Abstract
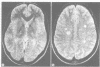
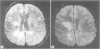
Forty one moderately impaired patients with clinically confirmed multiple sclerosis (MS) and a relapsing-remitting course were submitted to a neuropsychological battery and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to correlate the neuropsychological performances with the degree of cerebral demyelination. The neuropsychological results were indicative of a very mild overall impairment. The patients were subdivided into two groups (extensive periventricular demyelination or discrete lesions on MRI) and the results of neuropsychological tests compared. Patients with extensive periventricular demyelination had an inferior performance on concept formation, non-verbal reasoning and verbal memory tests.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basso A., Capitani E., Laiacona M. Raven's coloured progressive matrices: normative values on 305 adult normal controls. Funct Neurol. 1987 Apr-Jun;2(2):189–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Antona R., Baron J. C., Samson Y., Serdaru M., Viader F., Agid Y., Cambier J. Subcortical dementia. Frontal cortex hypometabolism detected by positron tomography in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain. 1985 Sep;108(Pt 3):785–799. doi: 10.1093/brain/108.3.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Renzi E., Faglioni P. Normative data and screening power of a shortened version of the Token Test. Cortex. 1978 Mar;14(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(78)80006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin G. M., Heaton R. K., Nelson L. M., Filley C. M., Seibert C. Correlation of neuropsychological and MRI findings in chronic/progressive multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1988 Dec;38(12):1826–1829. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.12.1826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton R. K., Nelson L. M., Thompson D. S., Burks J. S., Franklin G. M. Neuropsychological findings in relapsing-remitting and chronic-progressive multiple sclerosis. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1985 Feb;53(1):103–110. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.53.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. J., Paulson G. W., Shuttleworth E. C., Chakeres D., Clapp L. E., Pakalnis A., Weiss K., Rammohan K. Magnetic resonance imaging correlates of dementia in multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1987 Jul;44(7):732–736. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520190040015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., Kinkel W. R., Polachini I., Kinkel R. P. Correlations of nuclear magnetic resonance imaging, computerized tomography, and clinical profiles in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1986 Jan;36(1):27–34. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshner H. S., Tsai S. I., Runge V. M., Price A. C. Magnetic resonance imaging and other techniques in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1985 Sep;42(9):859–863. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060080037013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1444–1452. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon-Caen O., Jouvent R., Hauser S., Chaunu M. P., Benoit N., Widlöcher D., Lhermitte F. Cognitive function in recent-onset demyelinating diseases. Arch Neurol. 1986 Nov;43(11):1138–1141. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520110034010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medaer R., Nelissen E., Appel B., Swerts M., Geutjens J., Callaert H. Magnetic resonance imaging and cognitive functioning in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol. 1987 Dec;235(2):86–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00718015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield R. C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia. 1971 Mar;9(1):97–113. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(71)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orsini A., Grossi D., Capitani E., Laiacona M., Papagno C., Vallar G. Verbal and spatial immediate memory span: normative data from 1355 adults and 1112 children. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1987 Dec;8(6):539–548. doi: 10.1007/BF02333660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paty D. W., Oger J. J., Kastrukoff L. F., Hashimoto S. A., Hooge J. P., Eisen A. A., Eisen K. A., Purves S. J., Low M. D., Brandejs V. MRI in the diagnosis of MS: a prospective study with comparison of clinical evaluation, evoked potentials, oligoclonal banding, and CT. Neurology. 1988 Feb;38(2):180–185. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.2.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyser J. M., Edwards K. R., Poser C. M., Filskov S. B. Cognitive function in patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1980 Sep;37(9):577–579. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500580073013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser C. M., Paty D. W., Scheinberg L., McDonald W. I., Davis F. A., Ebers G. C., Johnson K. P., Sibley W. A., Silberberg D. H., Tourtellotte W. W. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):227–231. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. M., Hammeke T. A., McQuillen M. P., Khatri B. O., Lloyd D. Memory disturbance in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1984 Jun;41(6):625–631. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04210080033010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. M. Neuropsychology of multiple sclerosis: a critical review. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1986 Oct;8(5):503–542. doi: 10.1080/01688638608405173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotti G., Scialfa G., Biondi A., Landoni L., Caputo D., Cazzullo C. L. Magnetic resonance in multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiology. 1986;28(4):319–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00333437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbrock D., Seidel D., Gehlen W., Beyer H. K., Haan J., Dickmann E., Zeit T., Herbe E. MR imaging in multiple sclerosis: comparison with clinical, CSF, and visual evoked potential findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988 Jan-Feb;9(1):59–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J. The concept of subcortical and cortical dementia: another look. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jan;19(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby E. W., Grochowski E., Li D. K., Oger J., Kastrukoff L. F., Paty D. W. Serial magnetic resonance scanning in multiple sclerosis: a second prospective study in relapsing patients. Ann Neurol. 1989 Jan;25(1):43–49. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZUNG W. W. A SELF-RATING DEPRESSION SCALE. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1965 Jan;12:63–70. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1965.01720310065008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Burg W., van Zomeren A. H., Minderhoud J. M., Prange A. J., Meijer N. S. Cognitive impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis and mild physical disability. Arch Neurol. 1987 May;44(5):494–501. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520170024017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]