Abstract
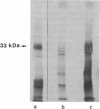
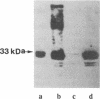
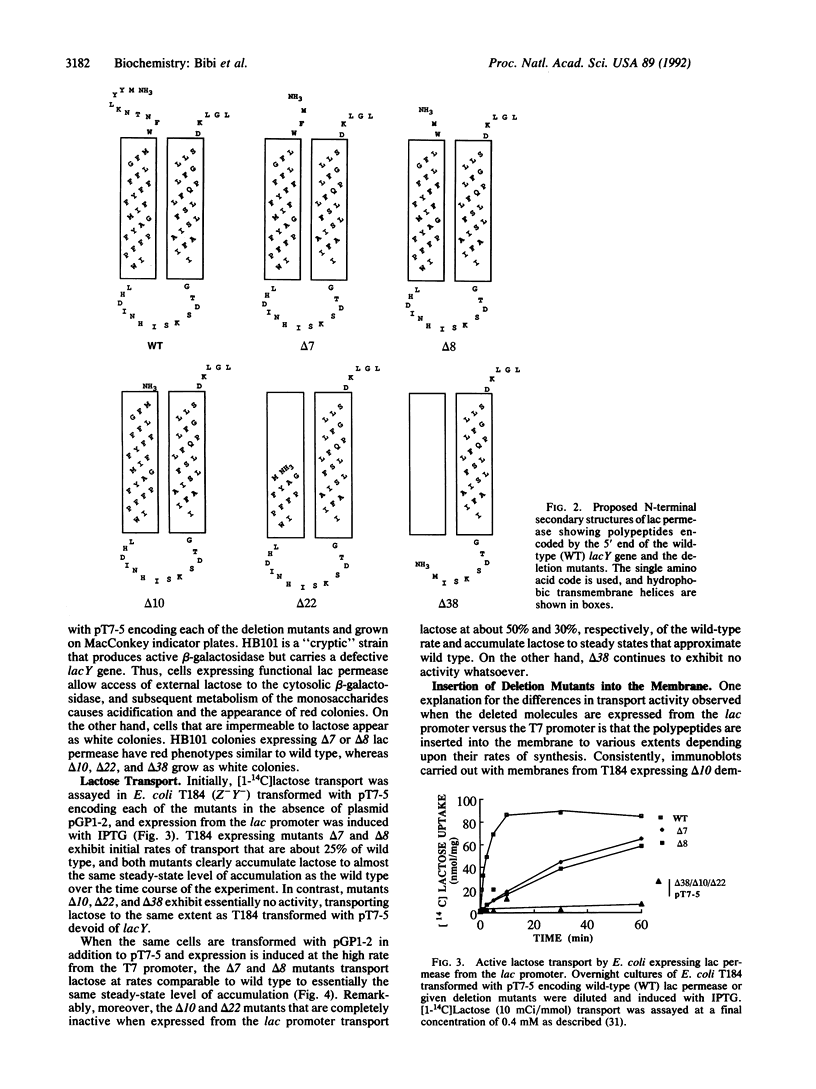
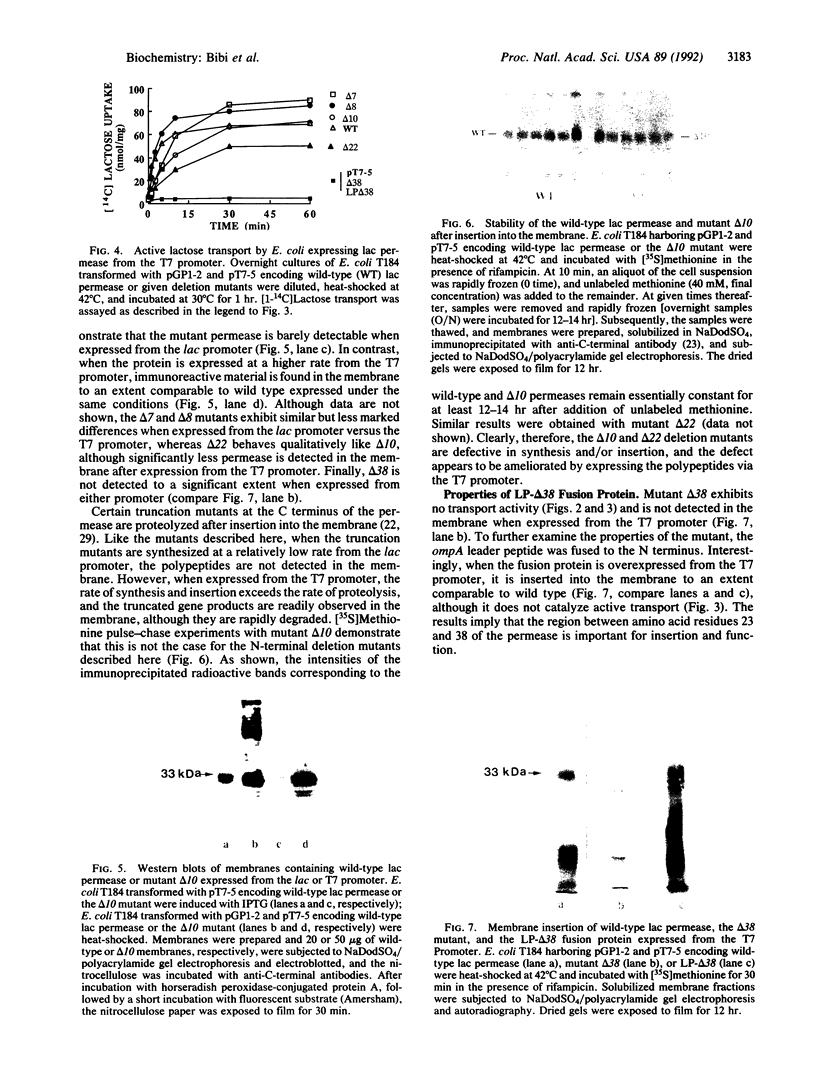
When the lactose (lac) permease of Escherichia coli is expressed from the lac promoter at relatively low rates, deletion of amino acid residues 2-8 (delta 7) or 2-9 (delta 8) from the hydrophilic N terminus has a relatively minor effect on the ability of the permease to catalyze active lactose transport. Activity is essentially abolished, however, and the permease is hardly detected in the membrane when two additional amino acid residues are deleted (delta 10), and mutants deleted of residues 2-23 (delta 22) or 2-39 (delta 38) also exhibit no activity and are not inserted into the membrane. Dramatically, when the defective deletion mutants are overexpressed at high rates via the T7 promoter, delta 10 and delta 22 are inserted into the membrane in a stable form and catalyze active lactose transport in a highly significant manner, whereas delta 38 is hardly detected in the membrane and exhibits no activity. Interestingly, a fusion protein consisting of delta 38 and the ompA leader peptide is inserted into the membrane but exhibits no transport activity. The results indicate that the N-terminal hydrophilic domain of lac permease and the N-terminal half of the first putative transmembrane alpha-helix are not mandatory for either membrane insertion or transport activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibi E., Verner G., Chang C. Y., Kaback H. R. Organization and stability of a polytopic membrane protein: deletion analysis of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7271–7275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocklage H., Müller-Hill B. lacZ--Y+ fusions in Escherichia coli. DNA sequencing reveals the eight N-terminal residues of lac permease as non-essential. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):561–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calamia J., Manoil C. lac permease of Escherichia coli: topology and sequence elements promoting membrane insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4937–4941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Herzlinger D., Mitchell R., DeChiara S., Danho W., Gabriel T. F., Kaback H. R. Intramolecular dislocation of the COOH terminus of the lac carrier protein in reconstituted proteoliposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Tahara S. M., Patel L., Goldkorn T., Kaback H. R. Preparation, characterization, and properties of monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6894–6898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco N., Viitanen P., Herzlinger D., Kaback H. R. Monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. 1. Functional studies. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3681–3687. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consler T. G., Tsolas O., Kaback H. R. Role of proline residues in the structure and function of a membrane transport protein. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1291–1298. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehring R., Beyreuther K., Wright J. K., Overath P. In vitro and in vivo products of E. coli lactose permease gene are identical. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):537–540. doi: 10.1038/283537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrmann M., Beckwith J. Proper insertion of a complex membrane protein in the absence of its amino-terminal export signal. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16530–16533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Boublik M., Kaback H. R. Structure of the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M., Blobel G. Bovine opsin has more than one signal sequence. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):338–343. doi: 10.1038/318338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkorn T., Rimon G., Kaback H. R. Topology of the lac carrier protein in the membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3322–3326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzlinger D., Carrasco N., Kaback H. R. Functional and immunochemical characterization of a mutant of Escherichia coli energy uncoupled for lactose transport. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):221–229. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzlinger D., Viitanen P., Carrasco N., Kaback H. R. Monoclonal antibodies against the lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli. 2. Binding studies with membrane vesicles and proteoliposomes reconstituted with purified lac carrier protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3688–3693. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson J. R., Coon M. J., Porter T. D. Purification and properties of a shortened form of cytochrome P-450 2E1: deletion of the NH2-terminal membrane-insertion signal peptide does not alter the catalytic activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9141–9145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna E., Hardy D., Pastore J. C., Kaback H. R. Sequential truncation of the lactose permease over a three-amino acid sequence near the carboxyl terminus leads to progressive loss of activity and stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2969–2973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. J., Foster D. L., Wilson T. H., Kaback H. R. Purification and reconstitution of functional lactose carrier from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11804–11808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Weigel U., Neuhaus J. M., Soppa J., Seckler R., Riede I., Bocklage H., Müller-Hill B., Aichele G., Wright J. K. Lactose permease of Escherichia coli: properties of mutants defective in substrate translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5535–5539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. G., Rosenbusch J. P. Topography of lactose permease from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15906–15914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepe P. D., Kaback H. R. Site-directed mutagenesis of tyrosine residues in the lac permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):6127–6132. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepe P. D., Zbar R. I., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R. A five-residue sequence near the carboxyl terminus of the polytopic membrane protein lac permease is required for stability within the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3992–3996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. The use of thin acrylamide gels for DNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Möröy T., Wright J. K., Overath P. Anti-peptide antibodies and proteases as structural probes for the lactose/H+ transporter of Escherichia coli: a loop around amino acid residue 130 faces the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2403–2409. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Wright J. K., Overath P. Peptide-specific antibody locates the COOH terminus of the lactose carrier of Escherichia coli on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10817–10820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Wright J. K. Sidedness of native membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli and orientation of the reconstituted lactose: H+ carrier. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):269–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stochaj U., Bieseler B., Ehring R. Limited proteolysis of lactose permease from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 15;158(2):423–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stochaj U., Ehring R. The N-terminal region of Escherichia coli lactose permease mediates membrane contact of the nascent polypeptide chain. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Mar 16;163(3):653–658. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stochaj U., Fritz H. J., Heibach C., Markgraf M., von Schaewen A., Sonnewald U., Ehring R. Truncated forms of Escherichia coli lactose permease: models for study of biosynthesis and membrane insertion. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2639–2645. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2639-2645.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Bramhall J., Riede I., Wright J. K., Fürst M., Aichele G., Wilhelm U., Overath P. Lactose carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Structure and expression of plasmids carrying the Y gene of the lac operon. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):223–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumble W. R., Viitanen P. V., Sarkar H. K., Poonian M. S., Kaback H. R. Site-directed mutagenesis of cys148 in the lac carrier protein of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 30;119(3):860–867. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90853-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viitanen P., Garcia M. L., Kaback H. R. Purified reconstituted lac carrier protein from Escherichia coli is fully functional. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1629–1633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H., Wright J. K., Jähnig F. The structure of the lactose permease derived from Raman spectroscopy and prediction methods. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3625–3631. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Iwaarden P. R., Pastore J. C., Konings W. N., Kaback H. R. Construction of a functional lactose permease devoid of cysteine residues. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9595–9600. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]