Abstract
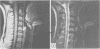
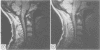
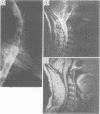
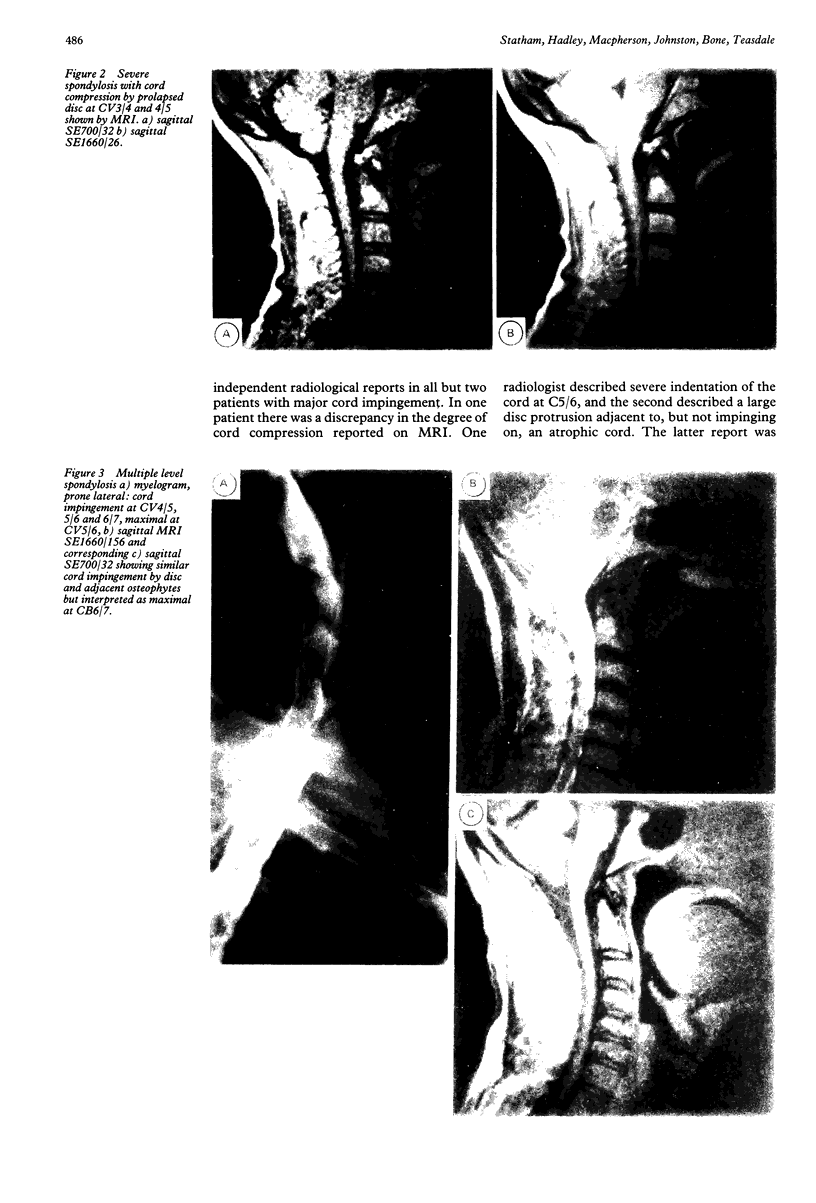
One hundred and two patients with suspected cervical spondylotic myelopathy were prospectively investigated using MRI as the initial imaging technique. The aim was to discover if clinicians could manage patients with MRI alone, or if they would find a second investigation necessary. Eighty two patients were managed using MRI alone, 34 of whom were treated surgically. Twenty patients had a second investigation: a myelogram in 18 and a CT myelogram in two. This was performed in nine patients to exclude structural pathology in the thoracic or lumbar region (which was not examined with MRI), and in 11 to obtain more specific information about the cervical region. Only five of these 20 patients had surgical treatment. The diagnosis changed after the second investigation in four patients, but management was not influenced in any of these. MRI is a satisfactory alternative to myelography for most patients with suspected cervical spondylotic myelopathy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper L. S., Chalmers T. C., McCally M., Berrier J., Sacks H. S. The poor quality of early evaluations of magnetic resonance imaging. JAMA. 1988 Jun 10;259(22):3277–3280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzmann D. R., Rubin J. B. Cervical spine: MR imaging with a partial flip angle, gradient-refocused pulse sequence. Part I. General considerations and disk disease. Radiology. 1988 Feb;166(2):467–472. doi: 10.1148/radiology.166.2.3336722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enzmann D. R., Rubin J. B., Wright A. Cervical spine MR imaging: generating high-signal CSF in sagittal and axial images. Radiology. 1987 Apr;163(1):233–238. doi: 10.1148/radiology.163.1.3823442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. A., Edwards J. H., Vacirca S. J., Stein H. L. 0.6 T MR imaging of the cervical spine: multislice and multiecho techniques. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1985 Mar-Apr;6(2):229–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. M., Holtås S., Cronqvist S., Brandt L. Comparison of myelography, CT myelography and magnetic resonance imaging in cervical spondylosis and disk herniation. Pre- and postoperative findings. Acta Radiol. 1989 May-Jun;30(3):233–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson P., Teasdale E., Coutinho C., McGeorge A. Iohexol versus iopamidol for cervical myelography: a randomised double blind study. Br J Radiol. 1985 Sep;58(693):849–851. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-58-693-849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaryk T. J., Modic M. T., Geisinger M. A., Standefer J., Hardy R. W., Boumphrey F., Duchesneau P. M. Cervical myelopathy: a comparison of magnetic resonance and myelography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1986 Mar-Apr;10(2):184–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modic M. T., Masaryk T. J., Mulopulos G. P., Bundschuh C., Han J. S., Bohlman H. Cervical radiculopathy: prospective evaluation with surface coil MR imaging, CT with metrizamide, and metrizamide myelography. Radiology. 1986 Dec;161(3):753–759. doi: 10.1148/radiology.161.3.3786728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modic M. T., Masaryk T. J., Ross J. S., Mulopulos G. P., Bundschuh C. V., Bohlman H. Cervical radiculopathy: value of oblique MR imaging. Radiology. 1987 Apr;163(1):227–231. doi: 10.1148/radiology.163.1.3823440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teasdale G. M., Hadley D. M., Lawrence A., Bone I., Burton H., Grant R., Condon B., Macpherson P., Rowan J. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in suspected lesions in the posterior cranial fossa. BMJ. 1989 Aug 5;299(6695):349–355. doi: 10.1136/bmj.299.6695.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]