Abstract
Introduction
Serum thrombopoietin (THPO) is a biomarker of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and the latent dementia phenotype, “δ”. Both associations may be specific to non-Hispanic whites (NHW), not Mexican-Americans (MA). In this analysis, we examine ethnicity's effect on THPO's association with change in δ scores, in the Texas Alzheimer's Research and Care Consortium (TARCC).
Methods
We constructed an ethnicity equivalent δ homolog (“dEQ”) among n = 1113 MA and n = 1958 NHW. dEQ was output as a composite “dEQ-score” for each of five annual TARCC waves. Those composites were used as indicators of a latent growth curve (LGC). The mean dEQ intercept (idEQ) and slope (ΔdEQ) were estimated in a random subset of N = 1528 participants and replicated in the remainder (n = 1544). THPO was regressed onto idEQ and ΔdEQ. Those associations were tested separately in MA and NHW.
Results
dEQ correlated strongly with CDR-SB (r = 0.99, P < .001) and achieved high AUCs for AD diagnosis at each wave (range = 0.95–0.99). THPO was significantly associated with idEQ but not ΔdEQ. That effect was observed in NHW only. In MA, THPO had no associations with either idEQ or ΔdEQ.
Discussion
We confirm THPO's ethnicity-specific association with δ in NHW. It is further clarified that this association is specific to δ's intercept and not its slope. This analysis provides a model for how dementia's specific serum biomarkers can be characterized.
Keywords: Aging, Cognition, Dementia, Functional status, Intelligence, THPO
1. Introduction
We have recently constructed a latent phenotype for dementia itself, as distinct from cognitive performance per se [1]. Our approach uses a novel confirmatory bifactor model in a structural equation model framework. Compared to observed measures, the latent variable “δ” (for dementia) is relatively free of demographic measurement bias, continuously distributed and appears to be “indifferent” to its cognitive indicators [2].
δ's indifference to its indicators suggests that it can be modeled in virtually any cognitive battery. We have demonstrated this down to the level of individual items [3]. Thus, we further distinguish between δ, that is, “the cognitive correlates of functional status”, and “d,” that is, δ's reification as a composite score in any specific cognitive battery. Across multiple batteries, these results in a set of δ homologs, all of which appear to share a similar psychometric profile.
δ homologs accurately diagnose dementia and have been associated with Alzheimer's Disease (AD) neuropathology [4], AD-specific CSF biomarkers [5], certain serum inflammatory proteins [6], baseline, prospective change, and future CDR scores [7], [8].
We recently demonstrated significant associations between δ and 10 serum proteins in the Texas Alzheimer's Research and Care Consortium (TARCC). They included thrombopoietin (THPO), platelet-derived growth factor, thrombospondin-1 (THBS1), and von-Willebrand factor [6]. THPO was the strongest. Its effect was comparable to education and APOE ɛ4, and stronger than age, yet independent of both. THPO was also the strongest predictor of clinical AD in O'Bryant et al.'s 2011 study [9]. That association was specific to AD in non-Hispanic whites (NHW) [10] but not in Mexican-Americans (MA) [11]. Similarly, THPO's association with δ scores was limited to NHW [6].
THPO regulates the proliferation and maturation of megakaryocytes and platelet production. However, δ is not related to vasculopathy-related biomarkers such as vascular cell adhesion molecule type 1 (VCAM-1), vascular endothelial growth factor, or homocysteine (HCY), nor is it associated with ischemic pathology (at autopsy) in the National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center [7]. Regardless, platelets have recently been recognized to contribute to innate immunity [12]. δ's serum biomarkers, in their aggregate, suggest that innate immunologic processes may be responsible for dementia severity as measured by δ [6].
The analyses to date have been cross sectional. However, δ's intercept and slope are independently associated with dementia severity, and δ's change over time is strongly related to change in dementia severity [7], [8]. It remains to be determined whether THPO is associated with δ's slope, and whether their association remains specific to NHW in TARCC's rapidly expanding cohort.
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
Subjects included n = 3072 TARCC participants: 1182 cases of AD, 611 “mild cognitive impairment” (MCI) cases, and 1276 controls. Each underwent serial annual standardized clinical examinations. Institutional review board approval was obtained at each site, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
2.2. δ's indicators
All tests were available in Spanish translation.
Logical memory II: [13] After a 30-minute delay, the subject recalls two paragraphs read aloud.
Visual reproduction I: [13] The subject immediately reproduces a set of figures after a brief exposure.
The Controlled Oral Word Association (COWA): [14] The patient is asked to name as many words as they can in 1 minute, beginning with a certain letter.
Digit Span Test (DST): [13] The DST sums the longest set of numbers that the subject can immediately recall in correct order (forward and backward).
Instrumental activities of daily living (IADL): [15] IADL's were assessed using informant ratings. Functional abilities were rated on a Likert scale ranging from 0 (no impairment) to 3 (specific incapacity). A total IADL score calculated as the sum of all eight items.
2.3. Clinical covariates
Education: Education was coded continuously as years of formal education.
Ethnicity: Ethnicity was determined by self-report and coded dichotomously as “Hispanic” and “non-Hispanic”.
Gender: Gender was coded dichotomously.
2.4. Clinical correlates
The Clinical Dementia Rating Scale sum of boxes (CDR): [16] The CDR estimates dementia severity. A clinician rates the participant on six domains—memory, orientation, judgment and problem solving, community affairs, home, and hobbies and personal care. Each is rated on a scale of 0.0–3.0. A total CDR “sum of boxes” (CDR-SB) score is summed across all domains.
2.5. Biomarkers
TARCC's methodology has been described elsewhere [17]. Briefly, nonfasting blood samples were collected in serum-separating tubes, allowed to clot at room temperature for 30 minutes, centrifuged, aliquoted, and stored at −80°C in plastic vials. Serum samples were sent frozen to rules-based medicine (RBM) (http://www.rulesbasedmedicine.com/) in Austin, TX. There, they were assayed without additional freeze-thaw cycles. RBM conducted multiplexed immunoassay via their human multianalyte profile (human MAP).
3. Statistical analyses
3.1. Analysis sequence
Data were inspected for normality and outliers (e.g., values >3 standard deviations) using univariate kurtosis and skewness statistics. Multicolinearity was assessed by noting the correlation among observed variables and the variance inflation factor (VIF) [18]. Multivariate normality in the structural models was assessed using Mardias coefficient [19].
The structural models were performed using Analysis of Moment Structures (AMOS) software [20]. The maximum likelihood estimator was chosen. Observed indicators were adjusted for age, education, ethnicity, and gender. The residual covariances between these variables were estimated if they were significant and improved fit.
TARCC's RBM biomarkers exhibit significant batch effects. Therefore, THPO's associations with latent variables were adjusted for dichotomous dummy variables coding batch.
We began with the confirmatory bifactor model published in Royall & Palmer [6] [i.e., d(=)]. However, we used a newer instance of TARCC's data set (circa 2015). The d(=) model necessitated additional modifications to regain factor equivalence.
We began by stratifying the sample on ethnicity: Hispanic MA (n = 1113) and NHW (n = 1958). Then, we tested the evolving δ homolog's cross ethnic factor equivalence, one indicator at a time, by comparing χ2 fit in constrained versus unconstrained models. Similarly, we examined group invariance of the residual variances of each indicator. We examined δ's indicators in the alphabetical sequence presented in Supplementary Fig. 1. Each consecutive nonsignificant constraint was held equal across groups in subsequent models. If a cognitive performance indicator was significantly affected by ethnicity, a replacement was chosen. The Wechsler Memory Scale Logical Memory I was replaced by LMII [13]. This became a new ethnicity equivalent d homolog, “dEQ”.
The latent variable dEQ was re-validated by its association with observed CDR-SB. We then tested dEQ's factor determinancy [21]. Next, we output the cross-ethnic constrained dEQ factor scores as new composite variables in each of five annual TARCC waves. These dEQ composites were each re-validated by ROC in the entire sample. Finally, histograms of dEQ scores were generated in each wave to confirm their distributions.
Thus, although dEQ was developed in an ethnicity stratified sample, its indicator loadings were engineered to be statistically indiscriminable across ethnicity and after that was achieved, the constrained loadings were used to generate a single d-score composite, which was applied to all participants regardless of ethnicity and at every wave.
Next, we re-divided the combined sample on the basis of a random split, into two similarly sized subgroups (groups 1 and 2). These groups were ethnically diverse. In group 1 (n = 1528), we constructed a latent growth curve (LGC) model using composite dEQ scores as its indicators (similarly to Gavett et al.) [7]. In the LGC, the dEQ composite indicators were adjusted for age, gender, and education. The wave 4 slope parameter was allowed to vary freely, to improve fit to nonlinear change. This resulted in two new latent variables: dEQ's intercept (idEQ) and 4-year slope (ΔdEQ). ΔdEQ was additionally adjusted for idEQ.
Next, we tested wave 1 serum THPO's associations idEQ and ΔdEQ, by multivariate regression. Significant associations were replicated in group 2 (n = 1544). Next, we tested THPO's association with idEQ and ΔdEQ in each ethnic subset separately (Hispanic: n = 1113; NHW: n = 1958).
3.2. Missing data
Some variables (e.g., VRI) were not used at all sites in the TARCC's first wave. In addition, biomarker data from batch 1 (n = 198) were excluded after it was discovered that serial analyses of selected RBM analytes could not be replicated in some cases. This left 888 subjects with complete biomarker data. In contrast, psychometrics and adjudicated clinical diagnoses were available on 3072 subjects, only 2113 of whom had complete data. Rather than using case-wise deletion, the missing biomarker and psychometric data were handled by full-information maximum likelihood (FIML) methods to address missing data in the AMOS software.
In contrast to list-wise or pair-wise deletion, FIML yields unbiased parameter estimates, preserves the overall power of the analysis, and is arguably superior to alternative methods, for example, multiple imputation [22], [23], [24] under assumptions of ignorable missing data patterns (e.g., missing at random [MAR]). We assert that the missing data pattern in this study is MAR due to the fact that missingness was, for the most part, due to study design rather than the inherent properties of the variables that are missing. Furthermore, the multiple covariates added to the model contribute to the assumption of MAR. Only the ROC analyses, performed in Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) [25], were limited to complete cases.
3.3. Factor determinancy
One potential limitation to the common factor model is that an infinite number of unique factor score composites can be derived from any factor [21]. These can be divided into “determinant” and “indeterminant” fractions [26]. Several statistical methods are available to test determinacy. We used Grice's “Refined Factor Score Evaluation Program (equation 5)” [21]. This method maximizes composite validity and is recommended when the factor composite scores are to be used as “observed” variables in subsequent analyses (i.e., as LGC indicators). We report two indices from this program's output: “total item squared multiple correlation” (TIMSC), and a “minimum correlation” (MC). Acceptable TIMSC and MC should be >0.50.
3.4. Fit indices
Fit was assessed using four common test statistics: chi-square, the ratio of the chi-square to the degrees of freedom in the model (CMIN/DF), the comparative fit index (CFI), and the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA). A nonsignificant chi-square signifies that the data are consistent with the model [27]. However, in large samples, these metric conflicts with other fit indices (insensitive to sample size) show that the model fits the data very well. A CMIN/DF ratio <5.0 suggests an adequate fit to the data [28]. The CFI statistic compares the specified model with a null model [29]. CFI values range from 0 to 1.0. Values <0.95 suggest model misspecification. Values approaching 1.0 indicate adequate to excellent fit. An RMSEA of ≤0.05 indicates a close fit to the data, with models <0.05 considered “good” fit, and up to 0.08 as “acceptable” [30]. All fit statistics should be simultaneously considered when assessing the adequacy of the models to the data.
3.5. Receiver-operating characteristic curves
A test's diagnostic accuracy can be evaluated by ROC [31]. Briefly, the true-positive rate (sensitivity) is plotted as a function of the false-positive rate (100 − specificity) for different cut-off scores. Each point of the ROC curve represents a sensitivity or specificity dyad. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) is a measure of how well a parameter can distinguish between two diagnostic groups. We distinguished “AD” versus NC. ROC analyses were performed in SPSS.
4. Results
Descriptive statistics are listed in Table 1. Although there are notable differences between diagnostic groups, no extreme outliers were detected. After log transformation of IADL, all variables displayed reasonably normal distributions (e.g., Kurtosis and skewness <2). Supplementary Table 1 presents dEQ's incremental χ2 change over increasingly constrained models. The sequence tested is presented in Supplementary Fig. 1. dEQ's final model fit well (χ2/df = 181/24, P < .001; CFI = 0.97; RMSEA = 0.05). dEQ achieved cross-ethnic invariance with regard to all indicator loadings and partial invariance of the residual variances (all indictors except IADL). Mean and variance equivalence could not be achieved because of the differences in the cross-ethnic distribution of TARCC diagnoses (Table 1). There was no evidence of multicollinearity among these variables as the inter-item correlations ranged from 0.29 to 0.57. In separate regression equations, the VIF was assessed for each combination of the five variables used in the latent variable model. There was no evidence of VIF significantly >1.0.
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics (analysis of variance)
| Variable | N | Total sample | Post hoc tests |
Main effect, P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD, N = 1182, Mean (SD) | MCI, N = 611, Mean (SD) | Controls, N = 1276, Mean (SD) | ||||
| Gender (% female) | 3071 | 61.0 | 56.0∗ | 56.0∗ | 68.0†‡ | <.001 |
| Ethnicity (% Hispanic) | 3071 | 36.0 | 14.0 | 47.0† | 52.0† | <.001 |
| Age at visit | 3072 | 70.9 (4.3) | 75.5 (8.4)∗‡ | 71.6 (8.7)∗† | 66.3 (9.1)†‡ | <.001 |
| Education | 3072 | 13.2 (4.3) | 14.0 (3.7)∗ | 12.6 (4.3) | 12.8 (4.7)† | .004 |
| CDR (sum of boxes) | 3066 | 2.5 (3.4) | 5.8 (3.4)∗‡ | 1.2 (0.9)∗† | 0.0 (0.1)†‡ | <.001 |
| GDS (30 item) | 2765 | 5.6 (5.3) | 6.0 (5.1)∗ | 7.1 (5.9)∗ | 4.6 (4.8)†‡ | <.001 |
| COWA | 2982 | 8.4 (3.6) | 7.3 (3.4)∗‡ | 8.2 (3.2)∗† | 9.5 (3.5)†‡ | <.001 |
| WMS LM II | 2529 | 8.2 (4.6) | 3.7 (2.4)∗‡ | 8.3 (3.4)∗† | 11.7 (3.0)†‡ | <.001 |
| WMS VR I | 2480 | 8.1 (4.0) | 5.4 (3.0)∗‡ | 87.8 (3.4)∗† | 9.9 (3.5)†‡ | <.001 |
| DIS | 2915 | 8.8 (3.1) | 8.2 (3.0)∗ | 8.6 (2.8)∗ | 9.4 (3.2)†‡ | <.001 |
| IADL (summed) | 2556 | 10.1 (4.8) | 14.9 (6.1)∗‡ | 8.4 (2.1)† | 7.9 (1.0)† | <.001 |
| Complete cases | 2113 | |||||
Abbreviations: CDR, Clinical Dementia Rating scale; COWA, Controlled Oral Word Association Test; DIS, Digit Span Test; GDS, Geriatric Depression Scale; IADL, instrumental activities of daily living; MMSE, mini-mental state examination; SD, standard deviation; WMS LM II, Weschler Memory Scale: Delayed Logical Memory; WMS VR II, Weschler Memory Scale: Delayed Visual Reproduction.
P < .05 versus controls by Tukey's HSD for unequal n's.
P < .05 versus AD by Tukey's HSD for unequal n's.
P < .05 versus MCI by Tukey's HSD for unequal n's.
The new latent variable “dEQ” is presented in Supplementary Fig. 1. Our bifactor model results in two latent variables, dEQ, and “g'”, which is δ's residual in Spearman's general intelligence factor “g” [1]. Both variables' indicator loadings (for the combined sample) are listed in Table 2 dEQ was strongly associated with IADL (r = 0.89, P < .001). g' had no association with IADL (by definition). In the full sample, dEQ correlated strongly with CDR-SB (r = 0.99, P < .001). Mardia's coefficient in this model was 2.37, indicating adequate multivariate normality. As a check on the adequacy of our missing data assumptions, the same model was run using complete data (n = 888). Although fit was slightly poorer, there were no statistically significant differences in the obtained parameter estimates.
Table 2.
Selected model “g” parameters in combined sample
| Indicators | Factor | β | S.E. | Beta | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIS | g' | 1 | 0.62 | ||
| WMS LM II | g' | 0.83 | 0.08 | 0.32 | <.001 |
| WMS VR I | g' | 0.89 | 0.07 | 0.40 | <.001 |
| COWA | g' | 1.17 | 0.07 | 0.64 | <.001 |
| DIS | dEQ | −0.25 | 0.02 | −0.37 | <.001 |
| WMS LM II | dEQ | −0.61 | 0.04 | −0.58 | <.001 |
| WMS VR I | dEQ | −0.48 | 0.03 | −0.52 | <.001 |
| COWA | dEQ | −0.34 | 0.03 | −0.45 | <.001 |
| IADL | dEQ | 1 | 0.89 | <.001 |
| Fit indices | |
|---|---|
| Χ2(df) | 181.0 (24) |
| Χ2/DF | 7.54, P < .001 |
| CFI | 0.967 |
| RMSEA | 0.046 |
Abbreviations: CFI, comparative fit index; COWA, Controlled Oral Word Association Test; DF, degrees of freedom; DST, Digit Span Test; IADL, Instrumental Activities of Daily Living; RMSEA, Root Mean Square Error of Association; S.E., Standard Error; WMS LM II, Weschler Memory Scale: Delayed Logical Memory; WMS VR I, Weschler Memory Scale: Immediate Visual Reproduction.
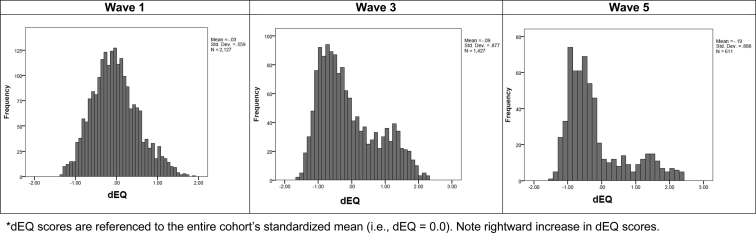
dEQ exhibited acceptable factor determinancy (i.e., TISMC = 0.89; MC = 0.59). We therefore output its factor scores at each wave as a set of composite variables. These achieved high AUCs (Supplementary Table 2). dEQ's distribution was increasingly bimodal over time (Fig. 1). Fig. 1 suggests a rightward (dementing) shift in the dEQ scores in a subset of TARCC's sample. As δ is a strong predictor of MCI conversion [5], this may reflect conversions to dementia among initially nondemented subjects (i.e., at lower baseline dEQ scores).
Fig. 1.
dEQ histograms for selected waves (dEQ scores are referenced to the entire cohort's standardized mean [i.e., dEQ = 0.0]). NOTE. Rightward increase in dEQ scores.
The dEQ composites were submitted to LGC as described above. ΔdEQ's model fit well (χ2/df = 422.2/24, P < .001; CFI = 0.97; RMSEA = 0.05). Note that the freely estimated factor loading on the last measurement occasion of the growth factor reveals that the true trajectory of ΔdEQ is not quite linear but reflects a gradual leveling off after four measurement occasion. This model resulted in two latent variables, idEQ and ΔdEQ. Both latent variables' indicator loadings (in group 1) are presented in Table 3. idEQ was strongly associated with ΔdEQ (r = 0.77, P ≤ .001).
Table 3.
LGC parameters in group 1 (N = 1528)
| Indicators | Factor | β | S.E. | Beta | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dEQ1 | idEQ | 1 | 0.77 | ||
| dEQ2 | idEQ' | 1 | 0.71 | ||
| dEQ3 | idEQ | 1 | 0.60 | ||
| dEQ4 | idEQ | 1 | 0.51 | ||
| dEQ5 | idEQ | 1 | 0.48 | ||
| dEQ1 | ΔdEQ | 0 | 0.37 | ||
| dEQ2 | ΔdEQ | 1 | 0.23 | ||
| dEQ3 | ΔdEQ | 2 | 0.39 | ||
| dEQ4 | ΔdEQ | 3 | 0.50 | ||
| dEQ5 | ΔdEQ | 3.35 | 0.08 | 0.52 | <.001 |
| Fit indices | |
|---|---|
| Χ2(df) | 422.2 (24) |
| Χ2/DF | 10.05, P < .001 |
| CFI | 0.973 |
| RMSEA | 0.054 |
Abbreviations: CFI, comparative fit index; DF, degrees of freedom; RMSEA, root mean square error of association; SE, standard error.
In the final MIMIC model is presented in Fig. 2. Random subset group 1's parameters are presented, and so the presented structural associations include subjects of both ethnicities. THPO was significantly associated with idEQ (r = 0.40, P < .001) but not ΔdEQ (r = −0.15, P = .175). The model's fit was not significantly altered when THPO's associations with idEQ and ΔdEQ, and idEQ's association with ΔdEQ was constrained to be equal across the two random subgroups [χ2 = 422.2(24) vs 427(47); Difference = 4.8 (23), P > .99]. Thus dEQ's intercept, its slope, their association with each other, and THPO's associations with idEQ, all replicated across subsamples.
Fig. 2.
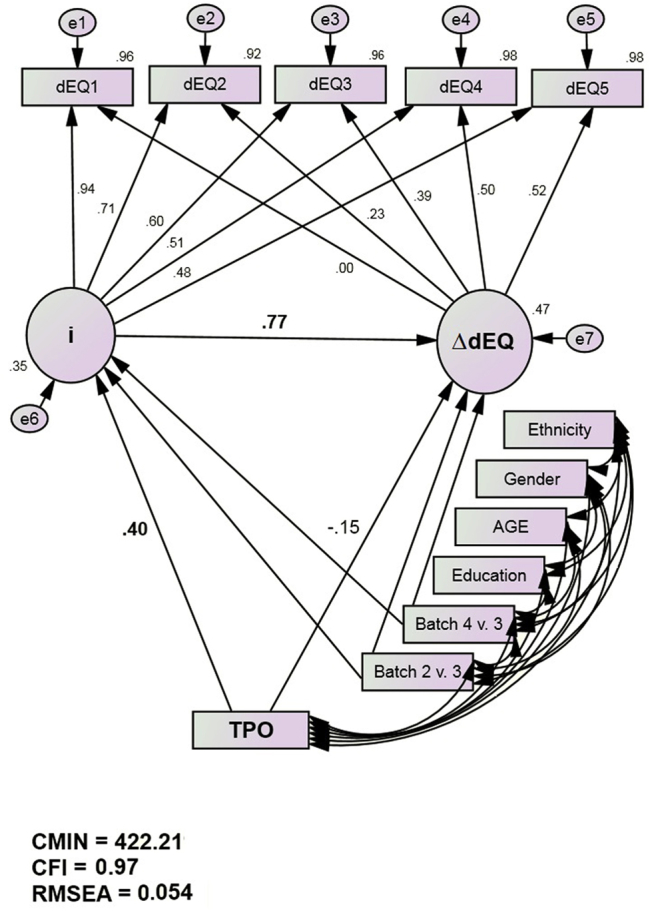
THPO predicts dEQ's intercept but not its slope (group 1 loadings. Standardized parameter estimates. dEQ indicators are adjusted for age, gender, and education [but not ethnicity]).
The sample was then stratified on ethnicity instead, to test for cross-ethnic differences in dEQ's temporal evolution and/or THPO's association with the LGC. The ethnicity stratified model fits well (χ2/df = 367.6/44, P < .001; CFI = 0.97; RMSEA = 0.05). Its fit was not significantly altered when idEQ and ΔdEQ's means were constrained to be equal across ethnicity [χ2 = 365.2(42) vs 367.6(44); Difference = 2.4(2), P > .25]. Thus, there are no cross-group differences in either dEQ's intercept or longitudinal rate of change.
THPO remained significantly associated with idEQ in NHW but was not significantly associated with either idEQ or ΔdEQ in MA (Table 4). These results are consistent with the observed nonlinear and ethnicity-specific trends in serum THPO levels as a function of categorical diagnosis (Supplementary Fig. 2). This figure and Table 4 reveal that THPO's relationship with idEQ in the random split (Fig. 2) is driven by NHW only.
Table 4.
THPO's Associations with dEQ intercept (idEQ) and slope (ΔdEQ) over five waves in TARCC, stratified by ethnicity
| Association | Hispanics (n = 1113) |
NHW (N = 1958) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta | P value | Beta | P value | |
| THPO > idEQ | 0.106 | .097 | 0.350 | <.001 |
| THPO > ΔdEQ | −0.095 | .238 | −0.066 | .546 |
NOTE. Standardized regression estimates, adjusted for batch effects and idEQ (ΔdEQ).
5. Discussion
We have confirmed an ethnicity-specific association between serum THPO levels and δ. This analysis extends our finding to longitudinal data and further clarifies their association by restricting it to δ's intercept in NHW and not its slope. No association was found between THPO and either parameter in MA.
This suggests that THPO may be a “trigger” of one or more dementing processes (in NHW) but may not contribute significantly to dementia's evolution over time. That insight suggests THPO's potential role in the transition from normal cognition to MCI. Supplementary Fig. 2 suggests that THPO levels differ most between NC and MCI (in NHW), then return toward the mean of NC as MCI progresses to AD. This hypothesis would require longitudinal biomarker data to confirm. Similar nonlinear trends have been reported for other blood-based AD-related biomarkers [32]. A nonlinear relationship between serum biomarker levels, and δ scores poses an obstacle to the identification of dementia-related biomarkers by categorical contrasts (i.e., AD vs NC).
The present analysis offers a model for how dementia's specific serum biomarkers can be characterized. It can easily be applied to each of TARCC's remaining serum proteins, to examine their potential associations with dEQ's intercept and longitudinal course, in either NHA or MA. We and others, in different cohorts and by different methods, have shown that change in δ is strongly associated with change in dementia severity, as measured by CDR [7], [8]. Additionally, Koppara et al. [5] have shown that δ homologs outperform the ADAS-COG and CERAD as predictors of MCI's conversion to AD over 3 years. Thus, THPO's association with dEQ's intercept in NHW is likely to be clinically salient and may offer a target for clinical intervention at AD's very inception.
THPO is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of thrombocytopenia, as are two THPO receptor agonists, romiplostim (Nplate; Amgen GmbH, Munich, Germany) and eltrombopag (Revolade, Promacta; GlaxoSmithKline GmbH, Munich, Germany). However, THPO's association with idEQ is positive, whereas dEQ's cognitive loadings are inverse. Thus, exposure to THPO or its agonists might undermine cognitive performance through idEQ. Moreover, as idEQ is strongly associated with ΔdEQ, THPO exposure might influence prospective cognitive declines.
Cognitive deficits are not frequently reported as side-effects of TPO and its agonists, but an effect on δ could easily be missed in raw performance data, especially in the context of systemic illness. However, “intellectual disability” (ID) has been associated with a mutation in the methyltransferase-like 23 gene (METTL23), an upstream modulator of THPO transcription. Overexpression of THPO appears to mediate the association between METTL23 and ID [33].
δ has been shown to be “agnostic” to dementia's etiology [7]. Although TARCC is likely to be highly enriched with AD cases, an estimated 20% of cases diagnosed with clinical “AD” by experienced clinicians may be without beta-amyloid by PiBPET [34]. Therefore, although TARCC purports to be a study of AD, dEQ's intercept and slope may yet be influenced additional dementing processes afflicting this cohort. As there is significant variability about THPO's association with idEQ (in NHW), THPO may not contribute to them all.
Although δ's ethnicity-specific biomarkers suggest biological heterogeneity within the demented fraction of TARCC participants, it should be recognized that Hispanic and NHW TARCC participants do not differ in their mean δ scores, either at a clinical diagnosis of “AD” or at the stage of MCI [6]. We have now shown that MA and NHW do not differ in their rates of change in dEQ scores over time. This suggests that the dementing processes afflicting Hispanic and NHW TARCC participants has a similar natural history in both groups.
Regardless, almost all the biomarkers that we have associated with δ to date have been specific to NHW. This result is consistent with a growing literature of ethnicity-specific AD biomarkers [10], [35], [36]. Additional analyses may identify MA-specific δ-related biomarkers and/or the biomarkers of ΔdEQ. Such analyses have the potential to distinguish the biological processes that initiate and maintain dementing processes over time, and the populations within which they operate. That understanding could better match future treatments to AD's natural history in individual patients.
Research in context.
-
1.
Systematic review: δ has only recently been described, and its literature is rapidly evolving. All relevant citations have been appropriately cited.
-
2.
Interpretation: Our findings confirm THPO's ethnicity-specific association with dementia. It is further clarified that this association is specific to δ's intercept and not its slope.
-
3.
Future directions: This analysis strengthens the case for THPO as a target for dementia-specific intervention in NHW. It suggests that such interventions may have to be applied early in dementia's evolution to be effective. Furthermore, it provides a model for how dementia's specific serum biomarkers can be characterized.
Acknowledgments
This study was made possible by the Julia and Van Buren Parr endowment for the study of Alzheimer's Disease and the Texas Alzheimer's Research Consortium (TARCC) funded by the state of Texas through the Texas Council on Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders and by a generous gift of Mr. Charles Butt in the memory of Mrs. Littlie Littrell. There was no involvement of a pharmaceutical or other company. The funders had no role in study design, data collection, and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the article.
D.R.R. and R.F.P. have disclosed the results of these analyses to the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UTHSCSA), which has filed patent application 2012.039.US1.HSCS and provisional patents 61/603,226 and 61/671,858 relating to the latent variable δ's construction and biomarkers. D.R.R. and R.F.P. have been engaged as consultants by Actavis + Allergan (formerly Forest Laboratories Inc.) regarding δ.
Investigators from the Texas Alzheimer's Research and Care Consortium: Baylor College of Medicine: Rachelle Doody MD, PhD, Mimi M. Dang MD, Valory Pavlik PhD, Wen Chan PhD, Paul Massman PhD, Eveleen Darby, Monica Rodriguear RN, Aisha Khaleeq; Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center: Chuang-Kuo Wu MD, PhD, Matthew Lambert PhD, Victoria Perez, Michelle Hernandez; University of North Texas Health Science Center: Thomas Fairchild PhD, Janice Knebl DO, Sid E. O'Bryant PhD, James R. Hall PhD, Leigh Johnson PhD, Robert C. Barber PhD, Douglas Mains, Lisa Alvarez, Rosemary McCallum; University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center: Perrie Adams PhD, Munro Cullum PhD, Roger Rosenberg MD, Benjamin Williams MD, PhD, Mary Quiceno MD, Joan Reisch PhD, Ryan Huebinger PhD, Natalie Martinez, Janet Smith; University of Texas Health Science Center—San Antonio: Donald Royall MD, Raymond Palmer PhD, Marsha Polk; Texas A&M University Health Science Center: Farida Sohrabji PhD, Steve Balsis PhD, Rajesh Miranda, PhD; Essentia Institute of Rural Health: Stephen C. Waring DVM, PhD; University of North Carolina: Kirk C. Wilhelmsen MD, PhD, Jeffrey L. Tilson PhD, Scott Chasse PhD.
Footnotes
Supplementary data related to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dadm.2016.02.003.
Supplementary data
Supplementary Figure 1.
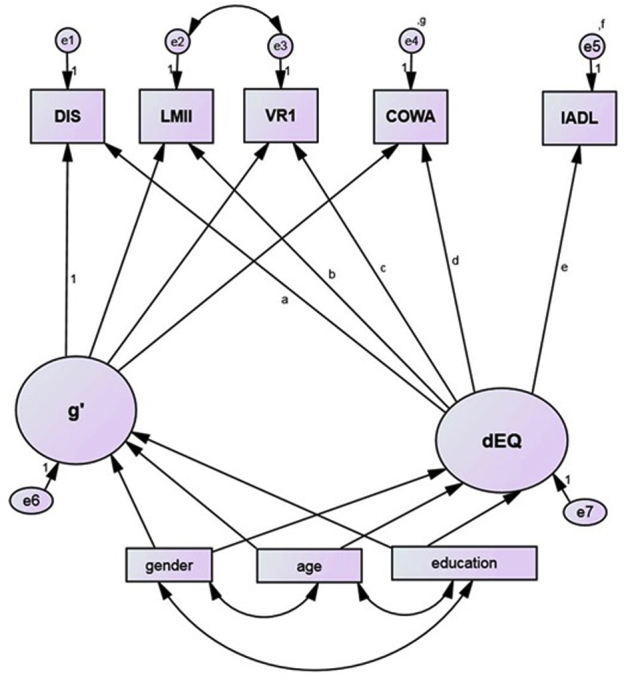
The latent variable dEQ's construction. Abbreviations: CFI, comparative fit index; COWA, Controlled Oral Word Association Test; DF, degrees of freedom; DST, Digit Span Test; IADL, instrumental activities of daily living; RMSEA, root mean square error of association; SE, standard error; WMS LM II, Weschler Memory Scale: delayed logical memory; WMS VR I, Weschler Memory Scale: immediate visual reproduction.
Supplementary Figure 2.
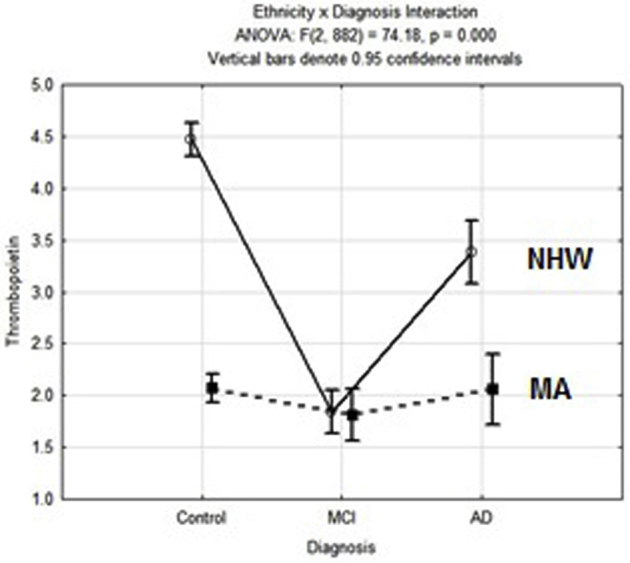
Observed serum THPO by diagnosis and ethnicity
References
- 1.Royall D.R., Palmer R.F., O'Bryant S.E. Validation of a latent variable representing the dementing process. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;30:639–649. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Royall D.R. Welcome back to your future: The psychometric assessment of dementia by the latent variable “δ”. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49:515–519. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Royall D.R., Palmer R.F., Matsuoka T., Kato Y., Taniguchi S., Ogawa M. Greater than the sum of its parts: δ can be constructed from item-level data. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49:571–579. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gavett B.E., John S.E., Gurnani A.S., Bussell C.A., Saurman J.L. The role of Alzheimer's and cerebrovascular pathology in mediating the effects of age, race, and apolipoprotein E genotype on dementia severity in pathologically confirmed Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49:531–545. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Koppara A., Wolfsgruber S., Kleineidam L., Schmidtke K., Frölich L., Kurz A. The latent dementia phenotype δ is associated with CSF biomarkers of Alzheimer Disease and predicts conversion to AD dementia in subjects with MCI. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49:547–560. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Royall D.R., Palmer R.F. Ethnicity moderates dementia's biomarkers. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;43:275–287. doi: 10.3233/JAD-140264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gavett B.E., Vudy V., Jeffrey M., John S.E., Gurnani A.S., Adams J.W. The δ latent dementia phenotype in the uniform data set: cross-validation and extension. Neuropsychology. 2015;29:344–352. doi: 10.1037/neu0000128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Palmer R.F., Royall D.R. Future dementia severity is almost entirely explained by the latent variable δ's intercept and slope. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49:521–529. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.O'Bryant S.E., Xiao G., Barber R., Huebinger R., Wilhelmsen K., Edwards M., Texas Alzheimer's Research & Care Consortium. Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative A blood-based screening tool for Alzheimer's disease that spans serum and plasma: findings from TARC and ADNI. PLoS One. 2011;6:e28092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.O'Bryant S.E., Xiao G., Zhang F., Edwards M., German D.C., Yin X. Validation of a serum screen for Alzheimer's disease across assay platforms, species, and tissues. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;42:1325–1335. doi: 10.3233/JAD-141041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.O'Bryant S.E., Xiao G., Edwards M., Devous M., Gupta V.B., Martins R. Biomarkers of Alzheimer's Disease among Mexican Americans. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;34:841–849. doi: 10.3233/JAD-122074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kissel K., Berber S., Nockher A., Santoso S., Bein G., Hackstein H. Human platelets target dendritic cell differentiation and production of proinflammatory cytokines. Transfusion. 2006;46:818–827. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2006.00802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wechsler D. 3rd ed. The Psychological Corporation; San Antonio, TX: 1997. Wechsler Memory Scale. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Benton A., Hamsher K. AJA Associates; Iowa City, Iowa: 1989. Multilingual Aphasia Examination. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lawton M.P., Brody E.M. Assessment of older people: self-maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist. 1969;9:179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hughes C.P., Berg L., Danziger W.L., Coben L.A., Martin R.L. A new clinical scale for the staging of dementia. Br J Psychiatry. 1982;140:566–572. doi: 10.1192/bjp.140.6.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Waring S., O'Bryant S.E., Reisch J.S., Diaz-Arrastia R., Knebl J., Doody R., for the Texas Alzheimer's Research Consortium The Texas Alzheimer's Research Consortium longitudinal research cohort: Study design and baseline characteristics. Texas Public Health Journal. 2008;60:9–13. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stine R.A. Graphical interpretation of variance inflation factors. Am Stat. 1995;49:53–56. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mardia KV. Tests of univariate and multivariate normality. In Krishnaiah PR, ed. Handbook of Statistics, Volume 1; 1980. p. 279–320. Chapter 9, North-Holland, Amsterdam.
- 20.Arbuckle J.L. SPSS; Chicago: 2006. AMOS 18 User's Guide. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Grice J.W. Computing and evaluation factor scores. Psychol Methods. 2001;6:430–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Graham J.W. Missing data analysis: Making it work in the real world. Annu Rev Psychol. 2009;6:549–576. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.58.110405.085530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Enders C.K., Bandalos D.L. The relative performance of full information maximum likelihood estimation for missing data in structural equation models. Struct Equ Modeling. 2001;8:430–457. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Newman D.A. Missing data techniques and low response rates: The role of systematic nonresponse parameters. In: Lance C.E., Vandenberg R.J., editors. Statistical and methodological myths and urban legends: Doctrine, verity and fable in the organizational and social sciences. Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group; New York, NY, US: 2009. pp. 7–36. xix. [Google Scholar]
- 25.PASW Statistics 18, Release Version 18.0.0. SPSS, Inc; Chicago, IL: 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Guttman L. The determinancy of factor score matrices with applications for five other problems of common factor theory. Br J Stat Psychol. 1955;8:65–82. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bollen K.A., Long J.S. Sage Publications; Thousand Oaks, CA: 1993. Testing structural equation models. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wheaton B., Muthén B., Alwin D.F., Summer G.F. Assessing reliability and stability in panel models. In: Heise D.R., editor. Sociology Methodology. Jossey-Bass; San Francisco, CA: 1977. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bentler P.M. Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychol Bull. 1990;107:238–246. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.107.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Browne M., Cudeck R. Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In: Bollen K.A., Long J.S., editors. Testing structural equation models. Sage Publications; Thousand Oaks, CA: 1993. pp. 136–162. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zweig M.H., Campbell G. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem. 1993;39:561–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mapstone M., Cheema A.K., Fiandaca M.S., Zhong X., Mhyre T.R., MacArthur L.H. Plasma phospholipids identify antecedent memory impairment in older adults. Nat Med. 2014;20:415–418. doi: 10.1038/nm.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Reiff R.E., Ali B.R., Baron B., Yu T.W., Ben-Salem S., Coulter M.E. METTL23, a transcriptional partner of GABPA, is essential for human cognition. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23:3456–3466. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Witte M.M., Trzepacz P., Case M., Yu P., Hochstetler H., Quinlivan M. Association between clinical measures and Florbetapir F18 PET neuroimaging in mild or moderate Alzheimer's disease dementia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;26:214–220. doi: 10.1176/appi.neuropsych.12120402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kwon O.D., Khaleeq A., Chan W., Pavlik V.N., Doody R.S. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and age at onset of Alzheimer's disease in a quadriethnic sample. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2010;30:486–491. doi: 10.1159/000322368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Janicki S.C., Park N., Cheng R., Clark L.N., Lee J.H., Schupf N. Estrogen receptor α variants affect age at onset of Alzheimer's disease in a multiethnic female cohort. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2014;38:200–213. doi: 10.1159/000355559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.