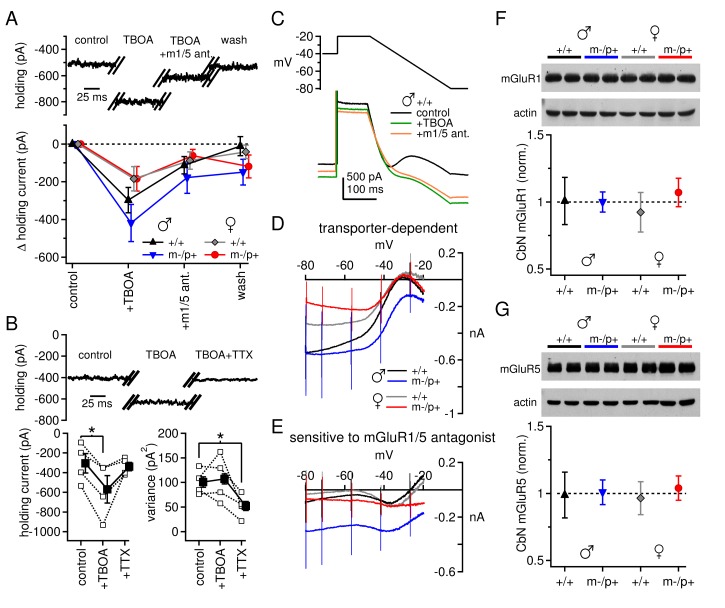
Figure 3. Differences in mGluR1/5-dependent currents depend on glutamate access to receptors rather than receptor expression.
(A) Increase in holding current in a +/+ male mouse by TBOA reversal by group I mGluR antagonists. (B) Increase in holding current by TBOA reversal by TTX. Top: sample traces from a C57BL/6 male mouse. Bottom: summary data for current amplitude (left) and variance (right). (C) Voltage ramp (top) and current (bottom) for a +/+ male in control, TBOA, and TBOA + mGluR1/5 antagonist(s). Each current is the mean of three traces. (D) Transporter-induced current (control current minus current in TBOA) vs. voltage. (E) TBOA-induced current sensitive to mGluR1/5 antagonist(s) (current in TBOA minus current in TBOA + mGluR1/5 antagonist), vs. voltage. In all figures, 'm1/5 ant.' indicates either CPCCOEt or JNJ16259685 + MPEP. (F) Representative blot (top) and summary (bottom) for normalized mGluR1 protein expression in the CbN of Gabrb3 mice. (G) As in (F), for mGluR5.