Abstract
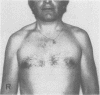
Two patients with isolated neurogenic hypertrophy of the trapezius muscle due to accessory nerve injury and a patient with neurogenic hypertrophy of the anterior tibial muscle due to chronic radicular lesion L4 are described. Electromyography of the affected muscles showed dense continuing spontaneous discharges of complex potentials. Muscle biopsy performed in two patients showed abundant hypertrophic muscle fibres, identified in one case by ATP-ase reaction as being of predominantly type I. In the majority of previously reported patients with neurogenic muscle hypertrophy confined to the calf muscle, a passive stretch mechanism was suggested as a cause of the hypertrophy. It is assumed that the excessive spontaneous muscle activity gave rise to the hypertrophy in these patients. This may also be true in previously reported patients with neurogenic hypertrophy and similar spontaneous activity in electromyography.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberca R., Rafel E., Castilla J. M., Gil-Peralta A. Increased mechanical muscle irritability syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand. 1980 Oct;62(4):250–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1980.tb03032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers J. W., Allen A. A., 2nd, Bastron J. A., Daube J. R. Limb myokymia. Muscle Nerve. 1981 Nov-Dec;4(6):494–504. doi: 10.1002/mus.880040606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernat J. L., Ochoa J. L. Muscle hypertrophy after partial denervation: a human case. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Aug;41(8):719–725. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.8.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorini T. E., Igarashi M. Postpoliomyelitis muscle pseudohypertrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1985 Oct;8(8):644–649. doi: 10.1002/mus.880080803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradi S., Grimby L., Lundemo G. Pathophysiology of fasciculations in ALS as studied by electromyography of single motor units. Muscle Nerve. 1982 Mar;5(3):202–208. doi: 10.1002/mus.880050305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper W. H., Ringel S. P., Treihaft M. M., Hall K. A. Calf enlargement from S-1 radiculopathy. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1985 Mar;62(3):442–444. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.3.0442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessandro R., Montagna P., Govoni E., Pazzaglia P. Benign familial spinal muscular atrophy with hypertrophy of the calves. Arch Neurol. 1982 Oct;39(10):657–660. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510220055013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B., Murphy S. R., Nigam M. P., Hills J. R. "Myopathic" changes in chronically denervated muscle. Arch Neurol. 1967 Jan;16(1):14–24. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470190018002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeryk B., Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., Nowak T. Spontaneous volleys of bizarre high frequency potentials (b.h.f.p.) in neuro-muscular diseases. Part 1. Occurrence of spontaneous volleys of b.h.f.p. in neuro-muscular diseases. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1974 Jun-Jul;14(3):303–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldspink G., Howells K. F. Work-induced hypertrophy in exercised normal muscles of different ages and the reversibility of hypertrophy after cessation of exercise. J Physiol. 1974 May;239(1):179–193. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper C. M., Jr, Thomas J. E., Cascino T. L., Litchy W. J. Distinction between neoplastic and radiation-induced brachial plexopathy, with emphasis on the role of EMG. Neurology. 1989 Apr;39(4):502–506. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.4.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein I., Parker M., Shebert R., Ayyar D. R., Levey G. S. Hypothyroidism presenting as muscle stiffness and pseudohypertrophy: Hoffmann's syndrome. Am J Med. 1981 Apr;70(4):891–894. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90550-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagueny A., Coquet M., Julien J., Vital C., Ferrer X., Larrieu J. L., Aupy M. Hypertrophie musculaire neurogène. Association à des activités électrophysiologiques anormales. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1987;143(3):189–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapresle J., Fardeau M., Said G. L'hypertrophie musculaire vraie secondaire à une atteinte nerveuse périphérique. Etude clinique et histologique d'une observation d'hypertrophie du mollet consécutive à une sciatique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1973 Mar;128(3):153–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina J. L., Chokroverty S., Reyes M. Localized myokymia caused by peripheral nerve injury. Arch Neurol. 1976 Aug;33(8):587–588. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500080065011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke U., Ricker K., Emser W., Boxler K. Unilateral calf enlargement following S1 radiculopathy. Muscle Nerve. 1982 Jul-Aug;5(6):434–438. doi: 10.1002/mus.880050604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagna P., Martinelli P., Rasi F., Cirignotta F., Govoni E., Lugaresi E. Muscular hypertrophy after chronic radiculopathy. Arch Neurol. 1984 Apr;41(4):397–398. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050160059017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. P., Leshner R. T., Campbell W. W., Jr Hypertrophia musculorum vera in familial ataxia. Arch Neurol. 1986 Feb;43(2):146–147. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520020040015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S., Kuroiwa Y., Miyajima H., Nishimura Y., Honda N. Unilateral true hypertrophy of the calf muscle. J Neurol. 1985;232(3):180–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00313899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pareyson D., Morandi L., Scaioli V., Marazzi R., Boiardi A., Sghirlanzoni A. Neurogenic muscle hypertrophy. Report of two cases. J Neurol. 1989 Jul;236(5):292–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00314459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A. N., Swami R. K. Muscle percussion and neostigmine test in the clinical evaluation of neuromuscular disorders. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 4;281(10):523–526. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909042811004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearn J., Hudgson P. Anterior-horn cell degeneration and gross calf hypertrophy with adolescent onset. A new spinal muscular atrophy syndrome. Lancet. 1978 May 20;1(8073):1059–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90910-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricker K., Rohkamm R., Moxley R. T., 3rd Hypertrophy of the calf with S-1 radiculopathy. Arch Neurol. 1988 Jun;45(6):660–664. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520300080023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G., Magistris M. R. Neuropathies with prolonged conduction block, single and grouped fasciculations, localized limb myokymia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1987 Nov;67(5):428–438. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(87)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ O., JAMPEL R. S. Congenital blepharophimosis associated with a unique generalized myopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1962 Jul;68:52–57. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1962.00960030056011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLA O. M., MARTIN A. W. Denervation hypertrophy and atrophy of the hemidiaphragm of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1953 Feb;172(2):324–332. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.172.2.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serratrice G., Pellissier J. F., Marini J. F., Valentin-Leccese P. Un cas de sciatique avec hypertrophie du mollet. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1989;145(6-7):474–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoehr M. Low frequency bizarre discharges. A particular type of electromyographical spontaneous activity in paretic skeletal muscle. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1978 Apr-May;18(2):147–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöhr M. Special types of spontaneous electrical activity in radiogenic nerve injuries. Muscle Nerve. 1982;5(9S):S78–S83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. G., Layzer R. B., Davis H. S., Fowler W. M., Jr Continuous muscle fiber activity in the Schwartz-Jampel syndrome. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1972 Nov;33(5):497–509. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(72)90213-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torbergsen T. A family with dominant hereditary myotonia, muscular hypertrophy, and increased muscular irritability, distinct from myotonia congenita thomsen. Acta Neurol Scand. 1975 Mar;51(3):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1975.tb07603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trontelj J., Stålberg E. Bizarre repetitive discharges recorded with single fibre EMG. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Apr;46(4):310–316. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.4.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenstein E., Watson R. T., Parker J. L. Myokymia, muscle hypertrophy and percussion "myotonia" in chronic recurrent polyneuropathy. Neurology. 1978 Nov;28(11):1130–1134. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.11.1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilescu C., Alexianu M., Dan A. Muscle hypertrophy and a syndrome of continuous motor unit activity in prednisone-responsive Guillain-Barré polyneuropathy. J Neurol. 1984;231(5):276–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00313668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Visser M., Verbeeten B., Jr, Lyppens K. C. Pseudohypertrophy of the calf following S1 radiculopathy. Neuroradiology. 1986;28(3):279–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00548206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]