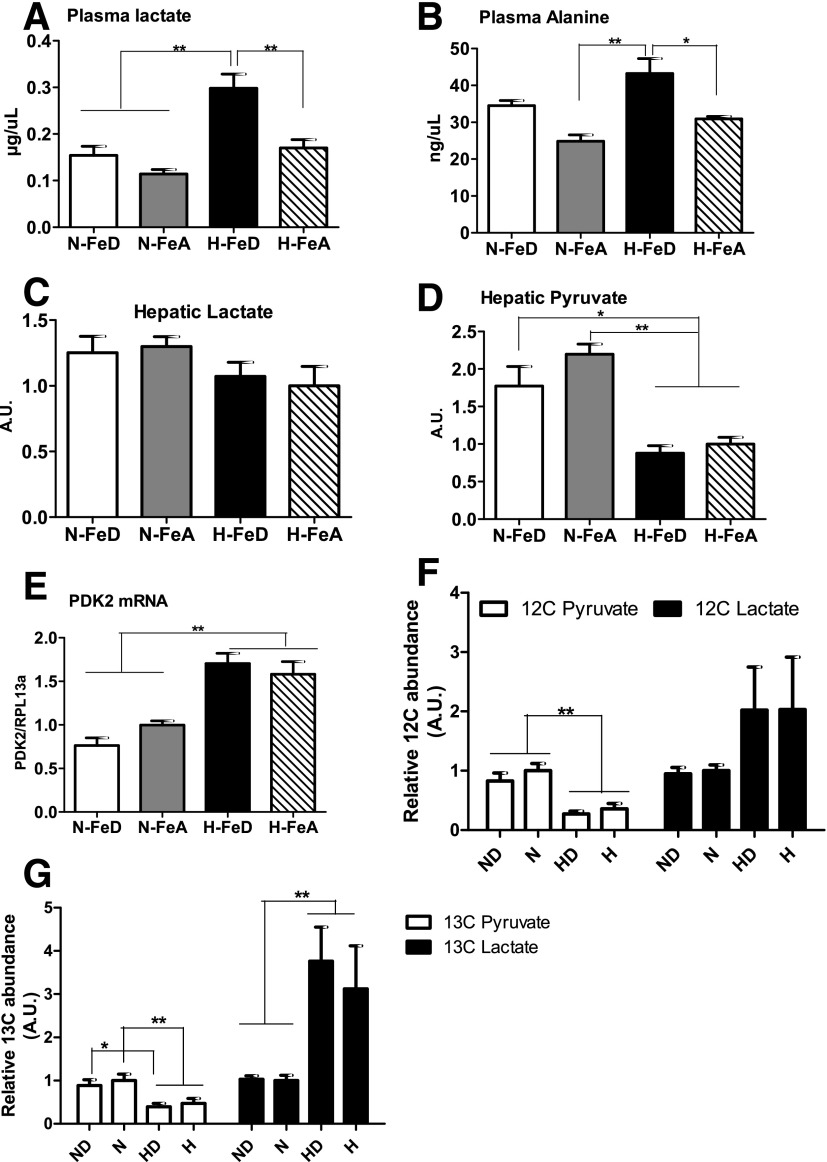
Figure 4.
Hypoxia with iron deficiency upregulates plasma levels of gluconeogenic substrates, and glucose is preferentially converted into lactate rather than pyruvate. Levels of plasma lactate (A) and alanine (B) were analyzed in N-FeD, N-FeA, H-FeD, and H-FeA mice. The levels of hepatic lactate (C) and pyruvate (D) were measured by GC-MS in freeze-clamped liver tissue. E: Relative mRNA abundance of PDK2, normalized to levels of RPL13a, was determined by quantitative RT-PCR in mouse liver. Values are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 4–5 per group). F: HepG2 cells were incubated at normoxia in absence or presence of 100 μmol/L DFO. HepG2 cells were exposed to hypoxia (1% O2 [H]) without or with iron depletion for 24 h. Relative abundances of [12C]lactate and pyruvate were quantified with GC-MS. G: After 24 h incubation with uniformly labeled [13C6]glucose in HepG2 cells, the levels of [U-13C]pyruvate and [U-13C]lactate were measured using GC-MS. The bars represent the mean ± SE of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. A.U., arbitrary units. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 indicate the difference among the groups.