Abstract
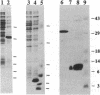
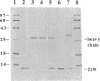
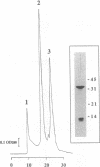
The two subunits of the human class I histocompatibility antigen (HLA)-A2 have been expressed at high levels (20-30 mg/liter) as insoluble aggregates in bacterial cells. The aggregates were dissolved in 8 M urea and then refolded to form an HLA-A2-peptide complex by removal of urea in the presence of an antigenic peptide. Two peptides from the matrix protein and nucleoprotein of influenza virus are known to bind to HLA-A2, and both support the refolding of the recombinant HLA-A2 molecule. An additional peptide, a nonamer from the gp120 envelope protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, also supported refolding. Yields of purified recombinant HLA-A2 are 10-15%. In the absence of an HLA-A2-restricted peptide, a stable HLA-A2 complex was not formed. Monoclonal antibodies known to bind to native HLA-A2 also bound to the recombinant HLA-A2-peptide complex. Three purified HLA-A2-peptide complexes refolded from bacterially produced protein aggregates crystallize under the identical conditions as HLA-A2 purified from human lymphoblastoid cells. Crystals of the recombinant HLA-A2 molecule in complex with the influenza matrix nonamer peptide, Mp(58-66), diffract to greater than 1.5-A resolution.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednarek M. A., Sauma S. Y., Gammon M. C., Porter G., Tamhankar S., Williamson A. R., Zweerink H. J. The minimum peptide epitope from the influenza virus matrix protein. Extra and intracellular loading of HLA-A2. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4047–4053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Crystallization and X-ray diffraction studies on the histocompatibility antigens HLA-A2 and HLA-A28 from human cell membranes. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchner J., Rudolph R. Renaturation, purification and characterization of recombinant Fab-fragments produced in Escherichia coli. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Feb;9(2):157–162. doi: 10.1038/nbt0291-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cresswell P., Turner M. J., Strominger J. L. Papain-solubilized HL-A antigens from cultured human lymphocytes contain two peptide fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadaglio G., Leroux A., Langlade-Demoyen P., Bahraoui E. M., Traincard F., Fisher R., Plata F. Epitope recognition of conserved HIV envelope sequences by human cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2302–2309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. J., Eisen H. N. Allorecognition of purified major histocompatibility complex glycoproteins by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. J., Eisen H. N. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize a reconstituted class I histocompatibility antigen (HLA-A2) as an allogeneic target molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5213–5217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Stevanović S., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):290–296. doi: 10.1038/351290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett T. P., Saper M. A., Bjorkman P. J., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Specificity pockets for the side chains of peptide antigens in HLA-Aw68. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):692–696. doi: 10.1038/342692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorga J. C., Madden D. R., Prendergast J. K., Wiley D. C., Strominger J. L. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of the human major histocompatibility antigen HLA-B27. Proteins. 1992 Jan;12(1):87–90. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotch F., Rothbard J., Howland K., Townsend A., McMichael A. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize a fragment of influenza virus matrix protein in association with HLA-A2. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):881–882. doi: 10.1038/326881a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky T. S., Lane W. S., Robinson R. A., Madden D. R., Wiley D. C. Identification of self peptides bound to purified HLA-B27. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):326–329. doi: 10.1038/353326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Eckels D. D., Lake P., Woody J. N., Green N. Human T-cell clones recognize chemically synthesized peptides of influenza haemagglutinin. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):66–69. doi: 10.1038/300066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacFerrin K. D., Terranova M. P., Schreiber S. L., Verdine G. L. Overproduction and dissection of proteins by the expression-cassette polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1937–1941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden D. R., Gorga J. C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The structure of HLA-B27 reveals nonamer self-peptides bound in an extended conformation. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):321–325. doi: 10.1038/353321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Thøgersen H. C. Synthesis and sequence-specific proteolysis of hybrid proteins produced in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:461–481. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Alpert B. N., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Carbohydrate moiety of HLA antigens. Antigenic properties and amino acid sequences around the site of glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7555–7567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Androlewicz M. J., Holmes N. J., Rothenberg B. E. Arginine 45 is a major part of the antigenic determinant of human beta 2-microglobulin recognized by mouse monoclonal antibody BBM.1. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6179–6186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibody to a human histocompatibility alloantigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):397–399. doi: 10.1038/276397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker K. C., Wiley D. C. Overexpression of native human beta 2-microglobulin in Escherichia coli and its purification. Gene. 1989 Nov 15;83(1):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Rask L., Lindblom J. B. Highly purified papain-solubilized HL-A antigens contain beta2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):35–39. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. A., Lettice L. A., Rota P., Santos-Aguado J., Rothbard J., McMichael A. J., Strominger J. L. Comparison between two peptide epitopes presented to cytotoxic T lymphocytes by HLA-A2. Evidence for discrete locations within HLA-A2. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4098–4103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saper M. A., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. Refined structure of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-A2 at 2.6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):277–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90567-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver M. L., Parker K. C., Wiley D. C. Reconstitution by MHC-restricted peptides of HLA-A2 heavy chain with beta 2-microglobulin, in vitro. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):619–622. doi: 10.1038/350619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Strominger J. L. Detergent-soluble HLA antigens contain a hydrophilic region at the COOH-terminus and a penultimate hydrophobic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2481–2485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam N. J., Spits H., Ploegh H. L. Monoclonal antibodies raised against denatured HLA-B locus heavy chains permit biochemical characterization of certain HLA-C locus products. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Bodmer H. Antigen recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:601–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ways J. P., Parham P. The antigenic structure of HLA-A2: an analysis with competitive binding assays and monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):856–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]