Abstract
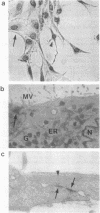
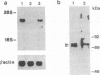
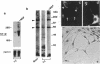
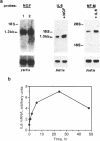
Neural crest cell derivatives have been suggested to be involved in thymus development. We established nonlymphoid thymic stromal cell cultures capable of supporting T-cell differentiation. In these nonlymphoid cell cultures, we identified cells with phenotypic and biochemical markers specific for neuronal cells. Neurofilament mRNA and 68- and 160-kDa neurofilament proteins, as well as 74-kDa synapsin I isoform, were expressed in many of the cultured cells. For example, neurofilament immunoreactivity was detected in 20-30% of the cells. To see whether thymic neuronal-like cells were involved in a neural differentiation pathway, we investigated the effect of nerve growth factor (NGF) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), two known neurotrophic factors. The expression of the above-described neural markers was enhanced by NGF and IL-6, which we report to be produced in an autocrine way by thymic stromal cell cultures. Finally, we found that IL-6 gene expression in these cell cultures was enhanced by NGF. Evidence is thus offered of a neuromodulatory loop within the thymic stromal cell population supported by local production of NGF and IL-6 and involving neural cell elements. Interestingly, IL-6, which is known to be implicated in thymocyte differentiation, also displays a neuromodulatory activity on thymic stromal cells, suggesting a multivalent role for this cytokine within the thymus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Axel R. A bipotential neuroendocrine precursor whose choice of cell fate is determined by NGF and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90823-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman D. E., Kirby M. L. Dependence of thymus development on derivatives of the neural crest. Science. 1984 Feb 3;223(4635):498–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6606851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. F., Fischer M., Frank G., Zlotnik A. Distinct patterns of lymphokine requirement for the proliferation of various subpopulations of activated thymocytes in a single cell assay. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 1;143(5):1598–1605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Benfenati F., Valtorta F., Greengard P. The synapsins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:433–460. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Cameron R., Greengard P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Shimizu K., Bowring M. A., Wells S. Expression of receptors for tetanus toxin and monoclonal antibody A2B5 by pancreatic islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felli M. P., Vacca A., Meco D., Screpanti I., Farina A. R., Maroder M., Martinotti S., Petrangeli E., Frati L., Gulino A. Retinoic acid-induced down-regulation of the interleukin-2 promoter via cis-regulatory sequences containing an octamer motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4771–4778. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Bevan M. J. H-2 antigens of the thymus determine lymphocyte specificity. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):766–775. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Malipiero U. V., Leist T. P., Zinkernagel R. M., Schwab M. E., Fontana A. On the cellular source and function of interleukin 6 produced in the central nervous system in viral diseases. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Apr;19(4):689–694. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geenen V., Defresne M. P., Robert F., Legros J. J., Franchimont P., Boniver J. The neurohormonal thymic microenvironment: immunocytochemical evidence that thymic nurse cells are neuroendocrine cells. Neuroendocrinology. 1988 Apr;47(4):365–368. doi: 10.1159/000124938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez J. C., Palacios R. Heterogeneity of thymic epithelial cells in promoting T-lymphocyte differentiation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):642–646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Lasek R. J. The slow component of axonal transport. Identification of major structural polypeptides of the axon and their generality among mammalian neurons. J Cell Biol. 1975 Aug;66(2):351–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruisbeek A. M., Zijlstra J. J., Kröse T. J. Distinct effects of T cell growth factors and thymic epithelial factors on the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes by thymocyte subpopulations. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):995–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J. M., Fredrickson G., Reis L. F., Diamantstein T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Vilcek J. Interleukin 2-dependent and interleukin 2-independent pathways of regulation of thymocyte function by interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8643–8647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le P. T., Lazorick S., Whichard L. P., Yang Y. C., Clark S. C., Haynes B. F., Singer K. H. Human thymic epithelial cells produce IL-6, granulocyte-monocyte-CSF, and leukemia inhibitory factor. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3310–3315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: thirty-five years later. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1145–1154. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02347.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum M. H., Carbonetto S., Grosveld F., Flavell D., Mushynski W. E. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional effects of nerve growth factor on expression of the three neurofilament subunits in PC-12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5662–5667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Effect of neuropeptides on production of inflammatory cytokines by human monocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1218–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.2457950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Squinto S., Ip N. Y., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. Neurotrophin-3: a neurotrophic factor related to NGF and BDNF. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1446–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G., Brewster D. R., Goetzl E. J. Specific stimulation of human T lymphocytes by substance P. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1613–1615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano C., Nichols R. A., Greengard P., Greene L. A. Synapsin I in PC12 cells. I. Characterization of the phosphoprotein and effect of chronic NGF treatment. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1294–1299. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01294.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano C., Nichols R. A., Greengard P. Synapsin I in PC12 cells. II. Evidence for regulation by NGF of phosphorylation at a novel site. J Neurosci. 1987 May;7(5):1300–1306. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-05-01300.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakamura S., Taga T., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Kaziro Y. Induction of neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells by B-cell stimulatory factor 2/interleukin 6. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3546–3549. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztein M. B., Goldstein A. L. Thymic hormones--a clinical update. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1986;9(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00201901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söder O., Hellström P. M. The tachykinins neurokinin A and physalaemin stimulate murine thymocyte proliferation. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;90(1):91–96. doi: 10.1159/000235006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe O., Akira S., Kamiya T., Wong G. G., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Genomic structure of the murine IL-6 gene. High degree conservation of potential regulatory sequences between mouse and human. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3875–3881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Hollinshead M., Fuller S. D., Tooze S. A., Huttner W. B. Morphological and biochemical evidence showing neuronal properties in AtT-20 cells and their growth cones. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;49(2):259–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J. Interleukin-6: an overview. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:253–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Callahan G. N., Althage A., Cooper S., Klein P. A., Klein J. On the thymus in the differentiation of "H-2 self-recognition" by T cells: evidence for dual recognition? J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):882–896. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):701–702. doi: 10.1038/248701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ewijk W. Immunohistology of lymphoid organs. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989 Jun;1(5):954–965. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]