Abstract
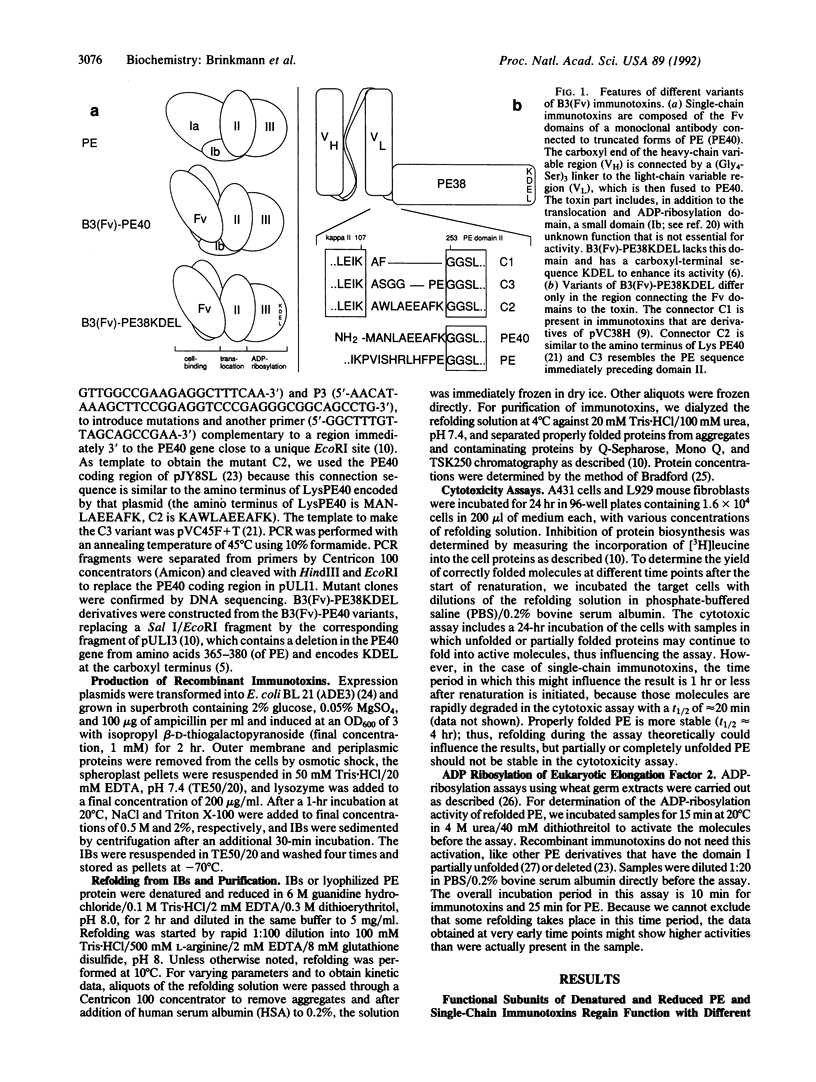
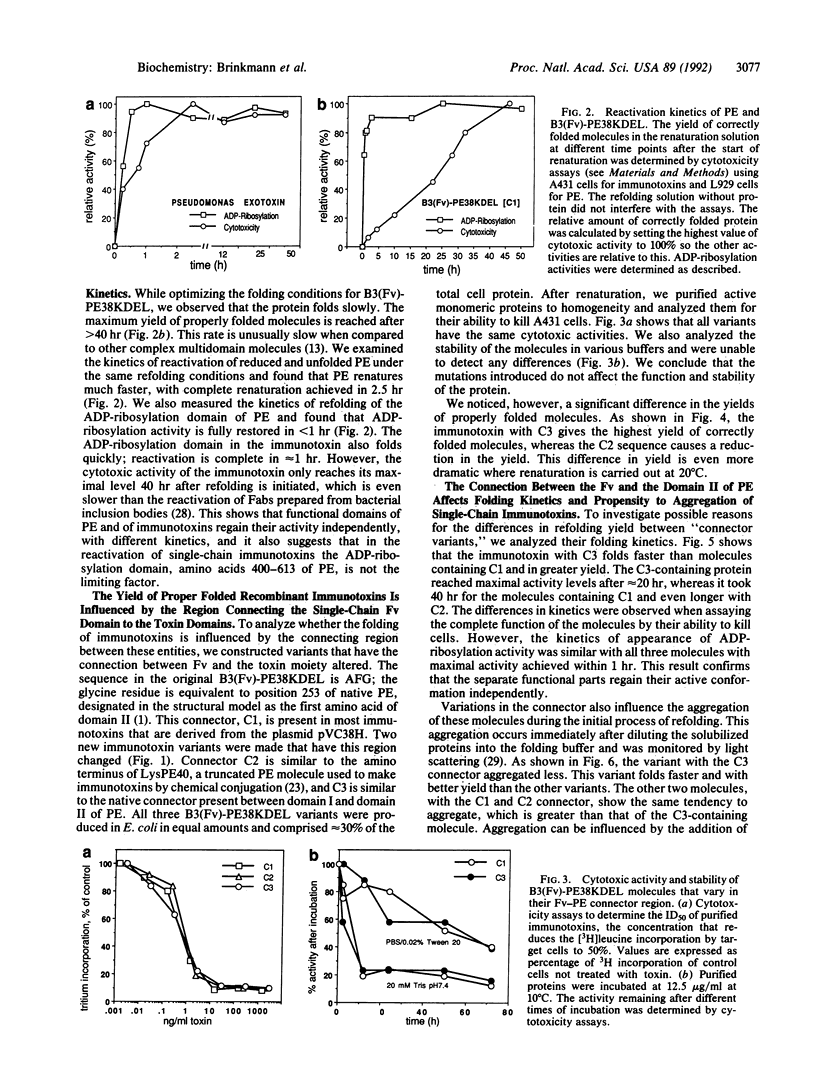
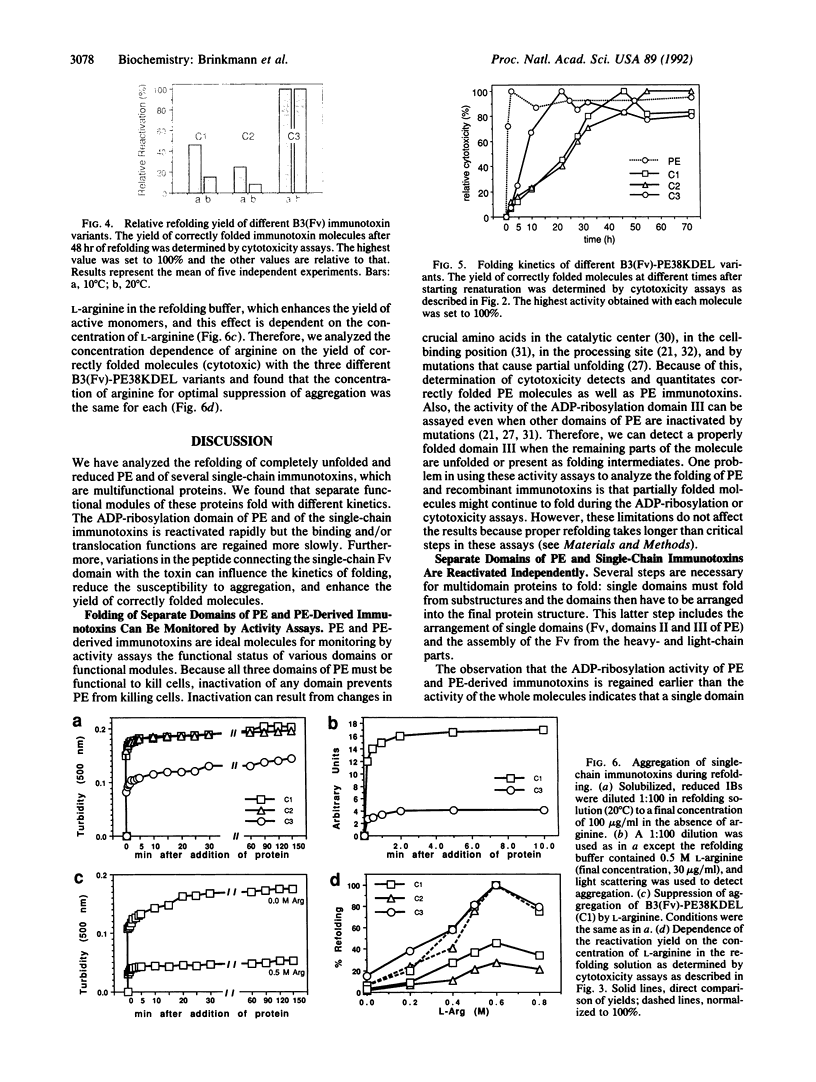
We have studied the refolding of completely unfolded and reduced Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE) and of recombinant single-chain immunotoxins made with monoclonal antibody B3 that are composed of a heavy-chain variable region connected by a flexible linker to the corresponding light-chain variable region (Fv), which is in turn fused to a truncated form of PE. We have found by direct activity assays that different functional domains of these multifunctional proteins fold independently with different kinetics. The ADP-ribosylation domain of PE and of the recombinant immunotoxin fold rapidly, whereas the assembly of the binding and/or translocation domains is regained more slowly. The complete refolding of native PE occurs more rapidly than the refolding of the recombinant immunotoxins. To determine the influence of the connector region between the B3(Fv) moiety and the toxin on the folding process of the recombinant immunotoxin B3(Fv)-PE38KDEL, we have made two different mutations in the peptide that connects the single-chain Fv domain to domain II of PE. These molecules show different folding kinetics, differences in their propensity to aggregate, and different yields of correctly folded molecules. A mutation that decreases aggregation increases the rate of formation and the yield of active immunotoxin molecules.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allured V. S., Collier R. J., Carroll S. F., McKay D. B. Structure of exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 3.0-Angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1320–1324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batra J. K., Jinno Y., Chaudhary V. K., Kondo T., Willingham M. C., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. Antitumor activity in mice of an immunotoxin made with anti-transferrin receptor and a recombinant form of Pseudomonas exotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8545–8549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann U., Pai L. H., FitzGerald D. J., Willingham M., Pastan I. B3(Fv)-PE38KDEL, a single-chain immunotoxin that causes complete regression of a human carcinoma in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8616–8620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner J., Rudolph R. Renaturation, purification and characterization of recombinant Fab-fragments produced in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Feb;9(2):157–162. doi: 10.1038/nbt0291-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner J., Rudolph R. Routes to active proteins from transformed microorganisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1991 Aug;2(4):532–538. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(91)90077-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Batra J. K., Gallo M. G., Willingham M. C., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. A rapid method of cloning functional variable-region antibody genes in Escherichia coli as single-chain immunotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1066–1070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Jinno Y., FitzGerald D., Pastan I. Pseudomonas exotoxin contains a specific sequence at the carboxyl terminus that is required for cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):308–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Jinno Y., Gallo M. G., FitzGerald D., Pastan I. Mutagenesis of Pseudomonas exotoxin in identification of sequences responsible for the animal toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16306–16310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Queen C., Junghans R. P., Waldmann T. A., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. A recombinant immunotoxin consisting of two antibody variable domains fused to Pseudomonas exotoxin. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):394–397. doi: 10.1038/339394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Collier R. J. Enzymatically active peptide from the adenosine diphosphate-ribosylating toxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):832–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.832-841.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautry-Varsat A., Garel J. R. Independent folding regions in aspartokinase-homoserine dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1396–1401. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. M., Collier R. J. Exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: substitution of glutamic acid 553 with aspartic acid drastically reduces toxicity and enzymatic activity. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4967–4971. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4967-4971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel J. R., Martel A., Muller K., Ikai A., Morishima N., Sutoh K. Role of subunit interactions in the self-assembly of oligomeric proteins. Adv Biophys. 1984;18:91–113. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(84)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. E., Rudolph R., Jaenicke R. A kinetic study of the competition between renaturation and aggregation during the refolding of denatured-reduced egg white lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 19;30(11):2790–2797. doi: 10.1021/bi00225a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Smith D. H., Baldridge J. S., Harkins R. N., Vasil M. L., Chen E. Y., Heyneker H. L. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression in Escherichia coli of the exotoxin A structural gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2645–2649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J., Fitzgerald D. J., Adhya S., Pastan I. Functional domains of Pseudomonas exotoxin identified by deletion analysis of the gene expressed in E. coli. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R. Folding and association of proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1987;49(2-3):117–237. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(87)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinno Y., Chaudhary V. K., Kondo T., Adhya S., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. Mutational analysis of domain I of Pseudomonas exotoxin. Mutations in domain I of Pseudomonas exotoxin which reduce cell binding and animal toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13203–13207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinno Y., Ogata M., Chaudhary V. K., Willingham M. C., Adhya S., FitzGerald D., Pastan I. Domain II mutants of Pseudomonas exotoxin deficient in translocation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):15953–15959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo T., FitzGerald D., Chaudhary V. K., Adhya S., Pastan I. Activity of immunotoxins constructed with modified Pseudomonas exotoxin A lacking the cell recognition domain. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9470–9475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitraki A., Fane B., Haase-Pettingell C., Sturtevant J., King J. Global suppression of protein folding defects and inclusion body formation. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):54–58. doi: 10.1126/science.1648264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Chaudhary V. K., Pastan I., FitzGerald D. J. Processing of Pseudomonas exotoxin by a cellular protease results in the generation of a 37,000-Da toxin fragment that is translocated to the cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20678–20685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai L. H., Batra J. K., FitzGerald D. J., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Anti-tumor activities of immunotoxins made of monoclonal antibody B3 and various forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3358–3362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantoliano M. W., Bird R. E., Johnson S., Asel E. D., Dodd S. W., Wood J. F., Hardman K. D. Conformational stability, folding, and ligand-binding affinity of single-chain Fv immunoglobulin fragments expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 22;30(42):10117–10125. doi: 10.1021/bi00106a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., FitzGerald D. Pseudomonas exotoxin: chimeric toxins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15157–15160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Lovelace E. T., Gallo M. G., Rutherford A. V., Magnani J. L., Willingham M. C. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies B1 and B3 that react with mucinous adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 15;51(14):3781–3787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seetharam S., Chaudhary V. K., FitzGerald D., Pastan I. Increased cytotoxic activity of Pseudomonas exotoxin and two chimeric toxins ending in KDEL. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17376–17381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegall C. B., Chaudhary V. K., FitzGerald D. J., Pastan I. Functional analysis of domains II, Ib, and III of Pseudomonas exotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14256–14261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaucheret H., Signon L., Le Bras G., Garel J. R. Mechanism of renaturation of a large protein, aspartokinase-homoserine dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2785–2790. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




