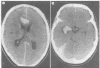
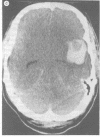
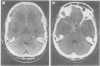
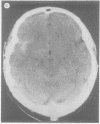
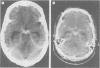
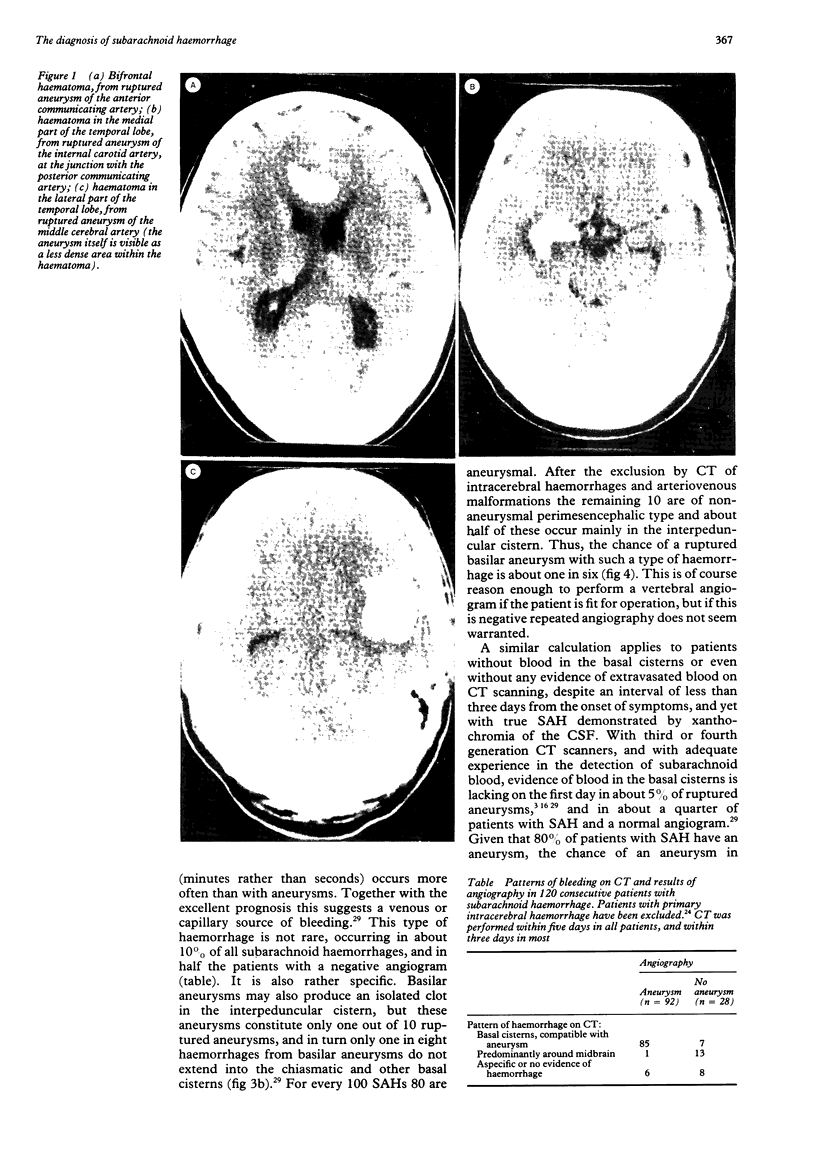
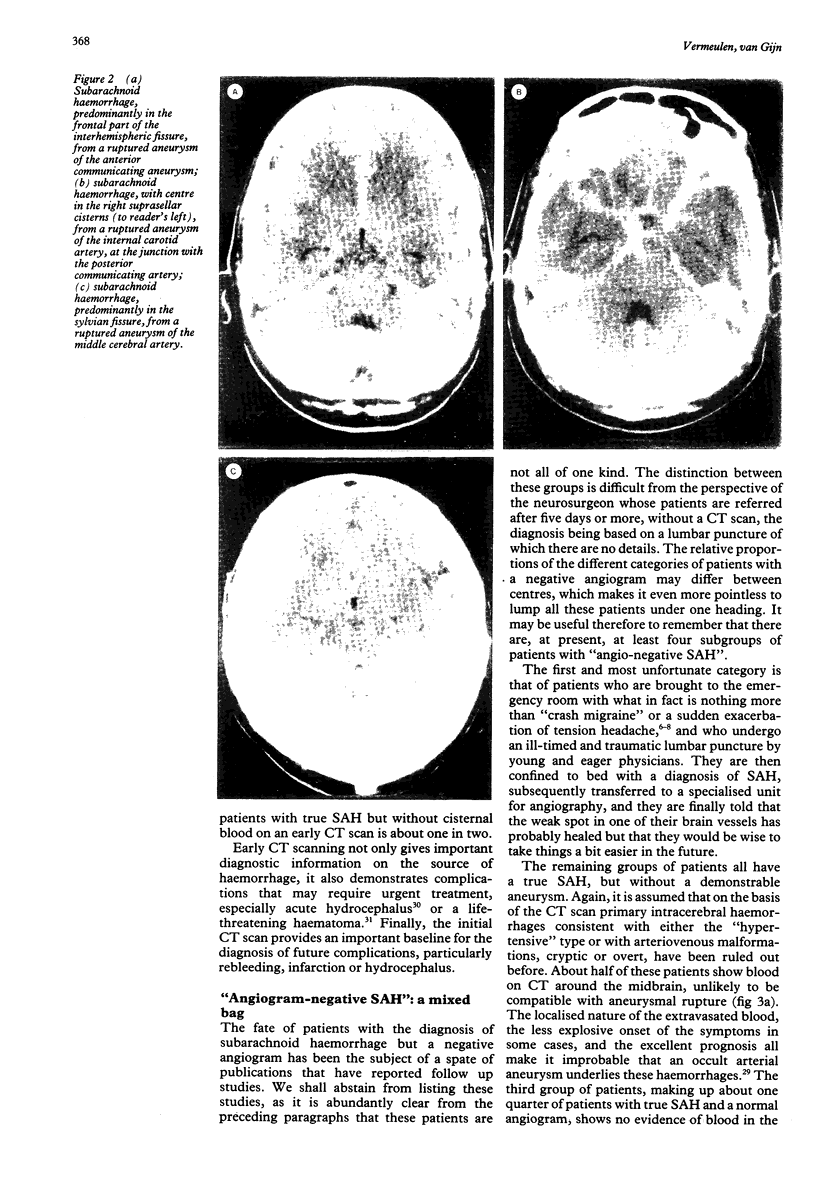
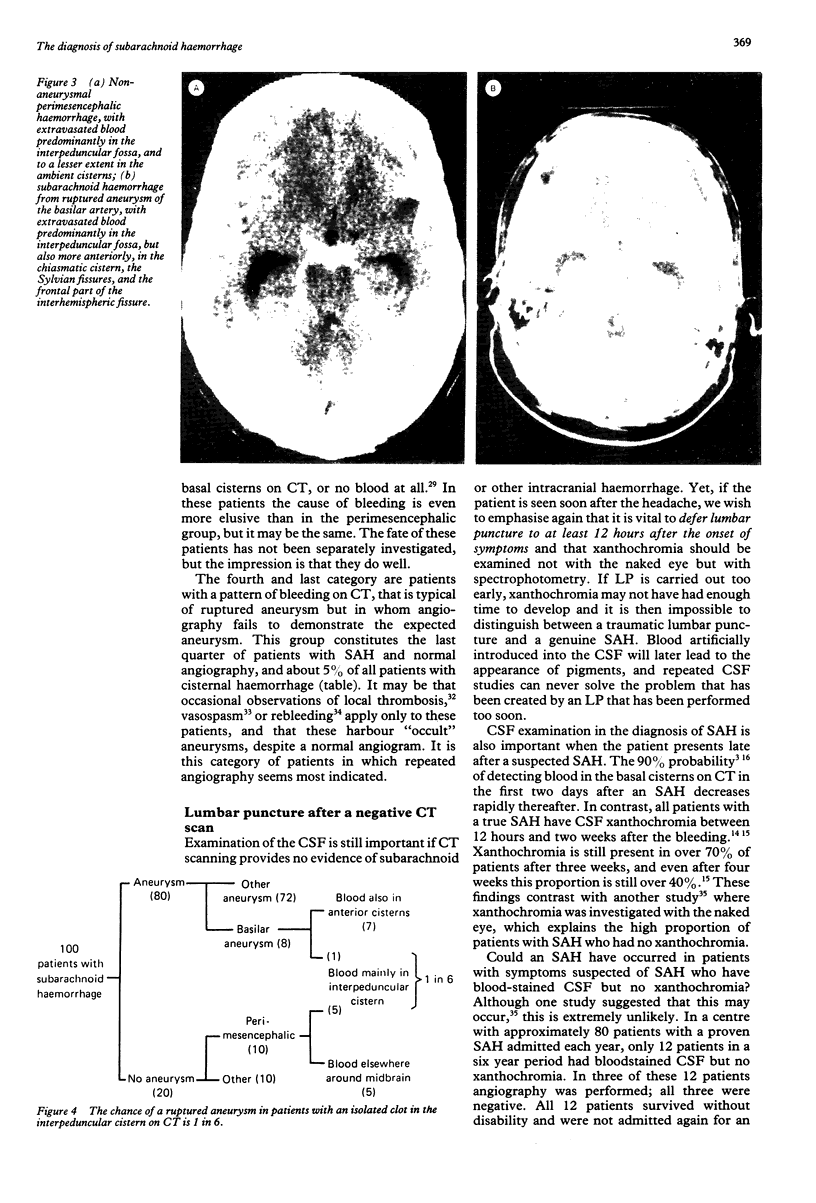
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams H. P., Jr, Kassell N. F., Torner J. C., Sahs A. L. CT and clinical correlations in recent aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a preliminary report of the Cooperative Aneurysm Study. Neurology. 1983 Aug;33(8):981–988. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.8.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARROWS L. J., HUNTER F. T., BANKER B. Q. The nature and clinical significance of pigments in the cerebrospinal fluid. Brain. 1955;78(1):59–80. doi: 10.1093/brain/78.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkovich A. J., Atlas S. W. Magnetic resonance imaging of intracranial hemorrhage. Radiol Clin North Am. 1988 Jul;26(4):801–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow P. Incidence of delayed cerebral ischaemia following subarachnoid haemorrhage of unknown cause. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985 Feb;48(2):132–136. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.48.2.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt L., Sonesson B., Ljunggren B., Säveland H. Ruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysm with intracerebral hemorrhage in younger patients appearing moribund: emergency operation? Neurosurgery. 1987 Jun;20(6):925–929. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198706000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buruma O. J., Janson H. L., Den Bergh F. A., Bots G. T. Blood-stained cerebrospinal fluid: traumatic puncture or haemorrhage? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Feb;44(2):144–147. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call G. K., Fleming M. C., Sealfon S., Levine H., Kistler J. P., Fisher C. M. Reversible cerebral segmental vasoconstriction. Stroke. 1988 Sep;19(9):1159–1170. doi: 10.1161/01.str.19.9.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day J. W., Raskin N. H. Thunderclap headache: symptom of unruptured cerebral aneurysm. Lancet. 1986 Nov 29;2(8518):1247–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Death by a thousand cuts. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jul 3;285(6334):1–2. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward R. D., O'Reilly G. V. Intracerebral haemorrhage. Accuracy of computerised transverse axial scanning in predicting the underlying aetiology. Lancet. 1976 Jan 3;1(7949):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92904-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijdra A., Vermeulen M., van Gijn J., van Crevel H. Rerupture of intracranial aneurysms: a clinicoanatomic study. J Neurosurg. 1987 Jul;67(1):29–33. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.1.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman J. Should computed tomography scanning replace lumbar puncture in the diagnostic process in suspected subarachnoid hemorrhage? Surg Neurol. 1986 Dec;26(6):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(86)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins A., Hadley D. M., Teasdale G. M., Condon B., Macpherson P., Patterson J. Magnetic resonance imaging of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1988 May;68(5):731–736. doi: 10.3171/jns.1988.68.5.0731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslyn J. N., Williams J. P., White J. L., White R. L. Simultaneous rupture of two intracranial aneurysms: CT diagnosis. Stroke. 1985 May-Jun;16(3):518–521. doi: 10.1161/01.str.16.3.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall B. E., Lee B. C., Claveria E. Computerized tomography and angiography in subarachnoid haemorrhage. Br J Radiol. 1976 Jun;49(582):483–501. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-49-582-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy R. F., Ebersole J. S. An evaluation of ambulatory, cassette EEG monitoring: I. Montage design. Neurology. 1983 Jan;33(1):1–7. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. T., Sage D. J. Detection of subarachnoid blood clot and other thin, flat structures by computed tomography. Radiology. 1977 Apr;123(1):79–84. doi: 10.1148/123.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS W. F., FROMMEYER W. B., Jr The in vitro behavior of erythrocytes in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Apr;45(4):508–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCORMICK W. F., NOFZINGER J. D. SACCULAR INTRACRANIAL ANEURYSMS: AN AUTOPSY STUDY. J Neurosurg. 1965 Feb;22:155–159. doi: 10.3171/jns.1965.22.2.0155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald A., Mendelow A. D. Xanthochromia revisited: a re-evaluation of lumbar puncture and CT scanning in the diagnosis of subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Mar;51(3):342–344. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.3.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasqualin A., Bazzan A., Cavazzani P., Scienza R., Licata C., Da Pian R. Intracranial hematomas following aneurysmal rupture: experience with 309 cases. Surg Neurol. 1986 Jan;25(1):6–17. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(86)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J. M., Pearce S. H. "Benign paroxysmal cranial neuralgia" or "cephalgia fugax". Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Apr 12;292(6526):1015–1016. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6526.1015-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., Kwun B. D., Teramura A., Hackett J. D., Morgan J. A., Nishizawa S., Bun T., Zervas N. T. Immunological reaction against the aging human subarachnoid erythrocyte. A model for the onset of cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1989 Nov;71(5 Pt 1):718–726. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.71.5.0718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roost K. T., Pimstone N. R., Diamond I., Schmid R. The formation of cerebrospinal fluid xanthochromia after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Enzymatic conversion of hemoglobin to bilirubin by the arachnoid and choroid plexus. Neurology. 1972 Sep;22(9):973–977. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.9.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruelle A., Cavazzani P., Andrioli G. Extracranial posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm causing isolated intraventricular hemorrhage: a case report. Neurosurgery. 1988 Dec;23(6):774–777. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198812000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salloum A., Lebel M., Reiher J. Accês cêphalalgiques simulant une hêmorragie mêningêe. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1977 Feb;133(2):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh S., Kadoya S. Magnetic resonance imaging of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroradiology. 1988;30(5):361–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00404098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid U. D., Steiger H. J., Huber P. Accuracy of high resolution computed tomography in direct diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms. Neuroradiology. 1987;29(2):152–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00327540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulder M., Hirano A., Elkin C. "Caval-septal" hematoma: does it exist? Neurosurgery. 1987 Aug;21(2):239–241. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198708000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotti G., Ethier R., Melançon D., Terbrugge K., Tchang S. Computed tomography in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Radiology. 1977 Apr;123(1):85–90. doi: 10.1148/123.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spetzler R. F., Winestock D., Newton H. T., Boldrey E. B. Disappearance and reappearance of cerebral aneurysm in serial arteriograms. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1974 Oct;41(4):508–510. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.41.4.0508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. L., Crowell R. M., Gandhi Y. N., Jafar J. J. Multiple intracranial aneurysms: magnetic resonance imaging for determination of the site of rupture. Report of a case. Neurosurgery. 1988 Jul;23(1):97–100. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198807000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderström C. E. Diagnostic significance of CSF spectrophotometry and computer tomography in cerebrovascular disease. A comparative study in 231 cases. Stroke. 1977 Sep-Oct;8(5):606–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOURTELLOTTE W. W., METZ L. N., BRYAN E. R., DEJONG R. N. SPONTANEOUS SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE. FACTORS AFFECTING THE RATE OF CLEARING OF THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID. Neurology. 1964 Apr;14:301–306. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.4.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Meulen J. P. Cerebrospinal fluid xanthochromia: an objective index. Neurology. 1966 Feb;16(2):170–178. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.2_part_1.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen M., Hasan D., Blijenberg B. G., Hijdra A., van Gijn J. Xanthochromia after subarachnoid haemorrhage needs no revisitation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Jul;52(7):826–828. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.7.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen M., van Gijn J., Hijdra A., van Crevel H. Causes of acute deterioration in patients with a ruptured intracranial aneurysm. A prospective study with serial CT scanning. J Neurosurg. 1984 May;60(5):935–939. doi: 10.3171/jns.1984.60.5.0935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijdicks E. F., Kerkhoff H., van Gijn J. Long-term follow-up of 71 patients with thunderclap headache mimicking subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet. 1988 Jul 9;2(8602):68–70. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Crevel H. Pitfalls in the diagnosis of rebleeding from intracranial aneurysm. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1980;82(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0303-8467(80)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gijn J., Hijdra A., Wijdicks E. F., Vermeulen M., van Crevel H. Acute hydrocephalus after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1985 Sep;63(3):355–362. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.63.3.0355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gijn J., van Dongen K. J. Computed tomography in the diagnosis of subarachnoid haemorrhage and ruptured aneurysm. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1980;82(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0303-8467(80)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gijn J., van Dongen K. J. The time course of aneurysmal haemorrhage on computed tomograms. Neuroradiology. 1982;23(3):153–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00347559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gijn J., van Dongen K. J., Vermeulen M., Hijdra A. Perimesencephalic hemorrhage: a nonaneurysmal and benign form of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology. 1985 Apr;35(4):493–497. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]