Abstract
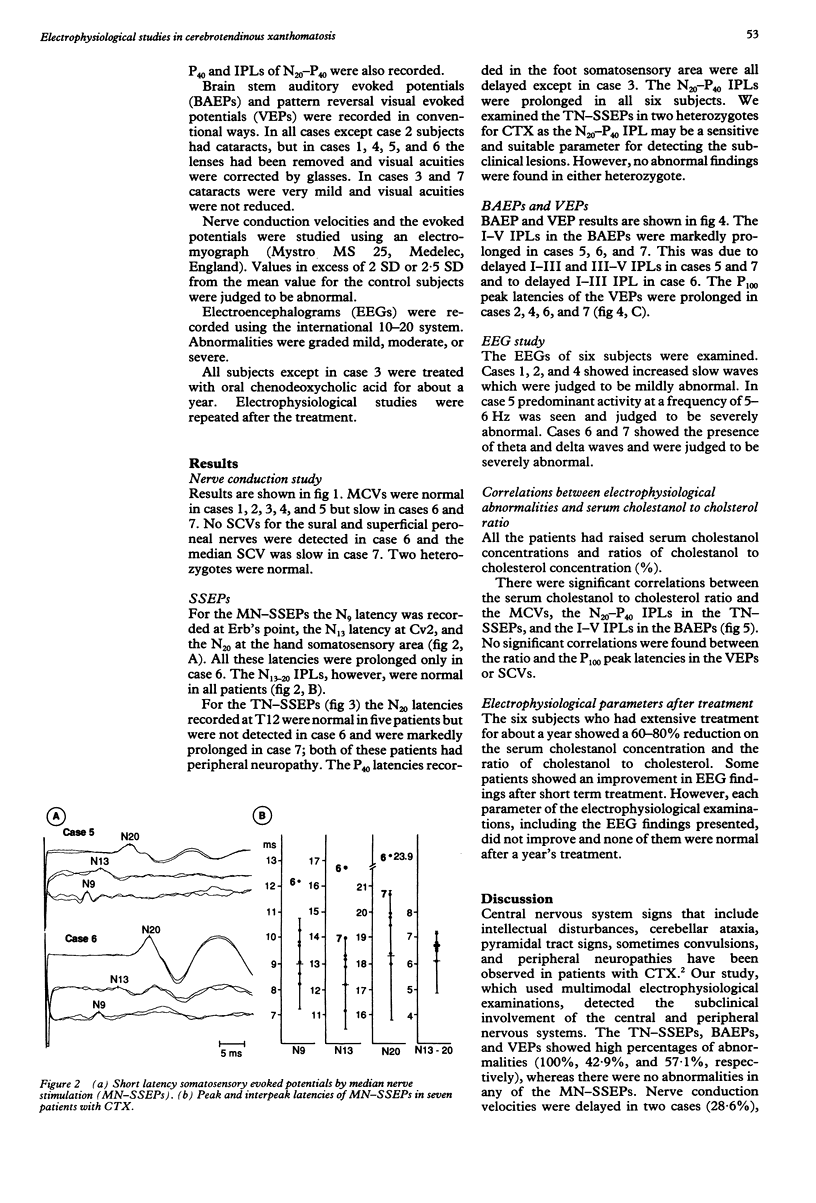
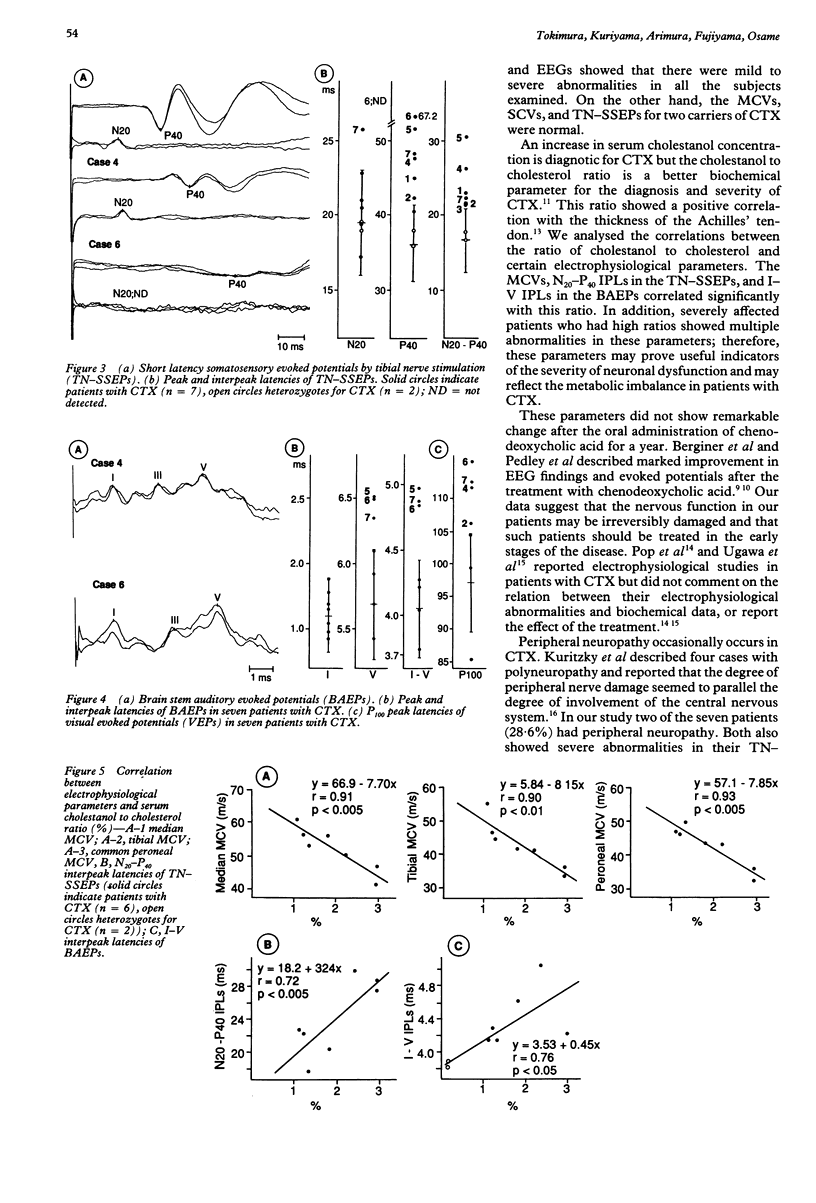
Seven patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX) were studied by electrophysiological techniques. The percentages of abnormalities detected in nerve conduction studies and electroencephalograms were 28.6% (two patients) and 100%, respectively. All patients showed prolonged central conduction times in short latency somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs) by tibial nerve stimulation but normal SSEPs by median nerve stimulation. Brain stem auditory evoked potentials and visual evoked potentials were abnormal in three (42.9%) and four patients (57.1%), respectively. These electrophysiological parameters were correlated with the ratio of serum cholestanol to cholesterol concentration. The results of SSEPs suggest that the polyneuropathy in CTX is caused by distal axonopathy affecting longer axons before shorter axons (central-peripheral distal axonopathy).
Full text
PDF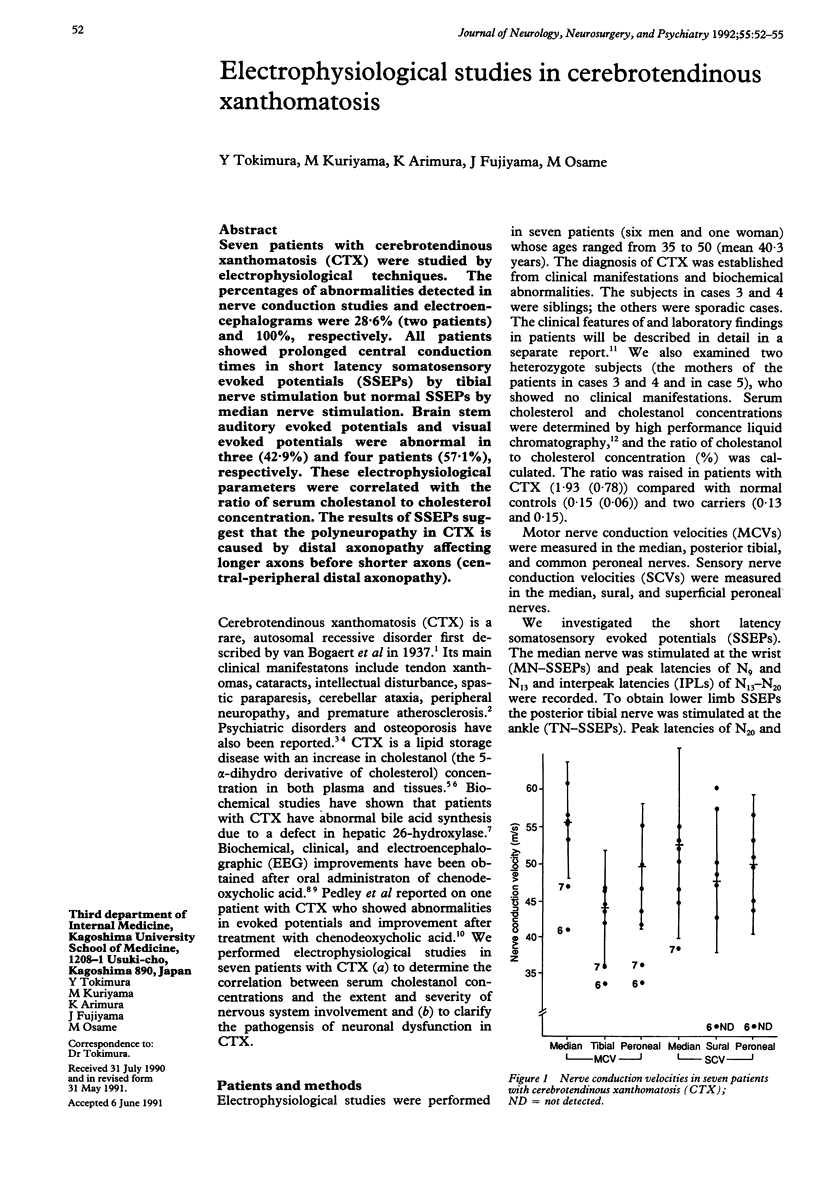

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argov Z., Soffer D., Eisenberg S., Zimmerman Y. Chronic demyelinating peripheral neuropathy in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jul;20(1):89–91. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berginer V. M., Foster N. L., Sadowsky M., Townsend J. A., 3rd, Siegel G. J., Salen G. Psychiatric disorders in patients with cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Am J Psychiatry. 1988 Mar;145(3):354–357. doi: 10.1176/ajp.145.3.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berginer V. M., Radwan H., Korczyn A. D., Kott E., Salen G., Shefer S. EEG in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX). Clin Electroencephalogr. 1982 Apr;13(2):89–96. doi: 10.1177/155005948201300204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berginer V. M., Salen G., Shefer S. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Neurol Clin. 1989 Feb;7(1):55–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berginer V. M., Salen G., Shefer S. Long-term treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis with chenodeoxycholic acid. N Engl J Med. 1984 Dec 27;311(26):1649–1652. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198412273112601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaghy M., King R. H., McKeran R. O., Schwartz M. S., Thomas P. K. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: clinical, electrophysiological and nerve biopsy findings, and response to treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid. J Neurol. 1990 Jun;237(3):216–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00314598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasama T., Byun D. S., Seyama Y. Quantitative analysis of sterols in serum by high-performance liquid chromatography. Application to the biochemical diagnosis of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jul 29;400:241–246. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)81617-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. A., Scheinberg L., Horoupian D. S., Salen G. Peripheral neuropathy in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Arch Neurol. 1985 Oct;42(10):1008–1010. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060090090022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuritzky A., Berginer V. M., Korczyn A. D. Peripheral neuropathy in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Neurology. 1979 Jun;29(6):880–881. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.6.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes J. H., Schimschock J. R., Swanson P. D. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. The storage of cholestanol within the nervous system. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jul;19(1):47–53. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00480010065004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oftebro H., Björkhem I., Skrede S., Schreiner A., Pederson J. I. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: a defect in mitochondrial 26-hydroxylation required for normal biosynthesis of cholic acid. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1418–1430. doi: 10.1172/JCI109806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi A., Yamashita Y., Goto I., Kuroiwa Y., Murakami S., Ikeda M. De- and remyelination and onion bulb in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Acta Neuropathol. 1979 Jan 12;45(1):43–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00691803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley T. A., Emerson R. G., Warner C. L., Rowland L. P., Salen G. Treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis with chenodeoxycholic acid. Ann Neurol. 1985 Oct;18(4):517–518. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pop P. H., Joosten E., van Spreeken A., Gabreëls-Festen A., Jaspar H., ter Laak H., Vos A. Neuroaxonal pathology of central and peripheral nervous systems in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX). Acta Neuropathol. 1984;64(3):259–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00688117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salen G. Cholestanol deposition in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. A possible mechanism. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Dec;75(6):843–851. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-6-843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugawa Y., Kohara N., Shimpo T., Mannen T. Central motor and sensory conduction in adrenoleukomyeloneuropathy, cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, HTLV-1-associated myelopathy and tabes dorsalis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Aug;51(8):1069–1074. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.8.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voiculescu V., Alexianu M., Popescu-Tismana G., Pastia M., Petrovici A., Dan A. Polyneuropathy with lipid deposits in Schwann cells and axonal degeneration in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Dec;82(1-3):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



