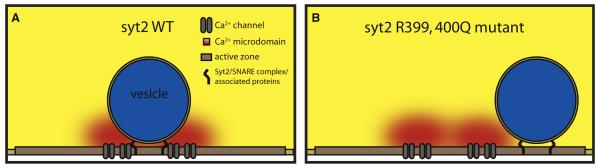
Figure 1. Overexpression of syt2 R399, 400Q Dissociates Ca2+ Channels and Synaptic Vesicles.
(A) In wild-type terminals, vesicles are positioned at the active zone close to calcium channels. This allows the vesicle to be exposed to the high calcium concentrations at the local calcium microdomain during calcium channel opening and ensures vesicle fusion.
(B) In terminals overexpressing the syt2 R399, 400Q mutant, vesicles show positioning defects, resulting in exposure of the vesicle to lower concentrations of calcium during calcium channel opening and impaired fusion. In this cartoon, the vesicle is misaligned with calcium channels at the active zone. Other interpretations are possible; for example, calcium channels may be misaligned at the active zone.