Abstract
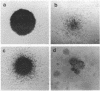
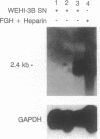
Full-length murine fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor 1 (FGFR-1L) cDNA was introduced into the FDC-P1 mouse myeloid progenitor cell line, which lacks FGF receptors and depends on interleukin 3 (IL-3) or granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) for its proliferation and survival. The expression of the FGFR-1L gene in FDC-P1 cells allowed these cells to grow in the presence of FGF and heparin. The resulting cell line, designated FD FGFR-1L.A, exhibited a more mature myeloid phenotype than did the parental FD FGFR-1L cells or uninfected FDC-P1 cells. They formed mainly dispersed colonies in soft-agar cultures when grown in the presence of FGF and heparin, suggestive of myeloid differentiation. The cells can be switched between growth on FGF/heparin and IL-3. Northern blot analysis and cytochemical staining demonstrated that FD FGFR-1L.A cells expressed myeloperoxidase mRNA and protein, biochemical markers specifically expressed during differentiation from the promyelocytic to the granulocytic stages, whereas the parental FD FGFR-1L cells and FDC-P1 cells failed to express this marker. These results indicate that the expression of FGFR-1L by FDC-P1 cells transmitted signals for growth in the presence of FGF and heparin and generated an additional signal for early myeloid differentiation but failed to commit FD FGFR-1L.A cells to terminal differentiation. This in vitro culture system can be used for molecular analysis of the regulation of cellular growth and differentiation mediated by the FGFs and their receptors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. J., Dam D., Lee S., Cotman C. W. Basic fibroblast growth factor prevents death of lesioned cholinergic neurons in vivo. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):360–361. doi: 10.1038/332360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Li M., Reid H. H. Expression of two different forms of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 in different mouse tissues and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7625–7629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Reid H. H., Bartlett P. F. Role of the c-myc and the N-myc proto-oncogenes in the immortalization of neural precursors. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Sep;24(1):9–20. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broad T. E., Ham R. G. Growth and adipose differentiation of sheep preadipocyte fibroblasts in serum-free medium. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 1;135(1):33–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Garland J., Scott D., Scolnick E., Metcalf D. Growth of factor-dependent hemopoietic precursor cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1036–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne C. A., Crumley G., Bellot F., Kaplow J. M., Searfoss G., Ruta M., Burgess W. H., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of two distinct high-affinity receptors cross-reacting with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2685–2692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliniak B. C., Rohrschneider L. R. Expression of the M-CSF receptor is controlled posttranscriptionally by the dominant actions of GM-CSF or multi-CSF. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1073–1083. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90510-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Fibroblast growth factor. Chemical structure and biologic function. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990 Aug;(257):231–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger J. S., Newburger P. E., Karpas A., Moloney W. C. Constitutive and inducible granulocyte-macrophage functions in mouse, rat, and human myeloid leukemia-derived continuous tissue culture lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Oct;38(10):3340–3348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapel A. J., Warren H. S., Hume D. A. Different colony-stimulating factors are detected by the "interleukin-3"-dependent cell lines FDC-Pl and 32D cl-23. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):786–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatten M. E., Lynch M., Rydel R. E., Sanchez J., Joseph-Silverstein J., Moscatelli D., Rifkin D. B. In vitro neurite extension by granule neurons is dependent upon astroglial-derived fibroblast growth factor. Dev Biol. 1988 Feb;125(2):280–289. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. L., Morse H. C., 3rd Murine hematopoietic cell surface antigen expression. Immunol Today. 1988 Nov;9(11):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lee P. L., Lu J., Williams L. T. Diverse forms of a receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4728–4736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T., Hayman M. J. Isolation of an additional member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, FGFR-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Baird A. A dual receptor system is required for basic fibroblast growth factor activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):229–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90173-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen J., Mäkelä T. P., Eerola E., Korhonen J., Hirvonen H., Claesson-Welsh L., Alitalo K. FGFR-4, a novel acidic fibroblast growth factor receptor with a distinct expression pattern. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. H., Ruggiero M., Fleming T. P., Di Fiore P. P., Greenberger J. S., Varticovski L., Schlessinger J., Rovera G., Aaronson S. A. Signal transduction through the EGF receptor transfected in IL-3-dependent hematopoietic cells. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):628–631. doi: 10.1126/science.3257584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid H. H., Wilks A. F., Bernard O. Two forms of the basic fibroblast growth factor receptor-like mRNA are expressed in the developing mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1596–1600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R., Metcalf D. Induction of macrophage colony-stimulating factor-dependent growth and differentiation after introduction of the murine c-fms gene into FDC-P1 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5081–5092. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C. Mesoderm induction and mesoderm-inducing factors in early amphibian development. Development. 1989 Apr;105(4):665–677. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobler A., Miller C. W., Johnson K. R., Selsted M. E., Rovera G., Koeffler H. P. Regulation of gene expression of myeloperoxidase during myeloid differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Aug;136(2):215–225. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venturelli D., Shirsat N., Gemperlein I., Bittenbender S., Hudson S., Rovera G. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA for murine myeloperoxidase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5852–5852. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]