Abstract
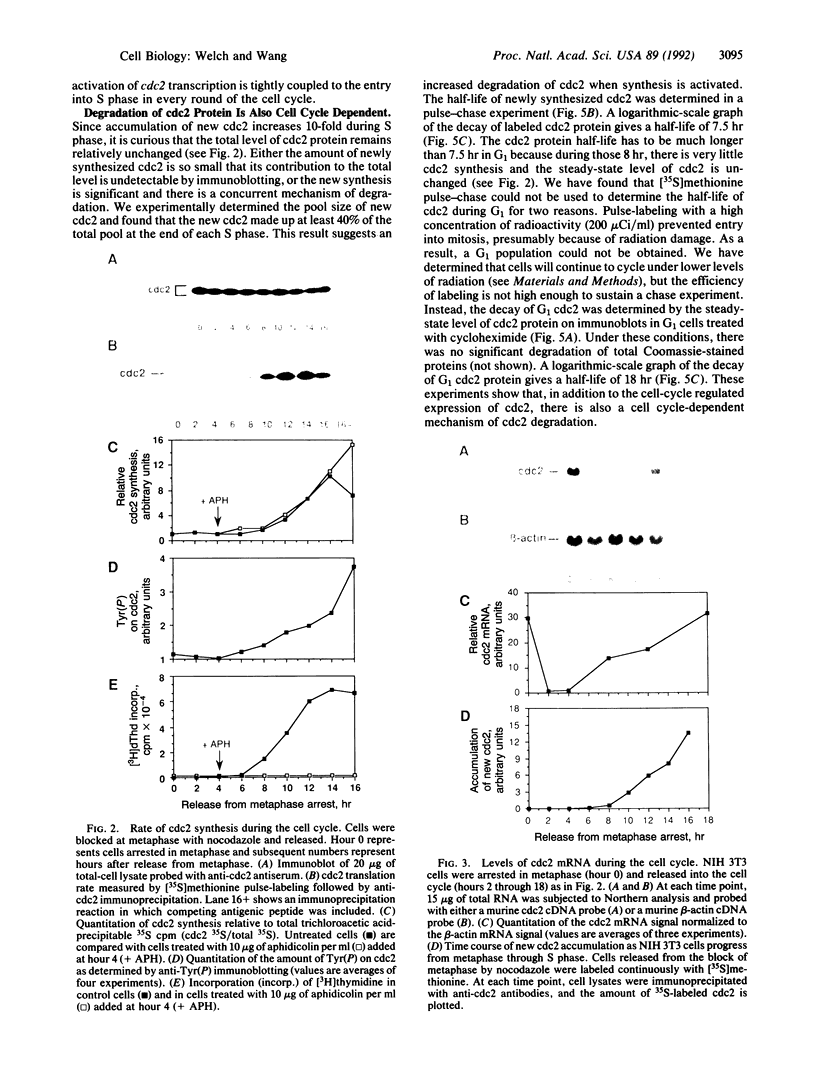
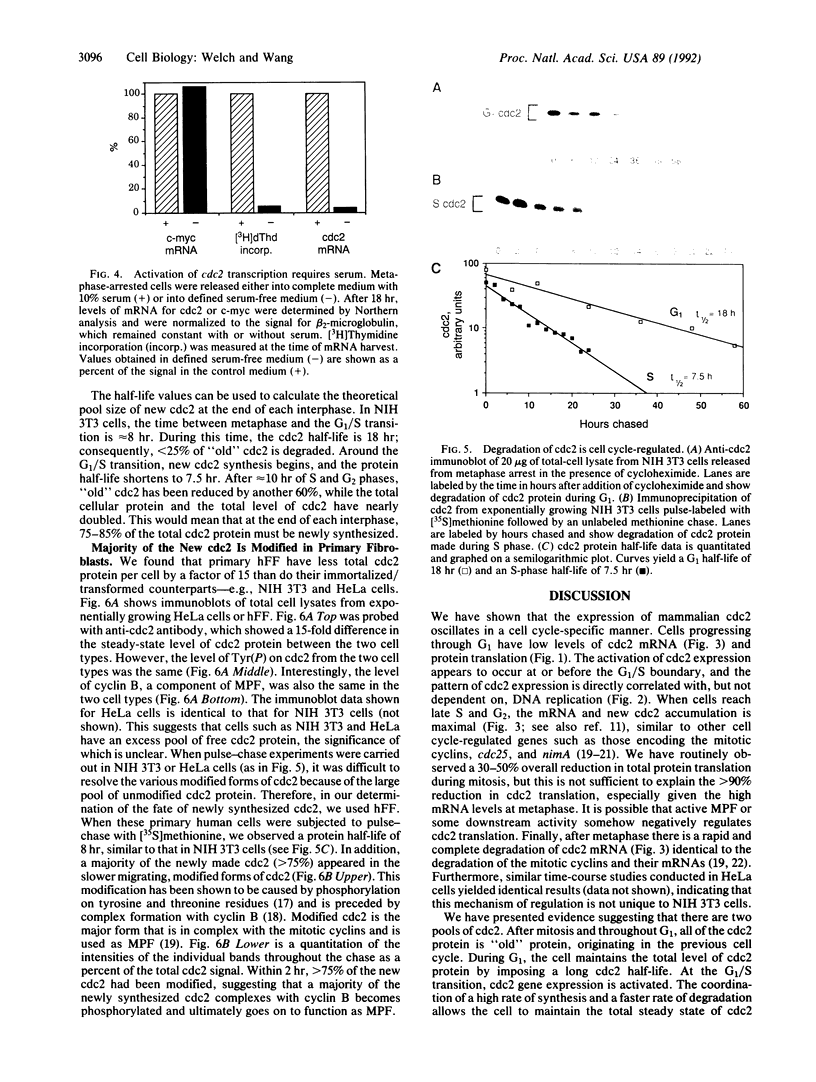
The product of the cdc2 gene (cdc2 or p34cdc2), the catalytic subunit of M phase-promoting factor (MPF), is held at a constant steady-state level throughout the cell cycle. In this report, we show that the constant concentration is maintained by a coordinated regulation of protein synthesis and degradation. At the end of each mitosis, cdc2 transcription is shut off, and the mRNA is rapidly degraded. A 12-fold activation of cdc2 gene transcription occurs every round of the cell cycle at the G1/S transition, in a growth factor-dependent manner. The increase in mRNA correlates with the accumulation of newly synthesized cdc2 during S and G2 phases. At the onset of mitosis, the translation of cdc2 mRNA is shut off. During G1 phase, the cdc2 protein has a relatively long half-life of 18 hr, so cdc2 made in the previous cell cycle is maintained. Once synthesis is activated at G1/S, a concurrent mechanism of degradation is activated, and the protein half-life is reduced to 7.5 hr. By the end of interphase, new cdc2 accounts for 75-85% of the total cdc2 pool. In addition, we show that greater than 75% of the new cdc2 complexes with cyclin, suggesting that a majority of the new cdc2 functions as MPF.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broek D., Bartlett R., Crawford K., Nurse P. Involvement of p34cdc2 in establishing the dependency of S phase on mitosis. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):388–393. doi: 10.1038/349388a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. The mammalian cdc2 protein kinase: mechanisms of regulation during the cell cycle. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;12:21–27. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_12.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Piwnica-Worms H., Morrison D., Druker B., Roberts T., Beach D. Human cdc2 protein kinase is a major cell-cycle regulated tyrosine kinase substrate. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):738–744. doi: 10.1038/336738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkacz B., Carr A., Nurse P. Transcription of the cdc2 cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):369–373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa Y., Piwnica-Worms H., Ernst T. J., Kanakura Y., Griffin J. D. cdc2 gene expression at the G1 to S transition in human T lymphocytes. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):805–808. doi: 10.1126/science.2237430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Spurr N. K., Nurse P. Regulated expression and phosphorylation of a possible mammalian cell-cycle control protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):676–679. doi: 10.1038/333676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. H., Russell P., Reed S. I. Periodic biosynthesis of the human M-phase promoting factor catalytic subunit p34 during the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3847–3851. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Hayles J., Nurse P. Regulation of the cell cycle timing of mitosis. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;12:1–8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_12.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. Regulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13856–13864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani S. A., May G. S., Morris N. R. Regulation of the mRNA levels of nimA, a gene required for the G2-M transition in Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1495–1504. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. p34cdc2: the S and M kinase? New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):389–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadhu K., Reed S. I., Richardson H., Russell P. Human homolog of fission yeast cdc25 mitotic inducer is predominantly expressed in G2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5139–5143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Th'ng J. P., Wright P. S., Hamaguchi J., Lee M. G., Norbury C. J., Nurse P., Bradbury E. M. The FT210 cell line is a mouse G2 phase mutant with a temperature-sensitive CDC2 gene product. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90164-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobey R. A., Valdez J. G., Crissman H. A. Synchronization of human diploid fibroblasts at multiple stages of the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Dec;179(2):400–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90279-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]