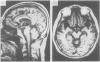
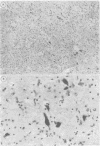
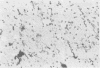
Abstract
Two patients with "pure akinesia" who showed the characteristic changes of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) at necropsy are described. They had akinesia but no rigidity or tremor, and ophthalmoplegia was not observed during the course of illness. The symptoms of "pure akinesia" was not improved by levodopa therapy but was considerably improved by L-threo-3,4-dihydroxy-phenylserine. At necropsy, pathological findings were not different from those reported for PSP. It is suggested that "pure akinesia" is an atypical manifestation of PSP, and that norepinephrinergic neurons may be involved in some types of PSP.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbeau A. Six years of high-level levodopa therapy in severely akinetic parkinsonian patients. Arch Neurol. 1976 May;33(5):333–338. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500050019004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal H., Miller C. Motor nuclear involvement in progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol. 1969 Apr;20(4):362–367. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480100038005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaventura I., Matias-Guiu J., Cervera C., Codina Puiggros A. Neuroacanthocytosis syndrome, apraxia of eyelid opening, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology. 1986 Sep;36(9):1276–1276. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.9.1276-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. G., Rosenberg L. E., Snodgrass P. J., Nuzum C. T. Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency: a cause of lethal neonatal hyperammonemia in males. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 4;288(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301042880101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David N. J., Mackey E. A., Smith J. L. Further observations in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology. 1968 Apr;18(4):349–356. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. H., Bergeron C., McLachlan D. R. Atypical presentation of progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol. 1985 Apr;17(4):337–343. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehaene I. Apraxia of eyelid opening in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol. 1984 Jan;15(1):115–116. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubas F., Gray F., Escourolle R. Maladie de Steele-Richardson-Olszewski sans ophtalmoplégie. Six cas anatomo-cliniques. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1983;139(6-7):407–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN J. E., COGAN D. G. APRAXIA OF LID OPENING. Arch Ophthalmol. 1965 Feb;73:155–159. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1965.00970030157003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Takahashi H., Takeda S., Ikuta F. [An autopsy case of progressive supranuclear palsy showing "pure akinesia without rigidity and tremor and with no effect by L-dopa therapy (Imai)"]. No To Shinkei. 1987 Feb;39(2):183–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai H., Narabayashi H., Sakata E. "Pure akinesia" and the later added supranuclear ophthalmoplegia. Adv Neurol. 1987;45:207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishino H., Higashi H., Kuroda S., Yabuki S., Hayahara T. Motor nuclear involvement in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Jun;22(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90248-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. A., Jankovic J., Ford J. Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinical features and response to treatment in 16 patients. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):273–278. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janati A. Progressive supranuclear palsy: report of a case with torticollis, blepharospasm, and dysfluency. Am J Med Sci. 1986 Dec;292(6):391–392. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198612000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinger K., Riederer P., Tomonaga M. Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinico-pathological and biochemical studies. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1980;(16):111–128. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-8582-7_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. E., Moore R. Y. Ascending projections of the locus coeruleus in the rat. II. Autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1977 May 20;127(1):25–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Ogomori K., Tateishi J., Prusiner S. B. Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest. 1987 Aug;57(2):230–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller W. C., Morantz R., Vetere-Overfield B., Waxman M. Autologous adrenal medullary transplant in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology. 1989 Aug;39(8):1066–1068. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.8.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen M. O. Progressive supranuclear palsy--20 years later. Acta Neurol Scand. 1985 Mar;71(3):177–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1985.tb03186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narabayashi H., Kondo T., Yokochi F., Nagatsu T. Clinical effects of L-threo-3,4-dihydroxyphenylserine in cases of parkinsonism and pure akinesia. Adv Neurol. 1987;45:593–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. C. Treatment of progressive supranuclear palsy with tricyclic antidepressants. Neurology. 1985 Aug;35(8):1189–1193. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.8.1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuwer M. R. Progressive supranuclear palsy despite normal eye movements. Arch Neurol. 1981 Dec;38(12):784–784. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510120084018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffenbach D. D., Layton D. D., Jr, Kearns T. P. Ocular manifestations in progressive supranuclear palsy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1972 Dec;74(6):1179–1184. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(72)90740-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst A. Dégénérescence neurofibrillaire sous-corticale sénile avec présence de tubules contournés et de filaments droits. Forme atypique de la paralysie supranucléaire progressive. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1977 Jun-Jul;133(6-7):417–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn N. P., Luthert P., Honavar M., Marsden C. D. Pure akinesia due to lewy body Parkinson's disease: a case with pathology. Mov Disord. 1989;4(1):85–89. doi: 10.1002/mds.870040112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE J. C., RICHARDSON J. C., OLSZEWSKI J. PROGRESSIVE SUPRANUCLEAR PALSY. A HETEROGENEOUS DEGENERATION INVOLVING THE BRAIN STEM, BASAL GANGLIA AND CEREBELLUM WITH VERTICAL GAZE AND PSEUDOBULBAR PALSY, NUCHAL DYSTONIA AND DEMENTIA. Arch Neurol. 1964 Apr;10:333–359. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460160003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin R. W., Ogomori K., Kitamoto T., Tateishi J. Increased tau accumulation in senile plaques as a hallmark in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jun;134(6):1365–1371. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele J. C. Progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain. 1972;95(4):693–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Pilleri G., Gemignani F., Lechi A. Neuronal loss in the basal nucleus of Meynert in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;61(2):157–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00697397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungerstedt U. Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1971;367:1–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1971.tb10998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Ujike H., Ogawa N. Effective treatment of pure akinesia with L-threo-3,4-dihydroxyphenylserine (DOPS): report of a case, with pharmacological considerations. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1985;8(4):334–342. doi: 10.1097/00002826-198512000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Horoupian D. S., Terry R. D. Immunocytochemical comparison of neurofibrillary tangles in senile dementia of Alzheimer type, progressive supranuclear palsy, and postencephalitic parkinsonism. Ann Neurol. 1983 Feb;13(2):172–175. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]