk G., Winkler H. Rat adrenal medulla: levels of chromogranins, enkephalins, dopamine beta-hydroxylase and of the amine transporter are changed by nervous activity and hypophysectomy. Neuroscience. 1987 Jul;22(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Effect of secretagogues on chromogranin A synthesis in bovine cultured chromaffin cells. Possible regulation by protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 15;260(3):915–922. doi: 10.1042/bj2600915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Secretion from chromaffin cells is controlled by chromogranin A-derived peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1712–1716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm A., Funakoshi A., Efendić S., Ostenson C. G., Hellerström C. Long term inhibitory effects of pancreastatin and diazepam binding inhibitor on pancreatic beta-cell deoxyribonucleic acid replication, polyamine content, and insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1991 Jun;128(6):3277–3282. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-6-3277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobhani I., Elouaer-Blanc L., Pauwels S., Lehy T., Rahier J., Mignon M., Bonfils S., Lewin M. J. Gastrin processing in primary culture of gastrinoma cells. Horm Res. 1989;32(1-3):71–73. doi: 10.1159/000181248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waschek J. A., Pruss R. M., Siegel R. E., Eiden L. E., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Regulation of enkephalin, VIP, and chromogranin biosynthesis in actively secreting chromaffin cells. Multiple strategies for multiple peptides. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:308–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler R., Meyerson G., Fischer-Colbrie R., Laslop A., Påhlman S., Floor E., Winkler H. Divergent changes of chromogranin A/secretogranin II levels in differentiating human neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):27–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80875-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Huttner W. B. Synaptophysin and chromogranins/secretogranins--widespread constituents of distinct types of neuroendocrine vesicles and new tools in tumor diagnosis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;58(2):95–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02890062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Apps D. K., Fischer-Colbrie R. The molecular function of adrenal chromaffin granules: established facts and unresolved topics. Neuroscience. 1986 Jun;18(2):261–290. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. V., Sumii K., Walsh J. H. Studies of regulation of gastrin synthesis and post-translational processing by molecular biology approaches. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;597:17–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]