Abstract
Background
Tongil (IR667-98-1-2) rice, developed in 1972, is a high-yield rice variety derived from a three-way cross between indica and japonica varieties. Tongil contributed to the self-sufficiency of staple food production in Korea during a period known as the `Korean Green Revolution'. We analyzed the nucleotide-level genome structure of Tongil rice and compared it to those of the parental varieties.
Results
A total of 17.3 billion Illumina Hiseq reads, 47× genome coverage, were generated for Tongil rice. Three parental accessions of Tongil rice, two indica types and one japonica type, were also sequenced at approximately 30x genome coverage. A total of 2,149,991 SNPs were detected between Tongil and Nipponbare varieties. The average SNP frequency of Tongil was 5.77 per kb. Genome composition was determined based on SNP data by comparing Tongil with three parental genome sequences using the sliding window approach. Analyses revealed that 91.8% of the Tongil genome originated from the indica parents and 7.9% from the japonica parent. Copy numbers of SSR motifs, ORF gene distribution throughout the whole genome, gene ontology (GO) annotation, and some yield-related QTLs or gene locations were also comparatively analyzed between Tongil and parental varieties using sequence-based tools. Each genetic factor was transferred from the parents into Tongil rice in amounts that were in proportion to the whole genome composition.
Conclusions
Tongil was derived from a three-way cross among two indica and one japonica varieties. Defining the genome structure of Tongil rice demonstrates that the Tongil genome is derived primarily from the indica genome with a small proportion of japonica genome introgression. Comparative gene distribution, SSR, GO, and yield-related gene analysis support the finding that the Tongil genome is primarily made up of the indica genome.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12284-014-0022-5) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Tongil rice, Three-way cross, Next-generation sequencing, SEG map, Indica/japonica hybridization
Background
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is a staple food for more than half of the world's population, providing about 19 percent of the world's and 29 percent of Asia's caloric supply (IRRI [2009]). Although demands on the nutritional and industrial functionality of rice are increasing, especially to improve human health and quality of life, improving the yield potential of rice is still a major challenge for rice breeders, who must address the rapid growth of the world population along with dramatic reductions in the amount of cultivated land (Khush [1999]), as well as environmental challenges (Nelson, International Food Policy Research Institute [2009]). Asian varieties of cultivated rice include two major subspecies, O. sativa indica and O. s. japonica, which are differentiated based on morphological and physiological characteristics and geographical distribution (Morishima and Oka [1981]; Sano and Morishima [1992]). O. s. indica cultivars have higher genetic diversity (Lu et al. [2002]), a broader cultivation range, and stronger resistance to prominent diseases and insect pests compared to O. s. japonica cultivars (Chung and Heu [1991]). Inter-subspecific hybridization between indica and japonica rice cultivars may enrich allelic variation and facilitate hybrid vigor by creating new genetic recombinations (Cheng et al. [2007]). In spite of these advantages, the introduction of desirable indica traits into the japonica variety has not been successful due to reproductive barriers and the incorporation of undesirable characteristics, such as low eating quality for people who prefer the taste of japonica rice (Chung and Heu [1991]).
Tongil rice (IR667-98-1-2) is the first semi-dwarf variety obtained by a three-way cross of indica/japonica varieties as part of a collaborative research project between the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) and the government of South Korea (Figure 1). The development of Tongil rice resulted in a significant yield increase from 4 to 5 t ha-1, corresponding to a 30% yield increase relative to the leading japonica varieties grown in Korea (Chung and Heu [1980]). After the introduction of Tongil rice in 1972, Korean rice production significantly increased and the South Korean government announced the achievement of agricultural self-sufficiency (the so-called `Green Revolution') in 1977. However, the genome characterization and structure of Tongil rice have never been analyzed.
Figure 1.

Morphological comparison of Tongil and parental lines. From left to right: Tongil, Yukara, IR8, and TN1. (A) The plant architecture of Tongil, its japonica parent (Yukara), and its indica parents (IR8 and TN1). (B) The panicle phenotype of Tongil and its parents. (C) The grain shapes and brown rice shapes of Tongil and its parents. Scale bars are included in each panel.
Rice is a useful model crop for studying genome structure due to its relatively small genome. Furthermore, its genetic and physical data have been extensively analyzed by the International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (IRGSP) (International Rice Genome Sequencing P [2005]). The recent improvement of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology has enabled high-throughput genotyping and elucidation of genome structures of various rice cultivars (Huang et al. [2009]; Huang et al. [2012]). Most sequence-based rice genome analyses are based on DNA polymorphisms, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertion-deletions (InDels). SNP detection is the first step for comparing DNA variation and is an effective tool to elucidate genome structure and composition (Feltus et al. [2004]; McNally et al. [2009]; Shen et al. [2010]; Chen et al. [2014]).
In this study, we sequenced the whole genomes of Tongil rice (Oryza sativa L.) and its parental varieties to analyze the genome structure of Tongil in detail and to identify regions of the indica and japonica parental genomes that introgressed in the Tongil genome. In addition, we analyzed previously reported yield-related genes (Gn1a, Ghd7, sd1, GS3 and qSW5), SSRs, GO annotation, and other genetic characteristics of the Tongil genome.
Results
Genome structure of Tongil
The whole genomes of Tongil and its three parental varieties, Yukara, IR8, and TN1 (Taichung Native 1), were sequenced on the Illumina-GAII platform. A large number of short reads were mapped onto the reference Nipponbare genome and then assembled into a consensus sequence. A total of 199,543,820 reads of the Tongil genome, corresponding to 17,339,883,560 bp (17.3 Gb), were generated, representing a 47-fold sequence depth and covering 88.8% of the Nipponbare pseudomolecules (Table 1 and Additional file 1: Table S1). We detected a total of 2,149,991 SNPs between Tongil and Nipponbare sequences (Additional file 2: Table S2). The two indica parents of Tongil, IR8 and TN1, had 6.22 and 6.04 SNPs per kb, respectively, whereas the japonica parent of Tongil, Yukara, had only 0.49 SNP per kb (Additional file 2: Table S2). Using the SNP data sets from Tongil and its parents, we defined the genomic origins of regions of the Tongil genome by SNP calling (Additional file 3: Figure S1; Additional file 4: Table S3; see also the SNP calling section in the Materials and Methods), and then performed a SEG-Map analysis (Zhao et al. [2010b]) of Tongil (Figure 2). The whole genome of Tongil consisted of an average contribution of 91.8% from indica, 7.9% from japonica, and 0.3% unknown (i.e., not defined as indica or japonica regions) (Figure 2 and Table 2). The contribution of indica to the Tongil genome varied across chromosomes, from 74% (Chr. 2) to 100% (Chr. 12). A relatively high proportion of the japonica genome was found on chromosomes 1, 2, and 3, whereas the japonica sequences were barely detectable on chromosomes 8 and 12. In addition, there were no differences in gene density between the indica- and japonica-derived genome regions of Tongil (Figure 2 and Table 2).
Figure 2.
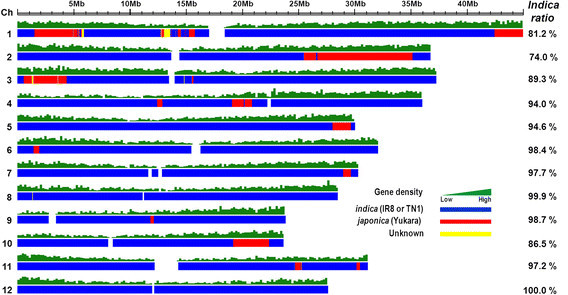
Indica / japonica genome organization on the 12 chromosomes of Tongil. Blue indicates the indica genome (TN1 and IR8); red indicates the japonica genome (Yukara); and yellow indicates a region from an unknown genome. The percentages describe the proportion of indica contribution on each chromosome.
Table 1.
General sequencing statistics for Tongil and its parental genomes
| Variety | Number of reads | Total read length (bp) | Mapped read length (bp) | Sequencing depth (×) | Coveragea)(%) | SNP frequency (SNPs/kb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tongil | 199,543,820 | 17,339,883,560 | 330,933,489 | 47 | 88.8 | 5.77 |
| Yukara | 114,615,268 | 12,429,060,750 | 345,058,384 | 34 | 92.6 | 0.49 |
| IR8 | 109,304,614 | 11,790,909,253 | 327,065,806 | 32 | 87.7 | 6.22 |
| TN1 | 105,708,026 | 11,299,286,038 | 326,132,058 | 30 | 87.5 | 6.04 |
a)Coverage to Nipponbare genome sequence.
Sequencing and mapping against the Nipponbare reference genome.
Table 2.
Determination of the indica / japonica genome origin of Tongil, based on a window size of 9
| Chromosome | Pseudomolecule | Indicaregion (bp) | Ratio (%) | Japonicaregion (bp) | Ratio (%) | Unknown region (bp) | Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45,038,604 | 36,563,905 | 81.2 | 7,596,808 | 16.9 | 877,891 | 2.0 |
| 2 | 36,792,247 | 27,235,850 | 74.0 | 9,544,379 | 25.9 | 12,018 | 0.0 |
| 3 | 37,312,367 | 33,336,733 | 89.3 | 3,748,667 | 10.1 | 226,967 | 0.6 |
| 4 | 36,060,865 | 33,898,364 | 94.0 | 2,150,911 | 6.0 | 11,590 | 0.0 |
| 5 | 30,073,438 | 28,436,341 | 94.6 | 1,637,097 | 5.4 | - | - |
| 6 | 32,124,789 | 31,619,689 | 98.4 | 499,676 | 1.6 | 5,424 | 0.0 |
| 7 | 30,357,780 | 29,667,148 | 97.7 | 690,632 | 2.3 | - | - |
| 8 | 28,530,027 | 28,487,631 | 99.9 | 333 | - | 42,063 | 0.2 |
| 9 | 23,895,721 | 23,592,877 | 98.7 | 302,844 | 1.3 | - | - |
| 10 | 23,703,430 | 20,504,662 | 86.5 | 3,198,768 | 13.5 | - | - |
| 11 | 31,219,694 | 30,345,040 | 97.2 | 846,802 | 2.7 | 27,852 | 0.1 |
| 12 | 27,679,166 | 27,679,166 | 100.0 | - | - | - | - |
| Total | 382,788,128 | 351,367,406 | 91.8 | 30,216,917 | 7.9 | 1,203,805 | 0.3 |
Gene distribution and gene ontology analysis of Tongil
We analyzed the gene content of Tongil to understand the relationship between the composition of the genome and genes (open reading frames: ORFs), and also to elucidate the distribution of indica- and japonica- originated genes (alleles) within the Tongil genome. The gene distribution ratio according to indica or japonica genome composition was similar to the genome distribution ratio (Table 2 and Additional file 5: Table S4). The origins of genes from the indica and japonica parents were 88.3% and 11.4%, respectively, suggesting that the average gene composition was similar to the genome composition ratio of Tongil, although the distribution of parental origin varied across chromosomes. We performed gene ontology (GO) analysis of the Tongil genome according to three categories to identify biological patterns using a list of genes derived from indica, japonica, and unknown genomes: cellular components, molecular functions, and biological processes (Additional file 6: Figure S2; Additional file 7: Figure S3; Additional file 8: Figure S4). The results of GO analysis revealed that the average contribution of the indica or japonica genome to each GO category was almost identical to the gene and genome distribution ratios. O. s. indica and O. s. japonica contributed 86.8% and 12.7% of the cellular components, 87.4% and 12.2% of the molecular functions, and 87.3% and 12.2% of the biological processes, respectively, to the Tongil genome. However, in the `molecular functions' category, all 17 genes related to channel regulator activity were derived from indica regions, whereas all adhesion-related genes in the biological processes category were derived solely from japonica regions.
Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in the Tongil genome
A total of 177 distinctive motif families were annotated on the Tongil genome (Additional file 9: Figure S5; Additional file 10: Figure S6). Di-nucleotide repeats were predominant among the classified repeats, and AT/TA repeats were the most abundant motifs in both indica- (29.09%) and japonica- derived (21.8%) regions within the Tongil genome. The next most abundant motif relative to AT/TA was CT/GA, and CGC was the most abundant motif among tri-nucleotide repeats. The di-, tri-, and tetra-nucleotide repeat patterns were different from that of the reference Nipponbare genome (McCouch et al. [2002]; Zhou et al. [2005]), and also differed from that of wheat (Weng et al. [2005]). A total of 90.1% of SSR motifs in the Tongil genome were from indica, 9.6% were from japonica, and 0.3% were from an unknown genome (Additional file 10: Figure S6).
Distribution of yield-related genes in the Tongil genome
One of the most important aims of this study was to explore which regions of the indica and japonica parental genomes have introgressed into the Tongil variety to provide its high-yield potential. Tongil is morphologically characterized by short plant height, lodging resistance, open plant architecture, medium-long erect leaves, thick leaf sheaths and culms, relatively long panicles, and easily shattered grain (Chung and Heu [1980]) (Figure 1). Although these phenotypic characteristics affect Tongil's high-yield potential, to date we have no molecular genetic evidence regarding the nature of these traits, with the exception of semi-dwarf gene 1 (sd1) (Chung and Heu [1980]). Therefore, we analyzed several well-characterized genes associated with high yield potential in the Tongil genome: sd1 (Nagano et al. [2005]; Sasaki et al. [2002]; Monna et al. [2002]), Ghd7 (Liu et al. [2013]; Xue et al. [2008]), Gn1a (Ashikari et al. [2005]; Miura et al. [2010]), qSW5 (Yan et al. [2011]; Shomura et al. [2008]), GS3 (Takano-Kai et al. [2009]; Fan et al. [2006]), and GW2 (Li et al. [2010]; Song et al. [2007]).
sd(semi-dwarf stature)
Semi-dwarf stature is one of the main genetic contributors to the success of the Green Revolution. The introduction of semi-dwarf genes increased yield by conferring lodging resistance, which enabled greater input of nitrogen fertilizer. Tongil was the first variety into which the sd1 allele was introduced in South Korea. Analysis of the sd1 gene, which encodes GA20ox-2 in Tongil and its parents, revealed that Tongil received its sd1 from an indica parent, IR8 or TN1; this allele contained a 383-bp deletion resulting in a frame-shift to form a stop codon (Figure 3A). We also confirmed other sd1 alleles derived from the native semi-dwarf rice variety Jikkoku (G281T) and the γ-ray-induced varieties Reimei (C1045G) and Calose76 (C796T) (Monna et al. [2002]; Sasaki et al. [2002]). However, Yukara, the japonica parent of Tongil, did not have any sd1 alleles.
Figure 3.
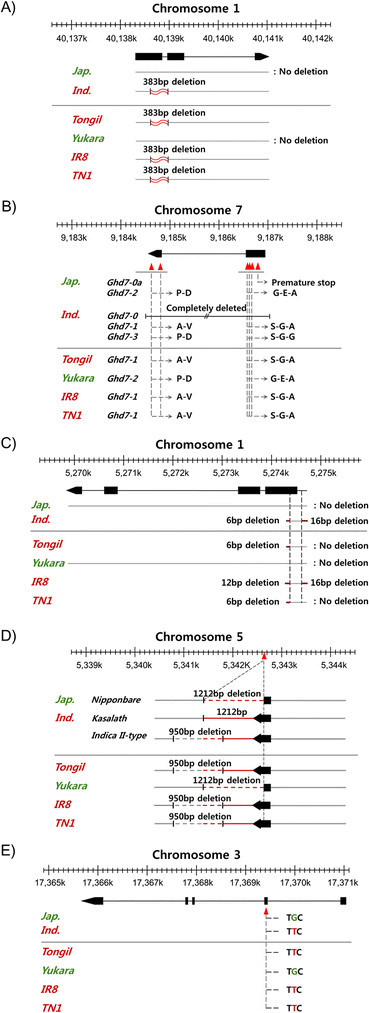
Indica / japonica region comparisons of high yield-related alleles or QTLs. A) sd1, B) Ghd7, C) Gn1a, D) qSW5, and E) GS3. Black arrows and box regions represent exons. Vertical, dashed lines refer to the same position in the genome or gene region.
Ghd(grain number, plant height, and heading date)
A gene encoding a CCT domain protein, Ghd7, is an important regulator of potential yield, plant height, and heading date in rice. Plant height and panicle size are increased under long-day conditions by the delay in heading date resulting from increased Ghd7 expression. Ghd7 has five natural variant haplotypes (Xue et al. [2008]). Among these, Tongil possesses the Ghd7-1 allele (A-G-S-V-A) derived from indica parent IR8 or TN1 (Figure 3B), which is considered to be the original, fully-functional wild-type allele; plants with this allele are relatively tall, late heading, have large panicles, and are widely grown. By contrast, the japonica parent of Tongil, Yukara, has the Ghd7-2 allele (A-E-G-D-P), which is weaker than Ghd7-1 and is found in temperate japonica varieties.
Gn1a(Grain number on chromosome 1)
Gn1a is one of the most effective QTLs for increasing grain number. It is predicted to encode a cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase (OsCKX2). Habataki, an indica rice variety, has a 16-bp deletion in the 5' UTR, a 6-bp deletion in the first exon, and three amino acid substitutions in the first and fourth exons of this gene. In addition, an 11-bp deletion in the third exon has been detected in the high-yielding rice variety 5150 (Ashikari et al. [2005]). Comparisons of DNA sequences between Tongil and parent varieties revealed that the Tongil sequence was identical to the TN1 allele, which had only a 6-bp deletion in the first exon and no 16 bp deletion in the 5' UTR, as in Habataki. On the other hand, IR8 contained a 16-bp deletion in the 5' UTR and a 12-bp deletion in the first exon, distinct from the pattern in the TN1 allele. We could not identify any variation in Yukara, which has the same allele sequence as Nipponbare (Figure 3C).
qSW5(QTL for seed width on chromosome 5)
qSW5 is responsible for seed width; the product of this gene controls cell number in the outer glume of the rice flower. The gene product increases seed width and seed weight by enlarging sink size. The Nipponbare-type allele, which contains a 1,212-bp deletion, is a loss-of-function allele relative to the Kasalath-type allele (Shomura et al. [2008]). In addition, the indica II-type allele has a 950-bp deletion relative to the Kasalath allele (Yan et al. [2011]). Comparisons of the qSW5 alleles between Tongil and parental varieties revealed that Tongil, IR8, and TN1 have the indica II-type allele, whereas Yukara has the Nipponbare allele (Figure 3D).
GS3(Grain length and weight; grain size 3)
GS3, which encodes a PEPB-like domain protein, was cloned from a QTL for grain length and weight on chromosome 3 in rice. A C-to-A substitution in the second exon of the GS3 gene is strongly associated with grain length and width: the A-allele confers significantly longer and thinner grains than the C-allele (Takano-Kai et al. [2009]; Fan et al. [2006]). Tongil possesses an A-allele originating from an indica parent, IR8 or TN1, whereas the japonica parent, Yukara has the C-allele (Figure 3E). In the case of another gene that controls grain width, GW2, there were no SNPs detected among any of the strains we sequenced or Nipponbare, indicating that GW2 is a highly conserved gene in rice and even in Zea mays (Li et al. [2010]; Song et al. [2007]).
Discussion
In this study, we used high-depth NGS analysis to demonstrate that the Tongil genome is composed of 91.8% indica, 7.9% japonica, and 0.3% unknown genome. The amounts and types of genes and SSRs in the Tongil genome were very similar to its genomic composition with respect to indica or japonica origin. This deviation from the expectation that about one-fourth of the Tongil genome originated from the japonica parent is likely due to the results of selection during the breeding process and/or to segregation distortion in favor of the indica genome because indica-type alleles and plants are favored among hybrid progenies from indica/japonica crosses (Harushima et al. [1996]; Lin et al. [1992]).
Tongil rice is highly successful in terms of grain yield in South Korea, although Korean climatic environments are not favorable to the cultivation of typical indica varieties (Chung and Heu [1991]). This may be attributable to its heightened adaptability compared to most indica varieties, perhaps due to the partial incorporation of the japonica parental genome.
From an agronomic viewpoint, rice yield is determined by the integration of four yield components: number of panicles per unit area, number of grains per panicle, filled grain ratio, and grain weight. Tongil is a heavy-panicle variety with more grains per panicle than its parental varieties (Chung and Heu [1991]). We manually sequenced the yield-related genes sd1, Gn1a, Ghd7, GS3, qSW5, and GW2 to determine which alleles came from the indica and japonica parents (Figure 3; Additional file 11: Table S5). The sd1, Gn1a, and Ghd7 alleles of Tongil originated from the indica parents, as did the GS3, qSW5, and GW2 alleles of Tongil, all of which are involved in determining seed size. Although Tongil and its indica parents share the same allele for these three genes, the seed shape of Tongil is closer to TN1 than that of IR8 (Figure 1). Thus, another gene or epistatic interaction may be involved in determining seed shape in the Tongil cultivar (Yan et al. [2011]). In fact, all of the alleles identified in Tongil were the same as those in TN1, one of the indica parents. Therefore, it is unlikely that a greater understanding of the high yield potential of Tongil could be achieved by analyzing these six yield-related genes. Complex genetic systems, including unknown genes and epistatic interactions, should be investigated in future studies.
Since the initial success of Tongil rice in Korea, numerous Tongil-type varieties of similar parentage or that were bred using Tongil rice as one of the parents have been developed to address future needs for food security. We predict that genomic information, including the SNP data provided in this study, will facilitate the efficient breeding of these and other Tongil-type varieties.
Conclusions
We determined the genome structure of Tongil rice, a successful cultivar derived from indica × japonica hybridization in Korea. Analyses of genome composition and genetic factors of Tongil rice demonstrate that the Tongil genome is derived mostly from the indica genome, with a small portion of japonica genome introgression. The approach used in this study to determine the parental origins of specific genome segments is applicable to the genomic dissection of agricultural breeding lines or varieties of diverse parental origins.
Methods
Plant materials
Plant lines subjected to whole-genome resequencing in the present study included Tongil (SNU accession no. 260697) and its parental lines: Yukara, an early maturing temperate japonica cultivar (RDA-Genebank Information Center accession no. IT004665); Taichung native 1 (TN1), the first semi-dwarf indica variety with high adaptability (RDA-Genebank Information Center accession no. IT004120); and IR8, an improved high-yielding semi-dwarf variety developed at the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI, IRTP 195). The Tongil variety was developed through a three-way cross, IR8//Yukara/TN1. With generation advancement after the cross, the most promising line, IR667-98-1-2, was selected and released to farmers in Korea under the name `Tongil' (Chung and Heu [1991]).
Whole-genome DNA sequencing
Four rice varieties were sequenced: Tongil and its parental varieties, Yukara, IR8, and TN1. Whole-genome shotgun sequencing of the four rice genomes was performed using the Illumina/Solexa GAII system. DNA sequencing, including construction of shotgun DNA libraries, was performed according to the methods recommended by the manufacturer (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Briefly, whole-genome DNA shotgun paired-end sequencing libraries were generated by fragmentation of DNA into 500-bp segments using a Covaris DNA shearing machine (Covaris, CA, US), followed by ligation of paired-end adapters ligation of 53 and 68 bp for sequencing on the FlowCell, size selection of the adapter-ligated fragments within the desired size range (500-600 bp), and PCR enrichment using complete primer constructs required for binding and clustering on the FlowCell. Illumina GAII sequencing was performed by identifying the emission color of single-base extensions on the FlowCell.
DNA variation
Illumina whole-genome shotgun 100-bp paired-end DNA sequencing data were filtered to obtain high-quality sequence data and to map reads to the Nipponbare reference genome sequence, which as downloaded from NCBI. Briefly, high-quality sequence with at least QC20-justified phred quality score was mapped to the reference Nipponbare sequence using CLC NGS Cell software (http://www.clcbio.com). The DNA sequence variation DB was converted to text format, including DNA variation based on the reference position, for the analysis of genome structure.
SNP calling - probabilities
Genotype calling to identify regions originating from the japonica and indica genomes was performed using the sliding-window approach suggested by Huang et al. (Huang et al. [2009]). In each window, the proportion of SNPs originating from each parent was examined for genotype calling. Huang et al. determined optimum window size by calculating the probability of finding a specific number of japonica SNPs in a window based on SNP error rates. Recent improvements in sequencing technology, however, resulted in fewer errors in SNP identification. Thus, the method suggested by Huang et al. ([2009]) was not directly applicable in this study. Even with a window size of 2, for example, calling accuracy could reach 99.99%. Instead of calculating this probability, the optimum window size was determined iteratively by comparing the portion of japonica SNPs (O) and the portion of the genome originating from japonica (P). Tongil was resequenced to obtain SNPs originating from its parents and to calculate the percentage of japonica SNPs in each chromosome. SEG-Map software (Huang et al. [2009]) was also used for genotype calling on each chromosome. Because the optimum window size was unknown, a range of window sizes from 1 to 199 was used. Then, the Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (E) between O and P was calculated as follows:
| 1 |
Here, an individual chromosome is denoted by i. The average percentage of japonica SNPs on each chromosome is denoted by Om. The optimal window size was defined as that with a maximum value of E; values of E ranged from -29 to 0.963. This maximum value of E occurred with a window size of 9. The percentage of indica SNPs was at its second highest (0.966) with a window size of 9. At a window size of 10, the E value dropped rapidly for japonica SNPs (0.037) and indica SNPs (-0.018). Thus, a window size of 9 was selected as the optimum for data analysis (Additional file 7: Figure S3).
Parental genome composition of Tongil
We compared DNA variation between the parental and Tongil genomes. Genomic regions originating from the japonica (Yukara) and indica (TN1 or IR8) parents were identified by comparing the Tongil genome sequence to parental sequences. Estimated indica and japonica regions in the Tongil genome sequence were calculated based on the methods of Zhao et al. (Zhao et al. [2010a]).
Gene ontology and classification
Annotated Nipponbare reference genes were classified based on parental origin in the Tongil genome and assigned to the three main GO-term categories (cellular component, molecular function, and biological process) using BLAST2GO software (www.blast2go.com) (Conesa et al. [2005]).
Simple sequence repeats (SSRs)
SSR loci were searched using SSR search software (Initiative [2000]) and classified with respect to their parental origin.
Authors' contributions
BK and HK conceived of the study and participated in its design. IC and BC performed bioinformatic analysis and data processing. BK and JL collected samples and phenotype data. DK, BK, GL, and JS analyzed the data and helped to draft the manuscript. TY, KK, DK, and JC helped to revise the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional files
Electronic supplementary material
Additional file 1: Table S1.: Mapping coverage of Tongil rice and its three parents. (DOCX 21 KB)
Additional file 2: Table S2.: SNPs and SNP frequency of Tongil and its three parents. (DOCX 21 KB)
Additional file 3: Figure S1.: Determination of window size followed by E-value calculation. The x-axis is the window size and the y-axis is the calculated E-value. (DOCX 24 KB)
Additional file 4: Table S3.: Genome region definition by the presence (O) or absence (X) of SNPs. (DOCX 19 KB)
Additional file 5:Table S4.: Gene distribution of Tongil. (DOCX 20 KB)
Additional file 6: Figure S2.: GO analysis according to the cellular components category of Tongil genes corresponding to indica/japonica sequences. (DOCX 22 KB)
Additional file 7: Figure S3.: GO analysis according to the molecular functions category of Tongil genes corresponding to indica/japonica sequences. (DOCX 22 KB)
Additional file 8: Figure S4.: GO analysis according to the biological processes category of Tongil genes corresponding to indica/japonica sequences. (DOCX 22 KB)
Additional file 9: Figure S5.: Copy number of SSR motif families in Tongil. (DOCX 1 MB)
Additional file 10: Figure S6.: List of SSR motif families in Tongil. (XLSX 1 MB)
Additional file 11: Table S5.: Comparison of alleles of yield-related genes in Tongil and its parents. (DOCX 20 KB)
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (Plant Molecular Breeding Center No. PJ008125), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Accession codes
Raw sequence data obtained in our study have been submitted to the NCBI Short Read Archive (Takano-Kai et al.) with the following accession numbers: Tongil [SRA: SRR923809, SRA: SRR923810], IR8 [SRA: SRR921498], TN1 [SRA: SRR921505], and Yukara [SRA: SRR925387].
Abbreviations
- SNP
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- NGS
Next generation sequencing
- IRGSP
International rice genome sequencing project
- SSR
Simple sequence repeat
- GO
Gene ontology
- SEG-map
Sequencing enabled genotyping for mapping recombination populations
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors have no potential competing interests to declare.
Contributor Information
Backki Kim, Email: uptfamily@hanmail.net.
Dong-Gwan Kim, Email: kimdg@snu.ac.kr.
Gileung Lee, Email: leegileung@nate.com.
Jeonghwan Seo, Email: rightseo@hotmail.com.
Ik-Young Choi, Email: choii@snu.ac.kr.
Beom-Soon Choi, Email: euphra@snu.ac.kr.
Tae-Jin Yang, Email: tjyang@snu.ac.kr.
Kwang Soo Kim, Email: luxkwang@snu.ac.kr.
Joohyun Lee, Email: edmund@konkuk.ac.kr.
Joong Hyoun Chin, Email: j.chin@irri.org.
Hee-Jong Koh, Email: heejkoh@snu.ac.kr.
References
- Ashikari M, Sakakibara H, Lin S, Yamamoto T, Takashi T, Nishimura A, Angeles ER, Qian Q, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production. Science. 2005;309(5735):741–745. doi: 10.1126/science.1113373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H, Xie W, He H, Yu H, Chen W, Li J, Yu R, Yao Y, Zhang W, He Y, Tang X, Zhou F, Deng XW, Zhang Q. A high-density SNP genotyping array for rice biology and molecular breeding. Mol Plant. 2014;7(3):541–553. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng SH, Zhuang JY, Fan YY, Du JH, Cao LY. Progress in research and development on hybrid rice: a super-domesticate in China. Ann Bot. 2007;100(5):959–966. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcm121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung GS, Heu MH. Selected papers from the 1979 International Rice Research. Manila: International Rice Research Institute; 1980. Status of japonica-indica hybridization in Korea; pp. 135–152. [Google Scholar]
- Chung GS, Heu MH. Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry 14. Germany: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg; 1991. Improvememt of Tongil-Type Rice Cultivars from Indica Japonica Hybridization in Korea; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Conesa A, Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. 2005;21(18):3674–3676. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C, Xing Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet. 2006;112(6):1164–1171. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltus FA, Wan J, Schulze SR, Estill JC, Jiang N, Paterson AH. An SNP resource for rice genetics and breeding based on subspecies indica and japonica genome alignments. Genome Res. 2004;14(9):1812–1819. doi: 10.1101/gr.2479404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harushima Y, Kurata N, Yano M, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T, Minobe Y, Nakagahra M. Detection of segregation distortions in an indica-japonica rice cross using a high-resolution molecular map. Theor Appl Genet. 1996;92(2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00223368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X, Feng Q, Qian Q, Zhao Q, Wang L, Wang A, Guan J, Fan D, Weng Q, Huang T, Dong G, Sang T, Han B. High-throughput genotyping by whole-genome resequencing. Genome Res. 2009;19(6):1068–1076. doi: 10.1101/gr.089516.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X, Kurata N, Wei X, Wang ZX, Wang A, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Liu K, Lu H, Li W, Guo Y, Lu Y, Zhou C, Fan D, Weng Q, Zhu C, Huang T, Zhang L, Wang Y, Feng L, Furuumi H, Kubo T, Miyabayashi T, Yuan X, Xu Q, Dong G, Zhan Q, Li C, Fujiyama A, Toyoda A, Lu T, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li J, Han B. A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature. 2012;490(7421):497–501. doi: 10.1038/nature11532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Initiative TAG. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 2000;408(6814):796–815. doi: 10.1038/35048692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IRRI (2009) IRRI World Rice Statistic. , [http://ricestat.irri.org:8080/wrs2/entrypoint.htm] IRRI (2009) IRRI World Rice Statistic.
- IRRI (2009) IRRI World Rice Statistic. , [http://ricestat.irri.org:8080/wrs2/entrypoint.htm] IRRI (2009) IRRI World Rice Statistic.
- Khush GS. Green revolution: preparing for the 21st century. Genome. 1999;42(4):646–655. doi: 10.1139/g99-044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q, Li L, Yang X, Warburton ML, Bai G, Dai J, Li J, Yan J. Relationship, evolutionary fate and function of two maize co-orthologs of rice GW2 associated with kernel size and weight. BMC Plant Biol. 2010;10:143. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin SY, Ikehashi H, Yanagihara S, Kawashima A. Segregation distortion via male gametes in hybrids between Indica and Japonica or wide-compatibility varieties of rice (Oryza sativa L) Theoret Appl Genetics. 1992;84(7-8):812–818. doi: 10.1007/BF00227389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T, Liu H, Zhang H, Xing Y. J Integr Plant Biol. 2013. Validation and characterization of Ghd7.1, a major QTL with pleiotropic effects on spikelets per panicle, plant height, and heading date in rice (Oryza sativa L.) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu BR, Zheng KL, Qian HR, Zhuang JY. Genetic differentiation of wild relatives of rice as assessed by RFLP analysis. Theor Appl Genet. 2002;106(1):101–106. doi: 10.1007/s00122-002-1013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L. Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.) DNA Res. 2002;9(6):199–207. doi: 10.1093/dnares/9.6.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally KL, Childs KL, Bohnert R, Davidson RM, Zhao K, Ulat VJ, Zeller G, Clark RM, Hoen DR, Bureau TE, Stokowski R, Ballinger DG, Frazer KA, Cox DR, Padhukasahasram B, Bustamante CD, Weigel D, Mackill DJ, Bruskiewich RM, Ratsch G, Buell CR, Leung H, Leach JE. Genomewide SNP variation reveals relationships among landraces and modern varieties of rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(30):12273–12278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900992106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A, Song XJ, Ito M, Asano K, Matsuoka M, Kitano H, Ashikari M. OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice. Nat Genet. 2010;42(6):545–549. doi: 10.1038/ng.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monna L, Kitazawa N, Yoshino R, Suzuki J, Masuda H, Maehara Y, Tanji M, Sato M, Nasu S, Minobe Y. Positional cloning of rice semidwarfing gene, sd-1: rice "green revolution gene" encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis. DNA Res. 2002;9(1):11–17. doi: 10.1093/dnares/9.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishima H, Oka HI. Phylogenetic Differentiation of Cultivated Rice.22. Numerical Evaluation of the Indica-Japonica Differentiation. Jpn J Breed. 1981;31(4):402–413. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs1951.31.402. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano H, Onishi K, Ogasawara M, Horiuchi Y, Sano Y. Genealogy of the "Green Revolution" gene in rice. Genes Genet Syst. 2005;80(5):351–356. doi: 10.1266/ggs.80.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Climate change: impact on agriculture and costs of adaptation. Food policy report, International Food Policy Research Institute, Washington, D.C; 2009.
- Sano R, Morishima H. Indica-Japonica Differentiation of Rice Cultivars Viewed from Variations in Key Characters and Isozymes, with Special Reference to Landraces from the Himalayan Hilly Areas. Theor Appl Genet. 1992;84(3-4):266–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00229481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki A, Ashikari M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Itoh H, Nishimura A, Swapan D, Ishiyama K, Saito T, Kobayashi M, Khush GS, Kitano H, Matsuoka M. Green revolution: a mutant gibberellin-synthesis gene in rice. Nature. 2002;416(6882):701–702. doi: 10.1038/416701a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Y, Wan Z, Coarfa C, Drabek R, Chen L, Ostrowski EA, Liu Y, Weinstock GM, Wheeler DA, Gibbs RA, Yu F. A SNP discovery method to assess variant allele probability from next-generation resequencing data. Genome Res. 2010;20(2):273–280. doi: 10.1101/gr.096388.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Ebitani T, Kanegae H, Konishi S, Yano M. Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat Genet. 2008;40(8):1023–1028. doi: 10.1038/ng.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet. 2007;39(5):623–630. doi: 10.1038/ng2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano-Kai N, Jiang H, Kubo T, Sweeney M, Matsumoto T, Kanamori H, Padhukasahasram B, Bustamante C, Yoshimura A, Doi K, McCouch S. Evolutionary history of GS3, a gene conferring grain length in rice. Genetics. 2009;182(4):1323–1334. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.103002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng DX, Xu SC, Lin RM, Wan AM, Li JP, Wu LR. Microsatellite marker linked with stripe rust resistant gene Yr9 in wheat. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2005;32(9):937–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue W, Xing Y, Weng X, Zhao Y, Tang W, Wang L, Zhou H, Yu S, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q. Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genet. 2008;40(6):761–767. doi: 10.1038/ng.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan S, Zou G, Li S, Wang H, Liu H, Zhai G, Guo P, Song H, Yan C, Tao Y. Seed size is determined by the combinations of the genes controlling different seed characteristics in rice. Theor Appl Genet. 2011;123(7):1173–1181. doi: 10.1007/s00122-011-1657-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao K, Wright M, Kimball J, Eizenga G, McClung A, Kovach M, Tyagi W, Ali ML, Tung CW, Reynolds A, Bustamante CD, McCouch SR. Genomic diversity and introgression in O. sativa reveal the impact of domestication and breeding on the rice genome. PLoS One. 2010;5(5):e10780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao QA, Huang XH, Lin ZX, Han B. SEG-Map: A Novel Software for Genotype Calling and Genetic Map Construction from Next-generation Sequencing. Rice. 2010b;3(2-3):98–102. doi: 10.1007/s12284-010-9051-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou LJ, Ao GH, Wu XJ, Li SG. SSR markers linked with early stability in rice. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2005;32(8):837–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1.: Mapping coverage of Tongil rice and its three parents. (DOCX 21 KB)
Additional file 2: Table S2.: SNPs and SNP frequency of Tongil and its three parents. (DOCX 21 KB)
Additional file 3: Figure S1.: Determination of window size followed by E-value calculation. The x-axis is the window size and the y-axis is the calculated E-value. (DOCX 24 KB)
Additional file 4: Table S3.: Genome region definition by the presence (O) or absence (X) of SNPs. (DOCX 19 KB)
Additional file 5:Table S4.: Gene distribution of Tongil. (DOCX 20 KB)
Additional file 6: Figure S2.: GO analysis according to the cellular components category of Tongil genes corresponding to indica/japonica sequences. (DOCX 22 KB)
Additional file 7: Figure S3.: GO analysis according to the molecular functions category of Tongil genes corresponding to indica/japonica sequences. (DOCX 22 KB)
Additional file 8: Figure S4.: GO analysis according to the biological processes category of Tongil genes corresponding to indica/japonica sequences. (DOCX 22 KB)
Additional file 9: Figure S5.: Copy number of SSR motif families in Tongil. (DOCX 1 MB)
Additional file 10: Figure S6.: List of SSR motif families in Tongil. (XLSX 1 MB)
Additional file 11: Table S5.: Comparison of alleles of yield-related genes in Tongil and its parents. (DOCX 20 KB)


