Abstract
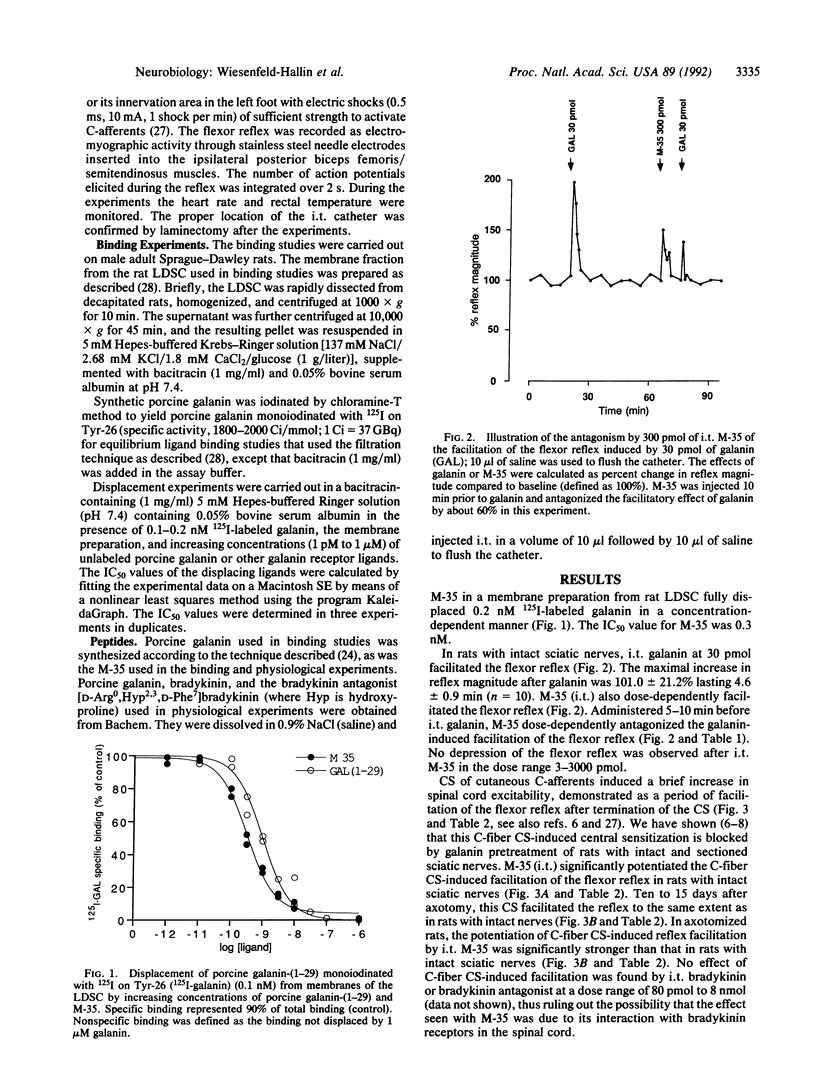
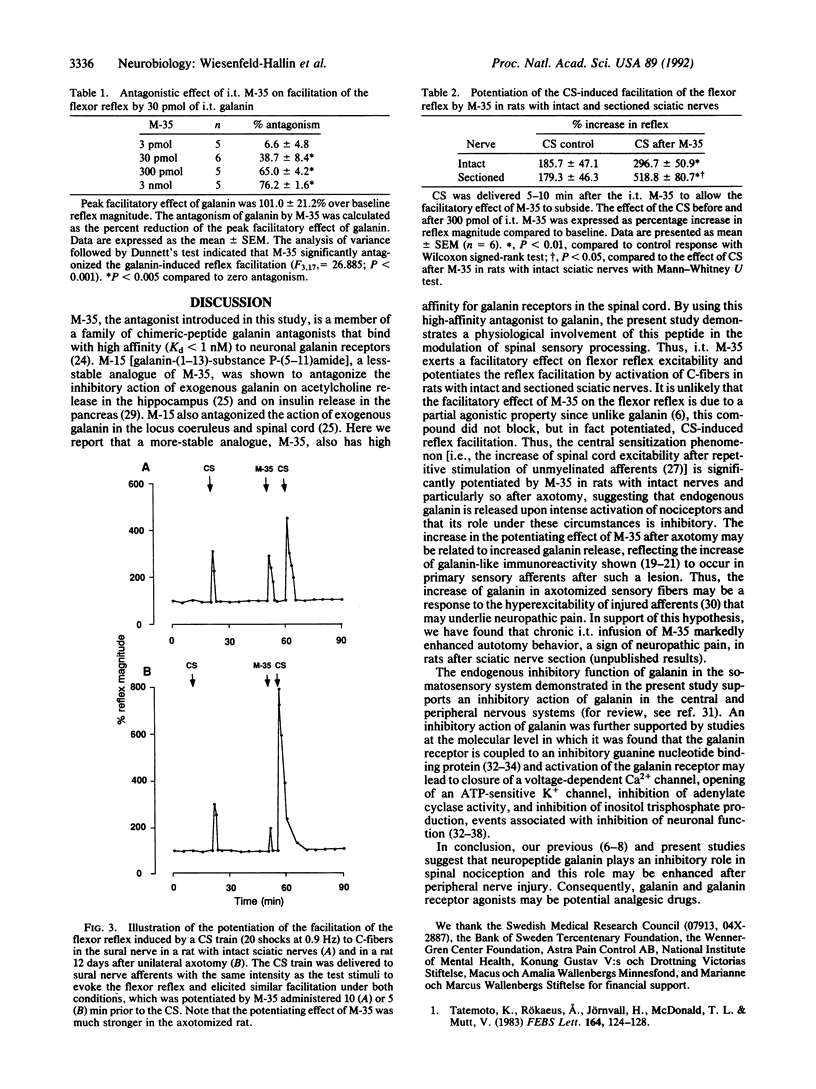
The endogenous inhibitory role of the neuropeptide galanin in pain transmission and spinal cord excitability was demonstrated by the use of a high-affinity galanin receptor antagonist, M-35 [galanin-(1-13)-bradykinin-(2-9)-amide]. M-35, which displaced 125I-labeled galanin from membranes of rat dorsal spinal cord with an IC50 of 0.3 nM, dose-dependently antagonized the effect of intrathecal galanin on the flexor reflex. M-35 potentiated the facilitation of the flexor reflex by conditioning stimulation of cutaneous unmyelinated afferents in rats with intact nerves and the potentiating effect of M-35 on the conditioning-stimulation-induced reflex facilitation of the cutaneous unmyelinated afferents was strongly enhanced after axotomy. These results demonstrate that endogenous galanin plays a tonic inhibitory role in the mediation of spinal cord excitability, and it is particularly noteworthy that this function of galanin is remarkably enhanced after peripheral nerve section.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrén B., Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O., Nilsson T. Galanin inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin release by a mechanism involving hyperpolarization and lowering of cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 14;140(3):1059–1063. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90742-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Laburthe M. Galanin receptor in the rat pancreatic beta cell line Rin m 5F. Molecular characterization by chemical cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20714–20717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Bedecs K., Land T., Langel U., Bertorelli R., Girotti P., Consolo S., Xu X. J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Nilsson S. M-15: high-affinity chimeric peptide that blocks the neuronal actions of galanin in the hippocampus, locus coeruleus, and spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10961–10965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ch'ng J. L., Christofides N. D., Anand P., Gibson S. J., Allen Y. S., Su H. C., Tatemoto K., Morrison J. F., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Distribution of galanin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system and the responses of galanin-containing neuronal pathways to injury. Neuroscience. 1985 Oct;16(2):343–354. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Bullett M. J., Li G. D., Wollheim C. B., Petersen O. H. Galanin activates nucleotide-dependent K+ channels in insulin-secreting cells via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):413–420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisone G., Langel U., Carlquist M., Bergman T., Consolo S., Hökfelt T., Undén A., Andell S., Bartfai T. Galanin receptor and its ligands in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 15;181(1):269–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani S., Amann R., Papini A. M., Maggi C. A., Meli A. Modulatory action of galanin on responses due to antidromic activation of peripheral terminals of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 12;163(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Villar M., Melander T. Increase of galanin-like immunoreactivity in rat dorsal root ganglion cells after peripheral axotomy. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Dec 29;83(3):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T., Tsunoo A., Kanazawa I., Otsuka M. Substance P: depletion in the dorsal horn of rat spinal cord after section of the peripheral processes of primary sensory neurons. Brain Res. 1979 May 25;168(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka L. M., McKeon T. W., Parsons R. L. Galanin-induced hyperpolarization and decreased membrane excitability of neurones in mudpuppy cardiac ganglia. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:107–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuraishi Y., Kawamura M., Yamaguchi T., Houtani T., Kawabata S., Futaki S., Fujii N., Satoh M. Intrathecal injections of galanin and its antiserum affect nociceptive response of rat to mechanical, but not thermal, stimuli. Pain. 1991 Mar;44(3):321–324. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(91)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindskog S., Ahrén B., Land T., Langel U., Bartfai T. The novel high-affinity antagonist, galantide, blocks the galanin-mediated inhibition of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90669-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor G. P., Gibson S. J., Sabate I. M., Blank M. A., Christofides N. D., Wall P. D., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. Effect of peripheral nerve section and nerve crush on spinal cord neuropeptides in the rat; increased VIP and PHI in the dorsal horn. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A. Distribution of galaninlike immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jun 22;248(4):475–517. doi: 10.1002/cne.902480404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post C., Alari L., Hökfelt T. Intrathecal galanin increases the latency in the tail-flick and hot-plate test in mouse. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Apr;132(4):583–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauviat M. P. Effect of palytoxin on the calcium current and the mechanical activity of frog heart muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):773–780. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14605.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Yada T., Russo L. L., Bliss C. R., Cormont M., Monge L., Van Obberghen E. Galanin can inhibit insulin release by a mechanism other than membrane hyperpolarization or inhibition of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7302–7309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehab S. A., Atkinson M. E. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) increases in the spinal cord after peripheral axotomy of the sciatic nerve originate from primary afferent neurons. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 30;372(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91456-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M. Galanin-like immunoreactivity in capsaicin sensitive sensory neurons and ganglia. Brain Res Bull. 1985 Aug;15(2):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(85)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steranka L. R., Manning D. C., DeHaas C. J., Ferkany J. W., Borosky S. A., Connor J. R., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin as a pain mediator: receptors are localized to sensory neurons, and antagonists have analgesic actions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3245–3249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Rökaeus A., Jörnvall H., McDonald T. J., Mutt V. Galanin - a novel biologically active peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):124–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villar M. J., Cortés R., Theodorsson E., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Schalling M., Fahrenkrug J., Emson P. C., Hökfelt T. Neuropeptide expression in rat dorsal root ganglion cells and spinal cord after peripheral nerve injury with special reference to galanin. Neuroscience. 1989;33(3):587–604. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90411-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villar M. J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Xu X. J., Theodorsson E., Emson P. C., Hökfelt T. Further studies on galanin-, substance P-, and CGRP-like immunoreactivities in primary sensory neurons and spinal cord: effects of dorsal rhizotomies and sciatic nerve lesions. Exp Neurol. 1991 Apr;112(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(91)90111-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D., Gutnick M. Ongoing activity in peripheral nerves: the physiology and pharmacology of impulses originating from a neuroma. Exp Neurol. 1974 Jun;43(3):580–593. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D., Woolf C. J. Muscle but not cutaneous C-afferent input produces prolonged increases in the excitability of the flexion reflex in the rat. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:443–458. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Villar M. J., Hökfelt T. The effects of intrathecal galanin and C-fiber stimulation on the flexor reflex in the rat. Brain Res. 1989 May 8;486(2):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90506-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Xu X. J., Håkanson R., Feng D. M., Folkers K. Plasticity of the peptidergic mediation of spinal reflex facilitation after peripheral nerve section in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Aug 24;116(3):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90089-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Xu X. J., Villar M. J., Hökfelt T. The effect of intrathecal galanin on the flexor reflex in rat: increased depression after sciatic nerve section. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Oct 23;105(1-2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. J., Hao J. X., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Håkanson R., Folkers K., Hökfelt T. Spantide II, a novel tachykinin antagonist, and galanin inhibit plasma extravasation induced by antidromic C-fiber stimulation in rat hindpaw. Neuroscience. 1991;42(3):731–737. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90041-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Hökfelt T. Intrathecal galanin blocks the prolonged increase in spinal cord flexor reflex excitability induced by conditioning stimulation of unmyelinated muscle afferents in the rat. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 15;541(2):350–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X.-J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Villar M. J., Fahrenkrug J., Hökfelt T. On the Role of Galanin, Substance P and Other Neuropeptides in Primary Sensory Neurons of the Rat: Studies on Spinal Reflex Excitability and Peripheral Axotomy. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(9):733–743. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Yagi N., Otsuka M., Yanaihara C., Yanaihara N. Inhibitory effects of galanin on the isolated spinal cord of the newborn rat. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Oct 8;70(2):278–282. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90477-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



