Abstract
The Drosophila snail gene is required for proper mesodermal development. Genetic studies suggest that it functions by repressing adjacent ectodermal gene expression including that of the single-minded (sim) gene. The snail gene encodes a protein with a zinc-finger motif, and here we report that the snail gene product is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. The snail protein recognizes a 14-base-pair consensus sequence that is found nine times in a 2.8-kilobase sim regulatory region. These results provide evidence for the direct control of sim transcription by snail.
Full text
PDF
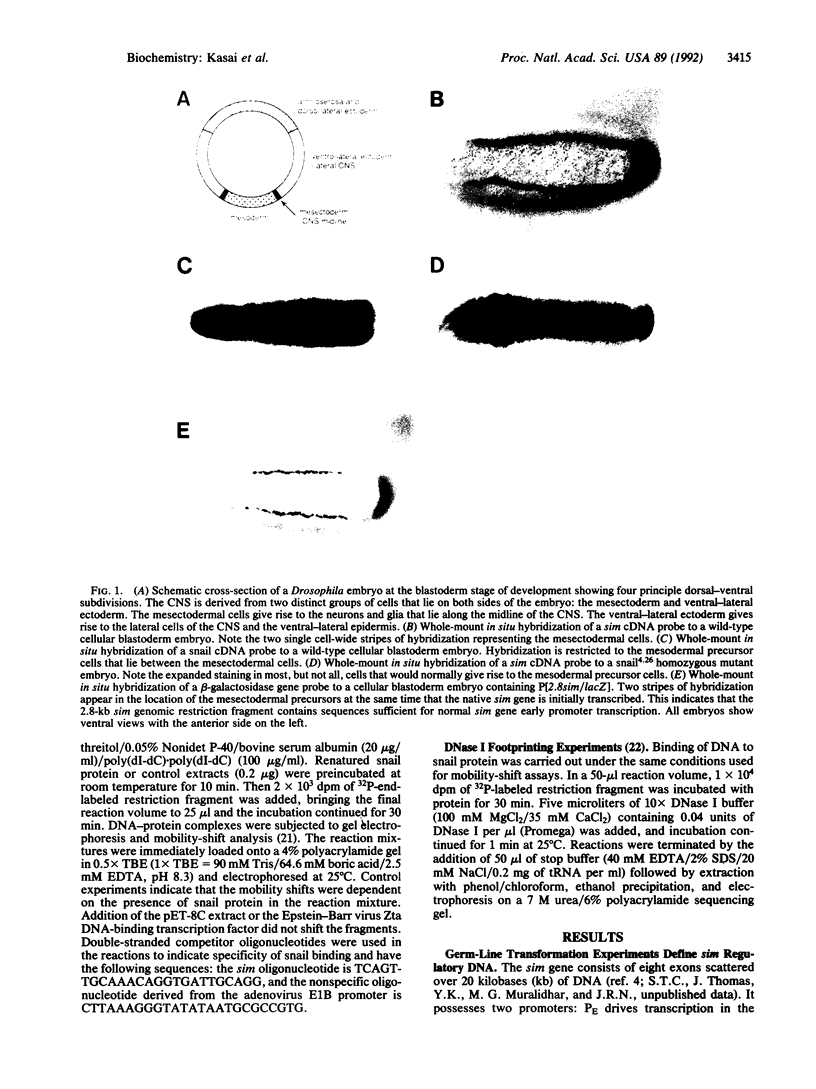



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberga A., Boulay J. L., Kempe E., Dennefeld C., Haenlin M. The snail gene required for mesoderm formation in Drosophila is expressed dynamically in derivatives of all three germ layers. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):983–992. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay J. L., Dennefeld C., Alberga A. The Drosophila developmental gene snail encodes a protein with nucleic acid binding fingers. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):395–398. doi: 10.1038/330395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B. Zebra patterns in fly embryos: activation of stripes or repression of interstripes? Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90711-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S. T., Thomas J. B., Goodman C. S. The Drosophila single-minded gene encodes a nuclear protein with sequence similarity to the per gene product. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90538-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hülskamp M., Tautz D. Gap genes and gradients--the logic behind the gaps. Bioessays. 1991 Jun;13(6):261–268. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klämbt C., Jacobs J. R., Goodman C. S. The midline of the Drosophila central nervous system: a model for the genetic analysis of cell fate, cell migration, and growth cone guidance. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):801–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90509-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosman D., Ip Y. T., Levine M., Arora K. Establishment of the mesoderm-neuroectoderm boundary in the Drosophila embryo. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):118–122. doi: 10.1126/science.1925551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leptin M., Grunewald B. Cell shape changes during gastrulation in Drosophila. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):73–84. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leptin M. twist and snail as positive and negative regulators during Drosophila mesoderm development. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1568–1576. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambu J. R., Franks R. G., Hu S., Crews S. T. The single-minded gene of Drosophila is required for the expression of genes important for the development of CNS midline cells. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90288-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nambu J. R., Lewis J. O., Wharton K. A., Jr, Crews S. T. The Drosophila single-minded gene encodes a helix-loop-helix protein that acts as a master regulator of CNS midline development. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1157–1167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankratz M. J., Jäckle H. Making stripes in the Drosophila embryo. Trends Genet. 1990 Sep;6(9):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90234-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao Y., Vaessin H., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Neuroectoderm in Drosophila embryos is dependent on the mesoderm for positioning but not for formation. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1577–1588. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Arora K. Dorsal ventral polarity and pattern formation in the Drosophila embryo. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;1(3):137–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G., Bennett M. F. Identification in Xenopus of a structural homologue of the Drosophila gene snail. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):967–973. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanojević D., Hoey T., Levine M. Sequence-specific DNA-binding activities of the gap proteins encoded by hunchback and Krüppel in Drosophila. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):331–335. doi: 10.1038/341331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Relocalization of the dorsal protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus correlates with its function. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse B., Stoetzel C., Gorostiza-Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F. Sequence of the twist gene and nuclear localization of its protein in endomesodermal cells of early Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2175–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. B., Crews S. T., Goodman C. S. Molecular genetics of the single-minded locus: a gene involved in the development of the Drosophila nervous system. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90537-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]