Abstract
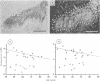
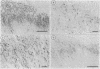
Using a computer-assisted image analyser, an immunohistochemical quantification method of substance P-like immunoreactivity (SPLI) in laminae I + II of spinal dorsal horn was established and applied to 13 patients with multiple system atrophy (MSA) with no disturbance of pain sensation, including olivo-ponto-cerebellar atrophy and striatonigral degeneration, and 13 neurologically normal controls. To investigate whether alteration of SPLI is related to an autonomic disorder, myelinated fibre counts of the fourth thoracic ventral roots were performed. Eleven of 13 MSA patients showed a significant decrease in small and large myelinated fibres, and were diagnosed with definite Shy-Drager syndrome (SDS), with the exception of two who had no apparent history of autonomic dysfunction. SPLIs in laminae I + II in 10 of these 11 patients, when adjusted for age, were significantly decreased at both levels of the fourth thoracic and third lumbar spinal segments. The results suggest the disorder of SP-containing synapses of primary afferent neurons and/or those of interneurons in SDS.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand P., Bannister R., McGregor G. P., Ghatei M. A., Mulderry P. K., Bloom S. R. Marked depletion of dorsal spinal cord substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide with intact skin flare responses in multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Feb;51(2):192–196. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.2.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber R. P., Vaughn J. E., Slemmon J. R., Salvaterra P. M., Roberts E., Leeman S. E. The origin, distribution and synaptic relationships of substance P axons in rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Mar 15;184(2):331–351. doi: 10.1002/cne.901840208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V., Palay S. L. Immunocytochemical identification of substance P cells and their processes in rat sensory ganglia and their terminals in the spinal cord: light microscopic studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3597–3601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A radioimmunoassay for measurement of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3). J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):583–592. doi: 10.1172/JCI107795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello A. C., Polak J. M., Pearse A. G. Substance P: a naturally occurring transmitter in human spinal cord. Lancet. 1976 Nov 13;2(7994):1054–1056. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90968-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Giulio A. M., Mantegazza P., Dona M., Gorio A. Peripheral nerve lesions cause simultaneous alterations of substance P and enkephalin levels in the spinal cord. Brain Res. 1985 Sep 9;342(2):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emson P. C. Neuropeptides and the pathology of Huntington's disease. Prog Brain Res. 1986;66:91–105. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64599-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichefet J. P., Sternon J. E., Franken L., Demanet J. C., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Etude anatomo-clinique d'un cas d'hypotension orthostatique "idiopathique". Considérations pathogéniques. Acta Cardiol. 1965;20(4):332–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. C., Burgis V., Harrell C. E., Edwards J. D. Dual actions of substance P on nociception: possible role of endogenous opioids. Science. 1978 Mar 24;199(4335):1359–1362. doi: 10.1126/science.204012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galassi G., Nemni R., Baraldi A., Gibertoni M., Colombo A. Peripheral neuropathy in multiple system atrophy with autonomic failure. Neurology. 1982 Oct;32(10):1116–1121. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.10.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamse R., Wax A., Zigmond R. E., Leeman S. E. Immunoreactive substance P in sympathetic ganglia: distribution and sensitivity towards capsaicin. Neuroscience. 1981;6(3):437–441. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbins I. L., Furness J. B., Costa M., MacIntyre I., Hillyard C. J., Girgis S. Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous, vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jun 12;57(2):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. G., Oppenheimer D. R. Orthostatic hypotension and nicotine sensitivity in a case of multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1969 Feb;32(1):28–34. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.32.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Rothfeld J. M. Quantitative immunocytochemistry of hypothalamic and pituitary hormones: validation of an automated, computerized image analysis system. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jan;33(1):11–20. doi: 10.1177/33.1.2578140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helen P., Panula P., Yang H. Y., Hervonen A., Rapoport S. I. Location of substance P-, bombesin-gastrin-releasing peptide, [Met5]enkephalin- and [Met5]enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7-like immunoreactivities in adult human sympathetic ganglia. Neuroscience. 1984 Jul;12(3):907–916. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Elfvin L. G., Schultzberg M., Goldstein M., Nilsson G. On the occurrence of substance P-containing fibers in sympathetic ganglia: immunohistochemical evidence. Brain Res. 1977 Aug 19;132(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Ljungdahl A., Terenius L., Elde R., Nilsson G. Immunohistochemical analysis of peptide pathways possibly related to pain and analgesia: enkephalin and substance P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3081–3085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancsó G., Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Kiraly E., Halász N., Nilsson G., Terenius L., Rehfeld J., Steinbusch H., Verhofstad A. Immunohistochemical studies on the effect of capsaicin on spinal and medullary peptide and monoamine neurons using antisera to substance P, gastrin/CCK, somatostatin, VIP, enkephalin, neurotensin and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Neurocytol. 1981 Dec;10(6):963–980. doi: 10.1007/BF01258524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L., Cuello A. C. Capsaicin-induced depletion of substance P from primary sensory neurones. Brain Res. 1978 Aug 18;152(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T., Tsunoo A., Kanazawa I., Otsuka M. Substance P: depletion in the dorsal horn of rat spinal cord after section of the peripheral processes of primary sensory neurons. Brain Res. 1979 May 25;168(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. H., Lee G. de J., Oppenheimer D. R., Spalding J. M. Autonomic failure with orthostatic hypotension due to intermediolateral column degeneration. A report of two cases with autopsies. Q J Med. 1966 Apr;35(138):276–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light A. R., Trevino D. L., Perl E. R. Morphological features of functionally defined neurons in the marginal zone and substantia gelatinosa of the spinal dorsal horn. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Jul 15;186(2):151–171. doi: 10.1002/cne.901860204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Dyck P. J. Splanchnic preganglionic neurons in man: II. Morphometry of myelinated fibers of T7 ventral spinal root. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Nov 28;40(3):219–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00691957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. A., Thomas J. E., Dyck P. J. The splanchnic autonomic outflow in Shy-Drager syndrome and idiopathic orthostatic hypotension. Ann Neurol. 1978 Dec;4(6):511–514. doi: 10.1002/ana.410040606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews M. R., Cuello A. C. Substance P-immunoreactive peripheral branches of sensory neurons innervate guinea pig sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1668–1672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutt J. G., Mrox E. A., Leeman S. E., Williams A. C., Engel W. K., Chase T. N. Substance P in human cerebrospinal fluid: reductions in peripheral neuropathy and autonomic dysfunction. Neurology. 1980 Dec;30(12):1280–1285. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.12.1280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehme P., Hilse H., Morgenstern E., Göres E. Substance P: does it produce analgesia or hyperalgesia? Science. 1980 Apr 18;208(4441):305–307. doi: 10.1126/science.6154313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Brandeis L., Cuello A. C. Depletion of substance P-containing axons in substantia gelatinosa of patients with diminished pain sensitivity. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):61–63. doi: 10.1038/295061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHY G. M., DRAGER G. A. A neurological syndrome associated with orthostatic hypotension: a clinical-pathologic study. Arch Neurol. 1960 May;2:511–527. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1960.03840110025004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobue G., Hashizume Y., Ohya M., Takahashi A. Shy-Drager syndrome: neuronal loss depends on size, function, and topography in ventral spinal outflow. Neurology. 1986 Mar;36(3):404–407. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.3.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura Y., Lee C. L., Perl E. R. Central projections of identified, unmyelinated (C) afferent fibers innervating mammalian skin. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):358–361. doi: 10.1126/science.3764416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Otsuka M. Regional distribution of substance P in the spinal cord and nerve roots of the cat and the effect of dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 4;87(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90774-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohgi H., Tabuchi M., Tomonaga M., Izumiyama N. Selective loss of small myelinated and unmyelinated fibers in Shy-Drager syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 1982;57(4):282–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00692184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]