Abstract
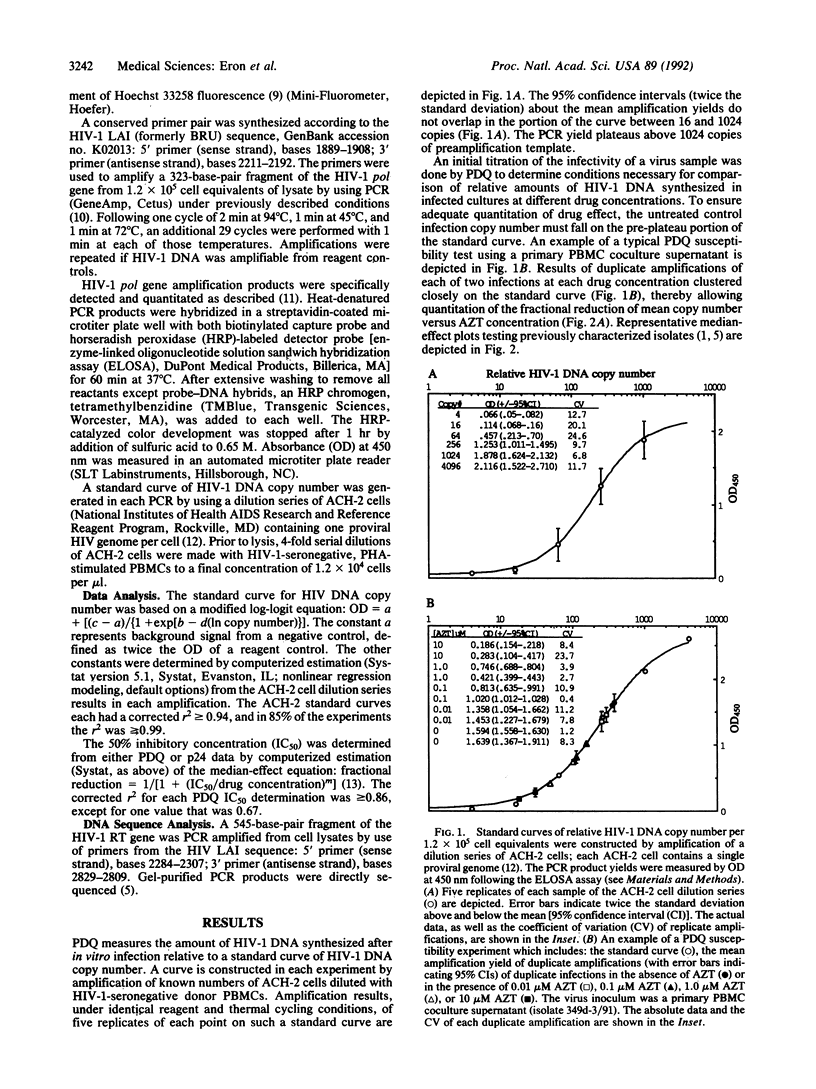
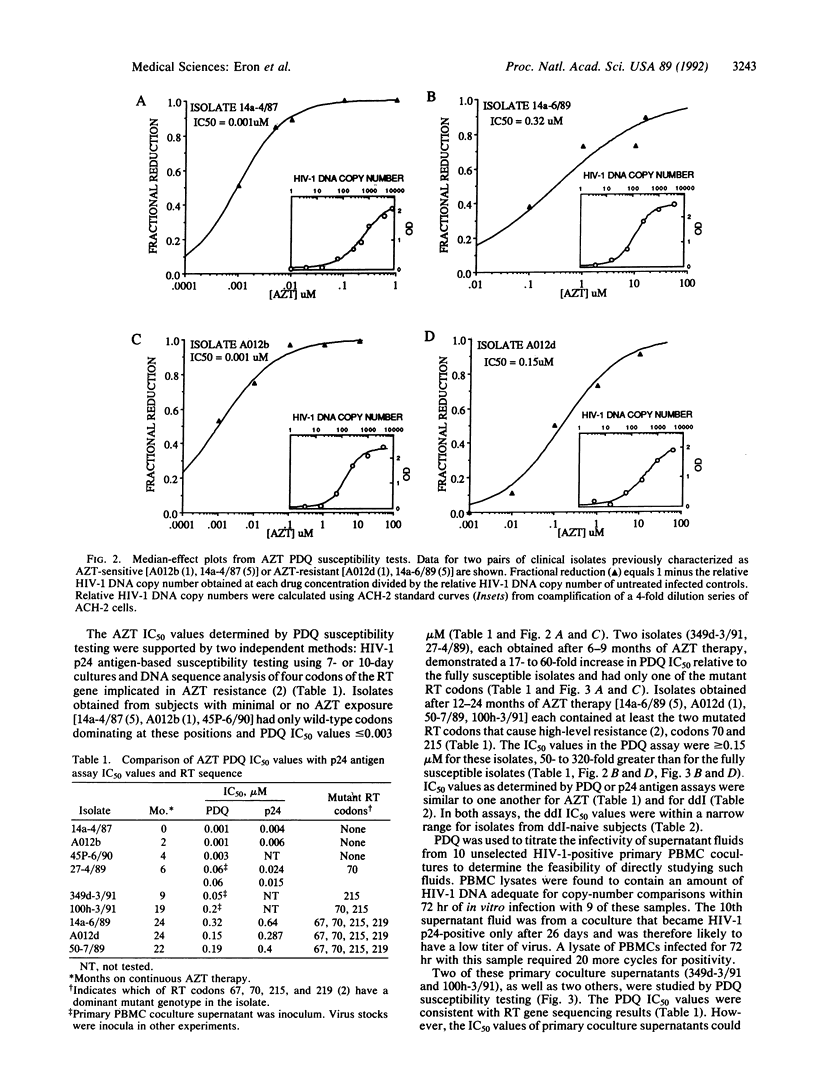
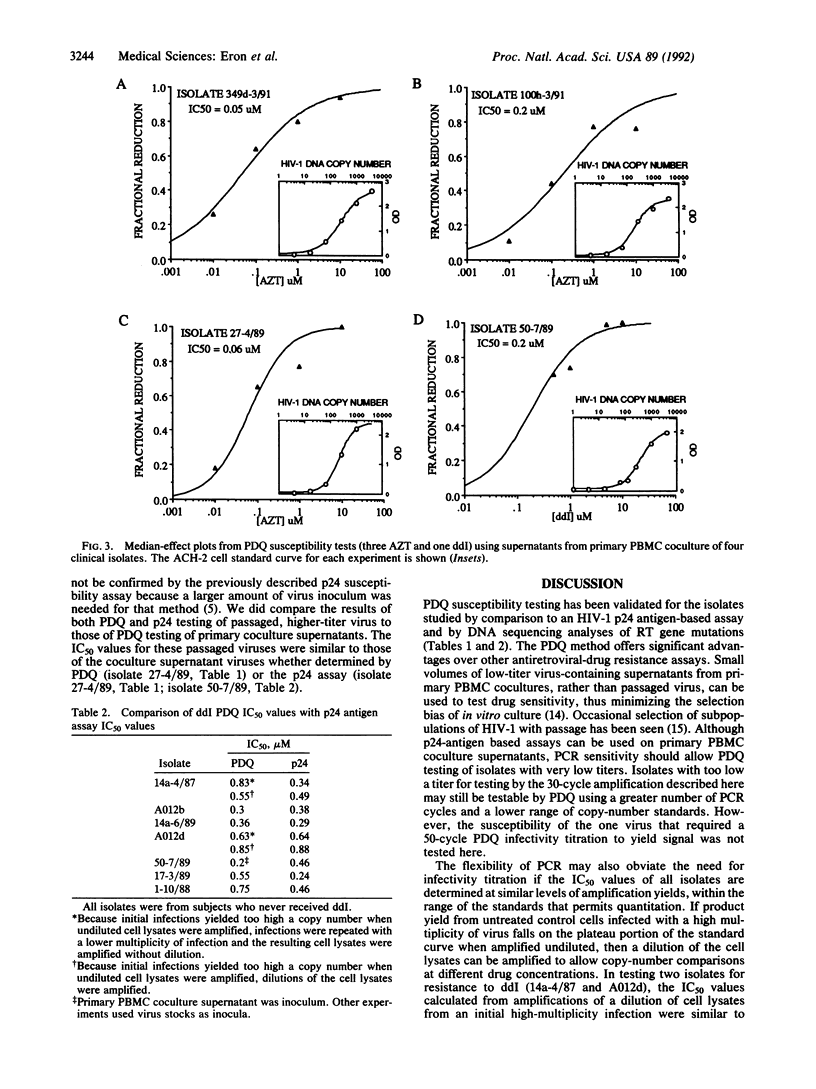
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) DNA quantitation (PDQ) susceptibility testing rapidly and directly measures nucleoside sensitivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) isolates. PCR is used to quantitate the amount of HIV-1 DNA synthesized after in vitro infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The relative amounts of HIV-1 DNA in cell lysates from cultures maintained at different drug concentrations reflect drug inhibition of virus replication. The results of PDQ susceptibility testing of 2- or 3-day cultures are supported by assays measuring HIV-1 p24 antigen production in supernatants of 7- or 10-day cultures. DNA sequence analyses to identify mutations in the reverse transcriptase gene that cause resistance to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine also support the PDQ results. With the PDQ method, both infectivity titration and susceptibility testing can be performed on supernatants from primary cultures of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PDQ susceptibility testing should facilitate epidemiologic studies of the clinical significance of drug-resistant HIV-1 isolates.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chou T. C. Derivation and properties of Michaelis-Menten type and Hill type equations for reference ligands. J Theor Biol. 1976 Jul 7;59(2):253–276. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouse K. A., Powell D., Washington I., Poli G., Strebel K., Farrar W., Barstad P., Kovacs J., Fauci A. S., Folks T. M. Monokine regulation of human immunodeficiency virus-1 expression in a chronically infected human T cell clone. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Japour A. J., Chatis P. A., Eigenrauch H. A., Crumpacker C. S. Detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clinical isolates with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine and dideoxyinosine by RNA.RNA hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3092–3096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson V. A., Merrill D. P., Videler J. A., Chou T. C., Byington R. E., Eron J. J., D'Aquila R. T., Hirsch M. S. Two-drug combinations of zidovudine, didanosine, and recombinant interferon-alpha A inhibit replication of zidovudine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 synergistically in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;164(4):646–655. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.4.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Chesebro B., Richman D. D. Susceptibilities of zidovudine-susceptible and -resistant human immunodeficiency virus isolates to antiviral agents determined by using a quantitative plaque reduction assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):436–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kellam P., Kemp S. D. Zidovudine resistance predicted by direct detection of mutations in DNA from HIV-infected lymphocytes. AIDS. 1991 Feb;5(2):137–144. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199102000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Martin L. S., Cort S. P., Mozen M., Heldebrant C. M., Evatt B. L. Thermal inactivation of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome virus, human T lymphotropic virus-III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus, with special reference to antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):875–877. doi: 10.1172/JCI112045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhans A., Cheynier R., Albert J., Seth M., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Morfeldt-Månson L., Asjö B., Wain-Hobson S. Temporal fluctuations in HIV quasispecies in vivo are not reflected by sequential HIV isolations. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):901–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90942-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Matthes E., Reuter P., Wenger R., Friese K., Kuchino Y., Schröder H. C. Effect of nonviable preparations from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 on nuclear matrix-associated DNA polymerase alpha and DNA topoisomerase II activities. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Guatelli J. C., Grimes J., Tsiatis A., Gingeras T. Detection of mutations associated with zidovudine resistance in human immunodeficiency virus by use of the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1991 Dec;164(6):1075–1081. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.6.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. S., Brian E. L., Pagano J. S. Resumption of virus production after human immunodeficiency virus infection of T lymphocytes in the presence of azidothymidine. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3769–3773. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3769-3773.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Martin J. L., Tudor-Williams G., Bach M. C., Vavro C. L., King D. M., Kellam P., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Resistance to ddI and sensitivity to AZT induced by a mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1716788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



