Figure 5. p38 MAPK regulates EGFR expression through the rapid degradation of MDM2 and increase in p53 stability.
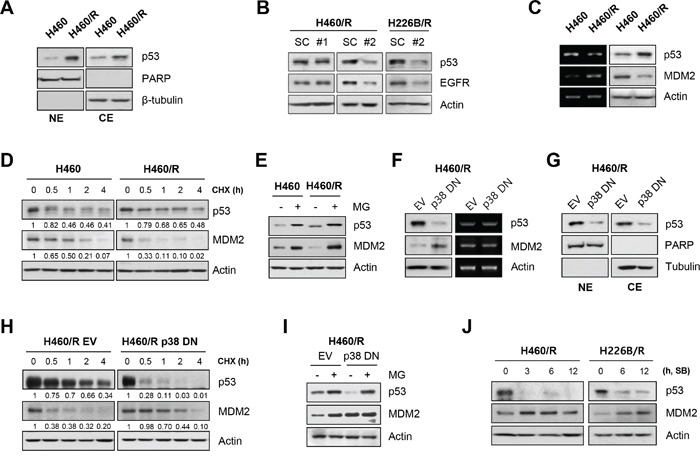
A. The nuclear translocation of p53 was examined using nuclear/cytosol extraction in H460 and H460/R cells. PARP and β-tubulin were used as markers of nuclear and cytosolic fractions, respectively. B. H460/R and H226B/R cells were transfected with scrambled (SC) or TP53 siRNAs (#1 or #2). At 48 h post-transfection, the cells were collected and assessed for western blot analysis to investigate the influence of p53 on the expression of EGFR. C. The basal expression level of p53 and MDM2 in H460 and H460/R cells was investigated using western blot (left) and RT-PCR (right) analyses. D. Cycloheximide (CHX) was added to the medium to stop protein translation. Cells were taken at the indicated time-points, and the protein turnover of p53 and MDM2 was determined using western blot analysis. The relative abundance of p53 and MDM2 compared with the untreated controls was calculated based on band intensity using ImageJ software. E. The cells were treated with MG-132 (MG; 10 μM) for 4 h, and the protein levels of p53 and MDM2 were determined using western blot analysis. F-I. H460/R cells were stably transfected with empty (EV) or p38 DN expression vectors. F. The protein level (left) and mRNA expression (right) of p53 and MDM2, G. the nuclear localization of p53, H. the protein turnover of p53 and MDM2 following CHX treatment, and I. the recovery of the amount of p53 and MDM2 protein following MG-132 treatment were assessed. J. H460/R and H226B/R cells were treated with SB203580 (SB; 50 μM) in a time-dependent manner. The expression changes in p53 and MDM2 were detected using western blot analysis.
