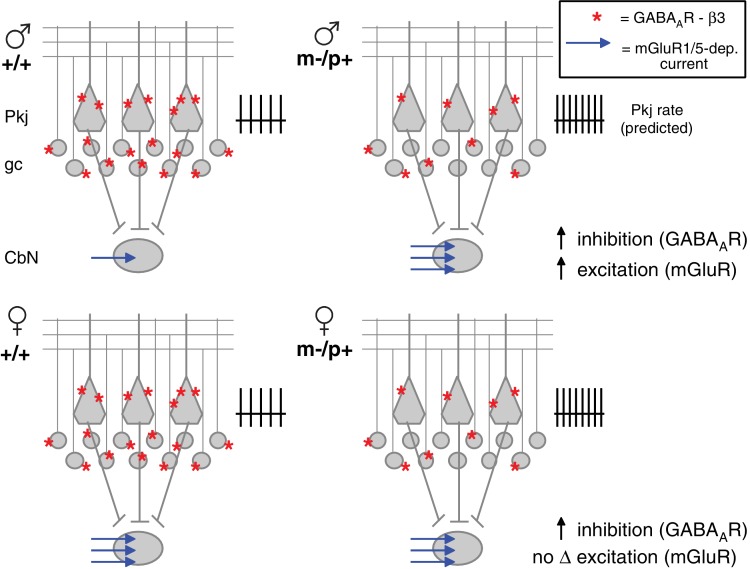
Figure 8. Diagram of sex differences in mGluR1/5 and compensatory changes in males with loss of GABAAR β3.
(Top:) Expected relative levels of GABAAR β3 expression (red asterisks) in the cerebellar cortex, and mGluR1/5-dependent current amplitude (blue arrows) in large CbN cells. For simplicity, only Purkinje cells (Pkj), granule cells (gc), and large CbN cells are depicted. The m-/p+ mutation reduces β3 expression, predicting a disinhibition of granule and Purkinje cells. The resulting increase in Purkinje cell firing rates should increase inhibition of CbN cells. (Top: ) Mutant males counteract the predicted increase in inhibition with increased via mGluR1/5-dependent inward currents. (Bottom: ) Wild-type females have more mGluR1/5-dependent current than wild-type males and presumably balance excitation and inhibition through other means. Mutant females do not up-regulate mGluR1/5-dependent current, and apparently do not compensate for the increased inhibition.