Abstract
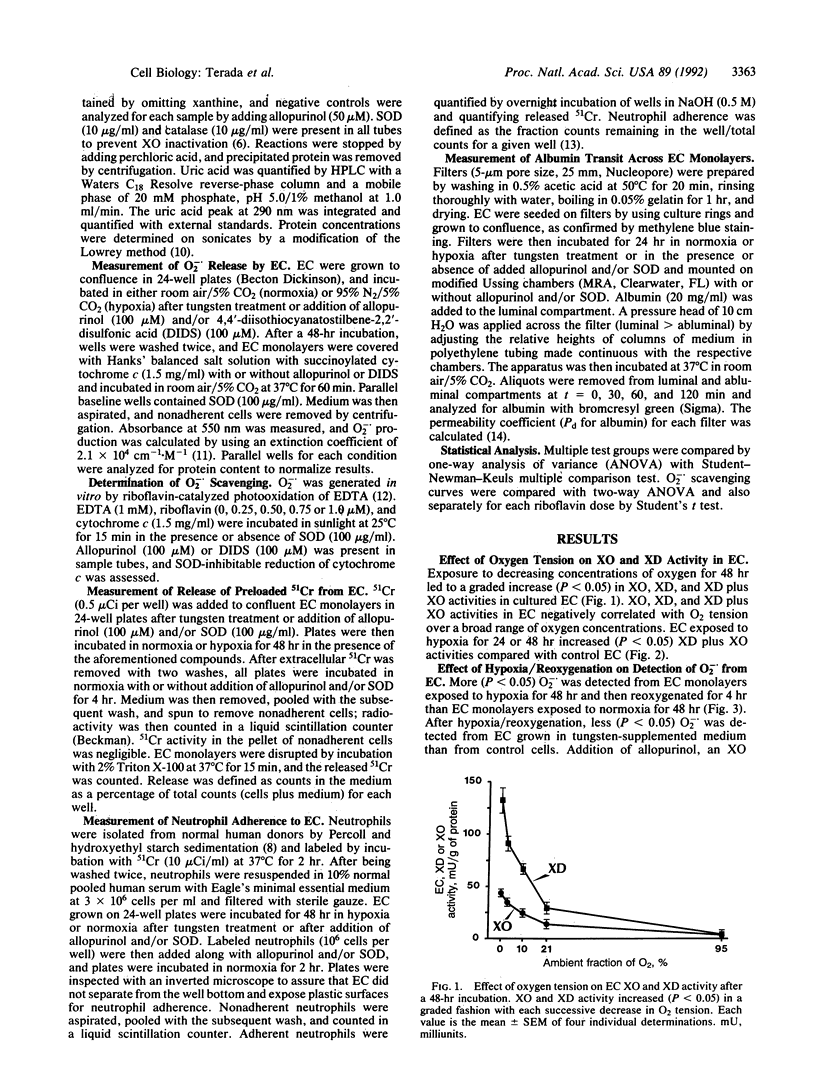
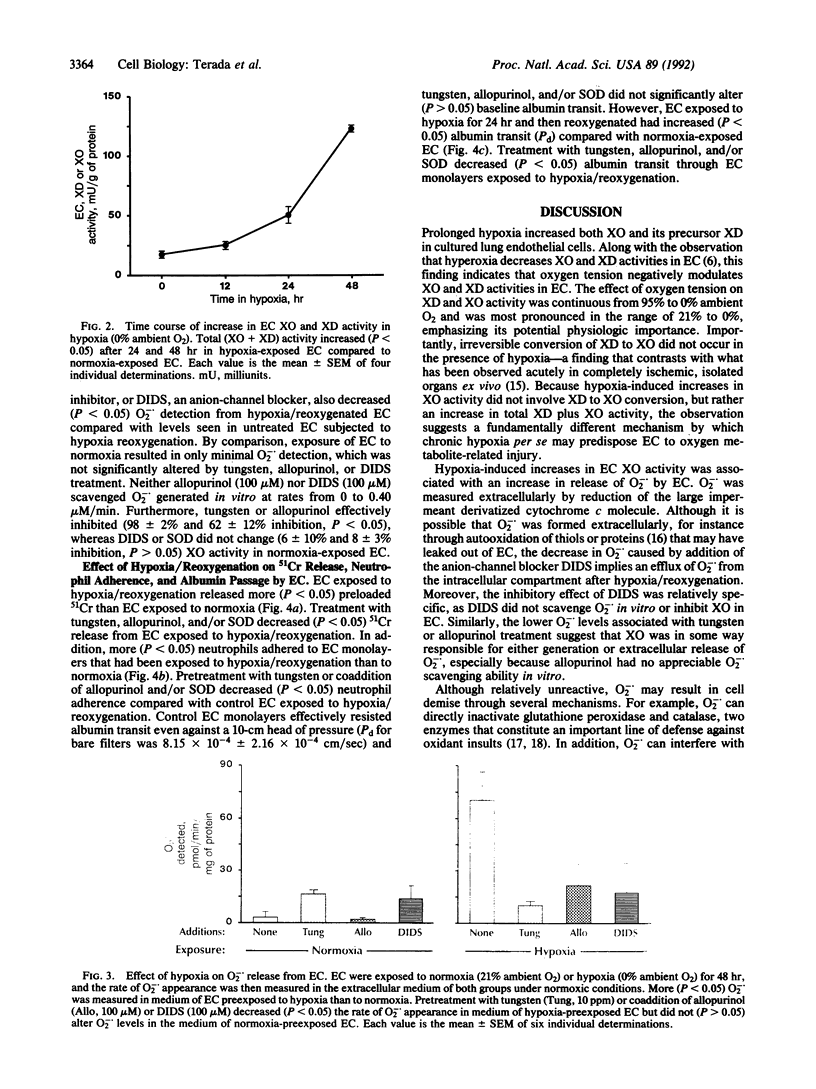
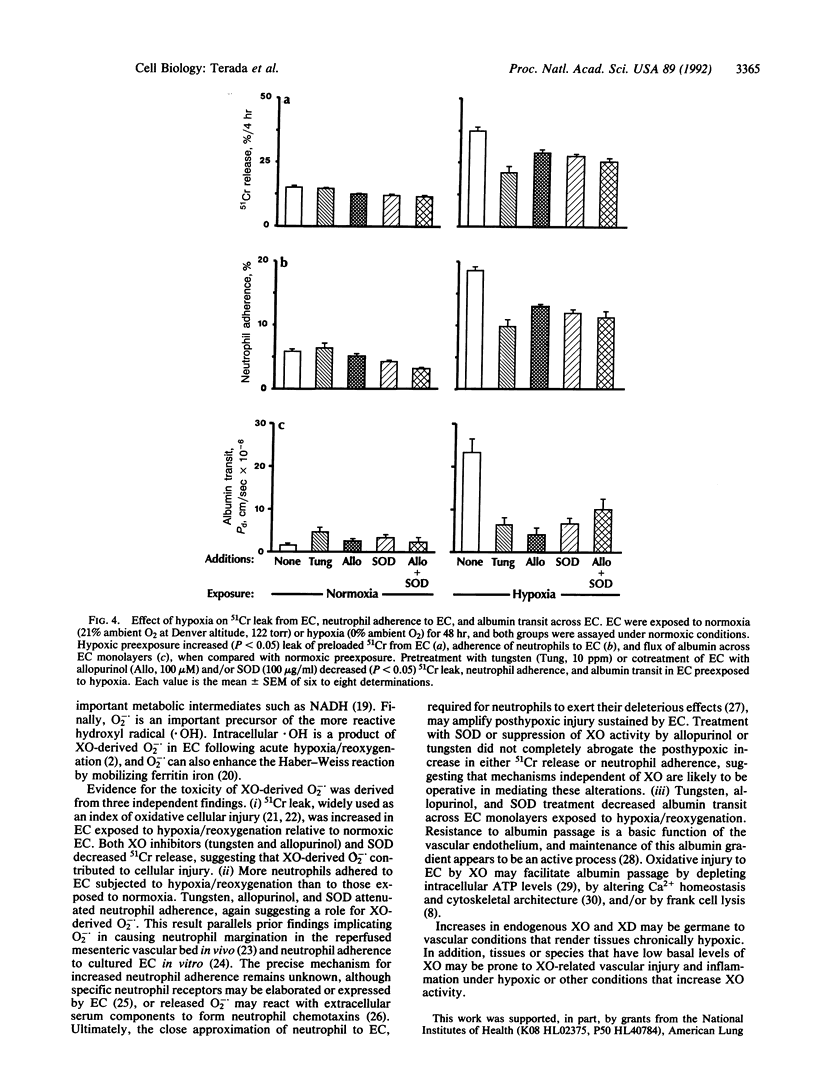
Exposure to decreasing oxygen tensions progressively increased xanthine dehydrogenase (XD) and xanthine oxidase (XO) activities over 48 hr in cultured pulmonary artery endothelial cells (EC) without altering XD/XO ratios. Increases in XD and XO activity in EC induced by hypoxia were associated upon reoxygenation with increased (P less than 0.05) extracellular superoxide anion (O2-.) levels that were inhibited by treatment with XO inhibitors (tungsten, allopurinol) or an anion-channel blocker (4,4'-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid). EC monolayers subjected to hypoxia/reoxygenation also leaked more preloaded 51Cr, were more adherent to neutrophils, and permitted greater albumin transit than control monolayers. Treatment with tungsten, allopurinol, and/or superoxide dismutase decreased (P less than 0.05) 51Cr release, neutrophil adherence, and albumin transit in EC monolayers exposed to hypoxia/reoxygenation. We conclude that prolonged hypoxia increases both XO and XD activity in EC and may predispose the endothelium to oxidative and inflammatory damage.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ager A., Gordon J. L. Differential effects of hydrogen peroxide on indices of endothelial cell function. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):592–603. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum J., Fridovich I. Inactivation of glutathione peroxidase by superoxide radical. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Aug 1;240(2):500–508. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M., Butler E. N., Repine J. E. Hyperoxia damages cultured endothelial cells causing increased neutrophil adherence. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Sep;128(3):469–472. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.3.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. C., Bielski B. H. Enzyme-catalyzed free radical reactions with nicotinamide adenine nucleotides. II. Lactate dehydrogenase-catalyzed oxidation of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by superoxide radicals generated by xanthine oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1317–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Corte E., Stirpe F. The regulation of xanthine oxidase. Inhibition by reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide of rat liver xanthine oxidase type D and of chick liver xanthine dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;117(1):97–100. doi: 10.1042/bj1170097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engerson T. D., McKelvey T. G., Rhyne D. B., Boggio E. B., Snyder S. J., Jones H. P. Conversion of xanthine dehydrogenase to oxidase in ischemic rat tissues. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1564–1570. doi: 10.1172/JCI112990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. N., Benoit J. N., Suzuki M., Grisham M. B. Leukocyte adherence to venular endothelium during ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):G683–G688. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.5.G683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover R. L., Briggs R. T., Karnovsky M. J. The adhesive interaction between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):423–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inauen W., Payne D. K., Kvietys P. R., Granger D. N. Hypoxia/reoxygenation increases the permeability of endothelial cell monolayers: role of oxygen radicals. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;9(3):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(90)90031-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarasch E. D., Bruder G., Heid H. W. Significance of xanthine oxidase in capillary endothelial cells. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1986;548:39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Critz A. M., Crandall E. D. Transport of water and solutes across sheep visceral pleura. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Oct;120(4):883–892. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.4.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Fridovich I. Superoxide radical inhibits catalase. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5751–5754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuthan H., Ullrich V., Estabrook R. W. A quantitative test for superoxide radicals produced in biological systems. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 1;203(3):551–558. doi: 10.1042/bj2030551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSEY V. The microestimation of succinate and the extinction coefficient of cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:255–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 17;312(3):159–163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra H. P. Generation of superoxide free radical during the autoxidation of thiols. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2151–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. D., Zimmerman G. A., Prescott S. M., McEver R. P., McIntyre T. M. Oxygen radicals induce human endothelial cells to express GMP-140 and bind neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):749–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrone W. F., English D. K., Wong K., McCord J. M. Free radicals and inflammation: superoxide-dependent activation of a neutrophil chemotactic factor in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1159–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratych R. E., Chuknyiska R. S., Bulkley G. B. The primary localization of free radical generation after anoxia/reoxygenation in isolated endothelial cells. Surgery. 1987 Aug;102(2):122–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Lind S. E., Shasby S. S., Goldsmith J. C., Hunninghake G. W. Reversible oxidant-induced increases in albumin transfer across cultured endothelium: alterations in cell shape and calcium homeostasis. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S. Active transendothelial transport of albumin. Interstitium to lumen. Circ Res. 1985 Dec;57(6):903–908. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.6.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Peach M. J. Granulocytes and phorbol myristate acetate increase permeability to albumin of cultured endothelial monolayers and isolated perfused lungs. Role of oxygen radicals and granulocyte adherence. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jan;127(1):72–76. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spragg R. G., Hinshaw D. B., Hyslop P. A., Schraufstätter I. U., Cochrane C. G. Alterations in adenosine triphosphate and energy charge in cultured endothelial and P388D1 cells after oxidant injury. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1471–1476. doi: 10.1172/JCI112126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Inauen W., Kvietys P. R., Grisham M. B., Meininger C., Schelling M. E., Granger H. J., Granger D. N. Superoxide mediates reperfusion-induced leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):H1740–H1745. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.5.H1740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada L. S., Beehler C. J., Banerjee A., Brown J. M., Grosso M. A., Harken A. H., McCord J. M., Repine J. E. Hyperoxia and self- or neutrophil-generated O2 metabolites inactivate xanthine oxidase. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Nov;65(5):2349–2353. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.5.2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada L. S., Leff J. A., Guidot D. N., Shibao G. A., Repine J. E. Metals inhibit riboflavin-catalyzed generation of superoxide anion in vitro. Inflammation. 1990 Apr;14(2):217–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00917460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. E., Morehouse L. A., Aust S. D. Ferritin and superoxide-dependent lipid peroxidation. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3275–3280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweier J. L., Kuppusamy P., Lutty G. A. Measurement of endothelial cell free radical generation: evidence for a central mechanism of free radical injury in postischemic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4046–4050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]