Abstract
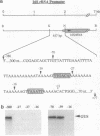
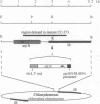
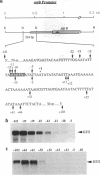
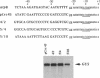
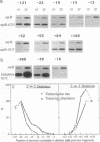
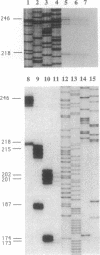
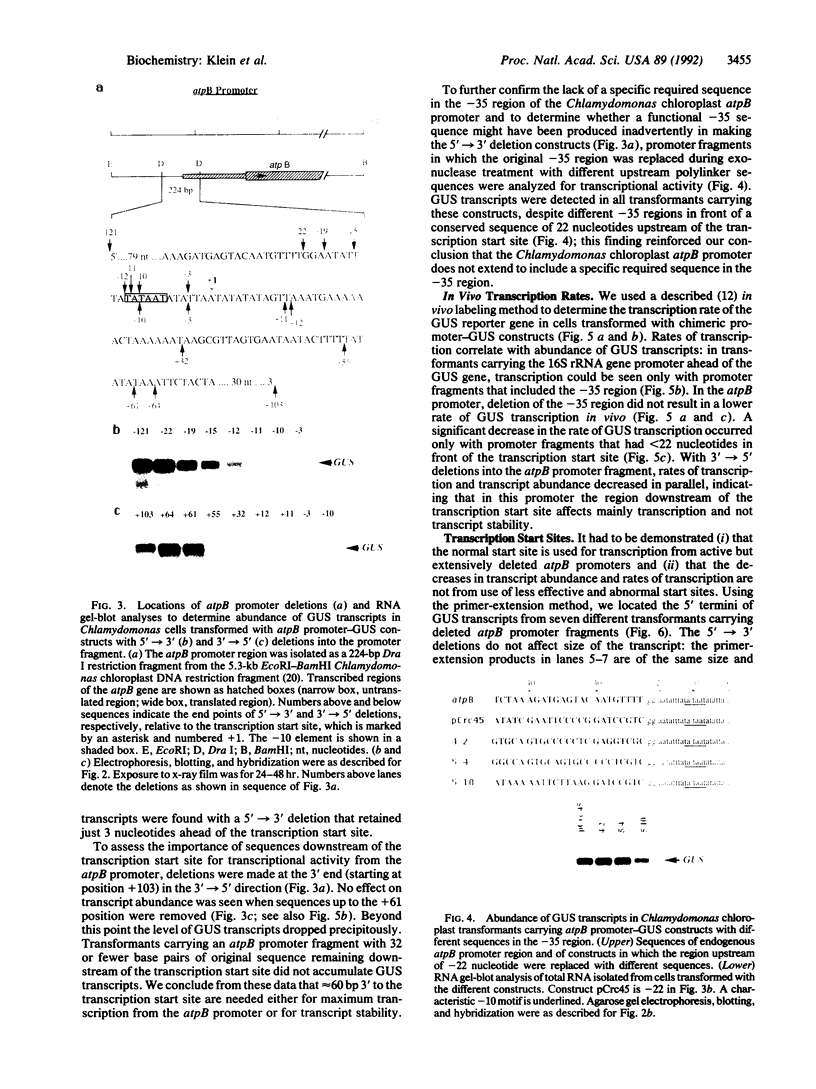
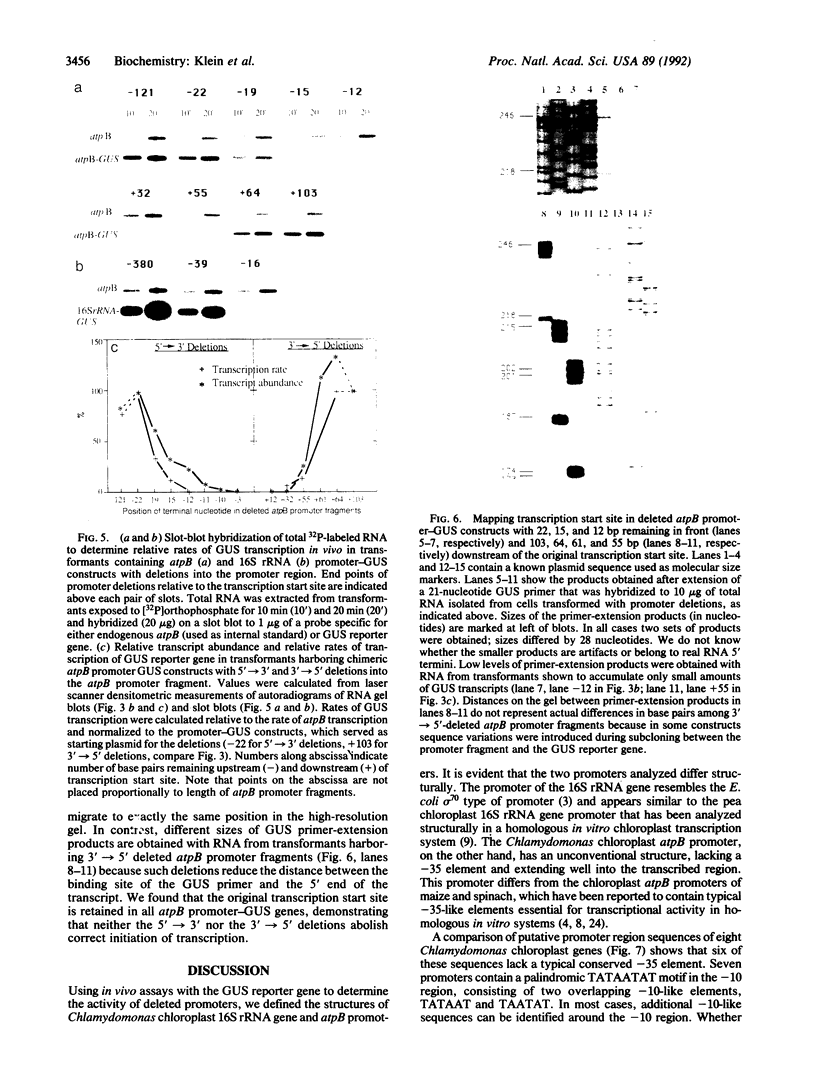
Structures of the promoters of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii plastid atpB and 16S rRNA-encoding genes were analyzed in vivo. Chimeric constructs, containing the Chlamydomonas chloroplast atpB or 16S rRNA-encoding gene promoter coupled to the Escherichia coli uidA (beta-glucuronidase, GUS) reporter gene and bordered by C. reinhardtii chloroplast sequences, were stably introduced into the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas by microprojectile bombardment. Activity of the promoters in the chloroplast of GUS gene-positive transformants was assayed by measuring the abundance of GUS transcripts and determining the relative rates of GUS transcription in vivo. Deletion analyses of the 16S rRNA gene and atpB promoter fragments showed that the two promoters differ structurally. The 16S rRNA gene promoter resembles the bacterial sigma 70 type with typical -10 and -35 elements. The atpB promoter, on the other hand, lacks a conserved motif in the -35 region but contains, in the -10 region, a characteristic octameric palindrome (TATAATAT) that is conserved in the promoter sequences of some other C. reinhardtii chloroplast genes. For maximum activity, the atpB promoter requires sequences of approximately 22 base pairs upstream and approximately 60 base pairs downstream of the transcription start site.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker E. J., Schloss J. A., Rosenbaum J. L. Rapid changes in tubulin RNA synthesis and stability induced by deflagellation in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2074–2081. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. C., Rogers S. A., Chen L. J., Orozco E. M., Jr A primary transcript in spinach chloroplasts that completely lacks a 5' untranslated leader region. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Jul;15(1):111–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00017728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Bogorad L., Shark K. B., Sanford J. C. Studies on Chlamydomonas chloroplast transformation: foreign DNA can be stably maintained in the chromosome. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):123–132. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Ellmore G. S., Klein U., Bogorad L. Transcriptional analysis of endogenous and foreign genes in chloroplast transformants of Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1059–1070. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W., Harris E. H., Hosler J. P., Johnson A. M., Jones A. R., Randolph-Anderson B. L., Robertson D., Klein T. M., Shark K. B. Chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas with high velocity microprojectiles. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1534–1538. doi: 10.1126/science.2897716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D., Gatenby A. A. Mutational analysis of the maize chloroplast ATPase-beta subunit gene promoter: the isolation of promoter mutants in E. coli and their characterization in a chloroplast in vitro transcription system. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3641–3648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. J., Rogers S. A., Bennett D. C., Hu M. C., Orozco E. M., Jr An in vitro transcription termination system to analyze chloroplast promoters: identification of multiple promoters for the spinach atpB gene. Curr Genet. 1990 Jan;17(1):55–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00313249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Sequence of the chloroplast 16S rRNA gene and its surrounding regions of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7609–7620. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Sequence of the chloroplast DNA region of Chlamydomonas reinhardii containing the gene of the large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase and parts of its flanking genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):775–793. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90547-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: absence of a "-35" region. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Chlamydomonas reinhardii gene for the 32 000 mol. wt. protein of photosystem II contains four large introns and is located entirely within the chloroplast inverted repeat. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2753–2762. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg B. M., Narita J. O., DeLuca-Flaherty C., Gruissem W., Rushlow K. A., Hallick R. B. Evidence for two RNA polymerase activities in Euglena gracilis chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14880–14887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Elsner-Menzel C., Latshaw S., Narita J. O., Schaffer M. A., Zurawski G. A subpopulation of spinach chloroplast tRNA genes does not require upstream promoter elements for transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7541–7556. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Zurawski G. Analysis of promoter regions for the spinach chloroplast rbcL, atpB and psbA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3375–3383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Zurawski G. Identification and mutational analysis of the promoter for a spinach chloroplast transfer RNA gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1637–1644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03831.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Burgess S. M., Hirsh D. beta-Glucuronidase from Escherichia coli as a gene-fusion marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8447–8451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klement J. F., Moorefield M. B., Jorgensen E., Brown J. E., Risman S., McAllister W. T. Discrimination between bacteriophage T3 and T7 promoters by the T3 and T7 RNA polymerases depends primarily upon a three base-pair region located 10 to 12 base-pairs upstream from the start site. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 5;215(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung S. D., Lin C. M. Chloroplast promoters from higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7543–7549. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kück U., Choquet Y., Schneider M., Dron M., Bennoun P. Structural and transcription analysis of two homologous genes for the P700 chlorophyll a-apoproteins in Chlamydomonas reinhardii: evidence for in vivo trans-splicing. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2185–2195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link G. DNA sequence requirements for the accurate transcription of a protein-coding plastid gene in a plastid in vitro system from mustard (Sinapis alba L.). EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1697–1704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff W. S., Siegele D. A., Cowing D. W., Gross C. A. The regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:355–387. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa M. D. Four T7 RNA polymerase promoters contain an identical 23 bp sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M., Darlix J. L., Erickson J., Rochaix J. D. Sequence organization of repetitive elements in the flanking regions of the chloroplast ribosomal unit of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8531–8541. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N. MITOTIC REPLICATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID IN CHLAMYDOMONAS REINHARDI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Jan;46(1):83–91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun E., Wu B. W., Tewari K. K. In vitro analysis of the pea chloroplast 16S rRNA gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5650–5659. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiller K., Eisermann A., Link G. The chloroplast transcription apparatus from mustard (Sinapis alba L.). Evidence for three different transcription factors which resemble bacterial sigma factors. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 23;198(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. P., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. The sequence of the chloroplast atpB gene and its flanking regions in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene. 1986;44(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaitlin D., Hu J., Bogorad L. Binding and transcription of relaxed DNA templates by fractions of maize chloroplast extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):876–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]