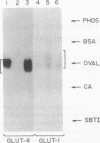
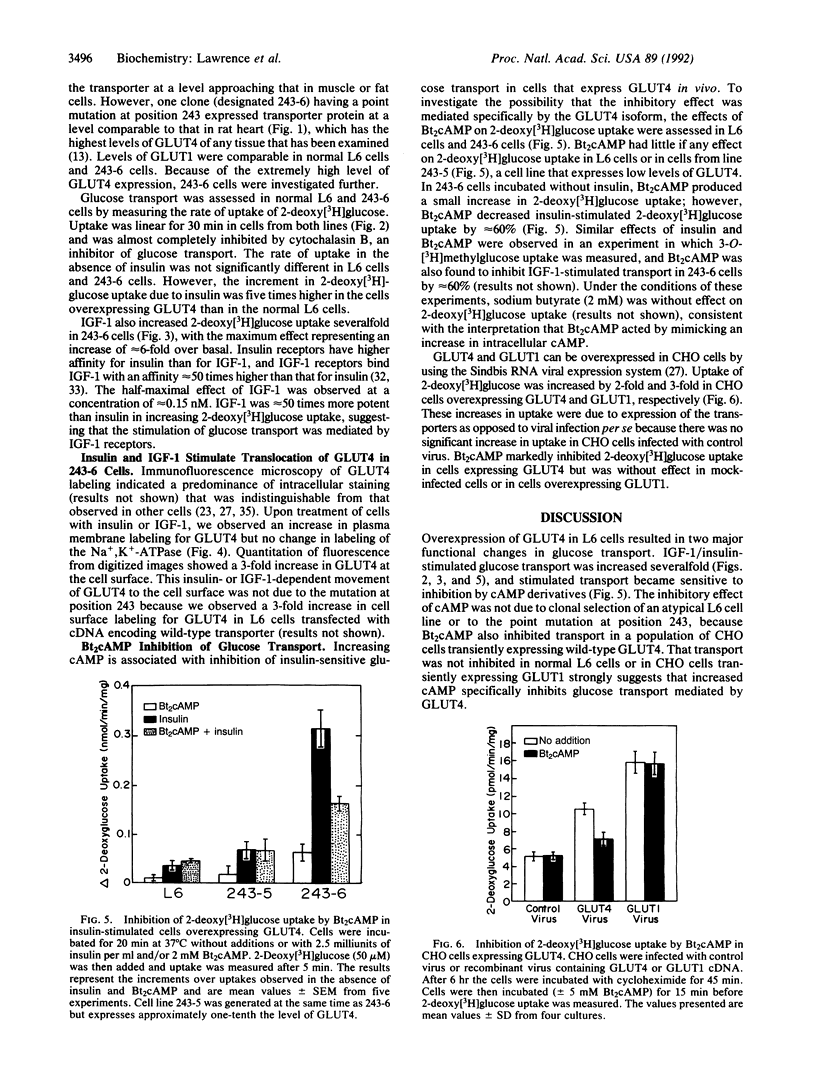
Abstract
The glucose transporter isoform GLUT4 is found only in cells that exhibit insulin-sensitive glucose transport. To investigate the function of this transporter, L6 myoblasts were stably transfected with GLUT4 cDNA. GLUT4 underwent insulin-dependent movement to the cell surface in myoblasts overexpressing the transporter. One cell line (243-6) expressed sufficient levels of the GLUT4 protein to study insulin-dependent glucose transport. Unlike wild-type L6 cells, 243-6 myoblasts exhibited two features that are characteristic of differentiated muscle fibers and adipocytes in vivo: a large insulin-stimulated component of glucose transport and inhibition of this stimulated component by cAMP. Relative to normal L6 cells, 243-6 cells responded to insulin or insulin-like growth factor 1 with a 5-fold larger increase in 2-deoxy[3H]glucose uptake. N6,O2'-Dibutyryladenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (Bt2cAMP) did not inhibit transport in normal L6 myoblasts, which express only GLUT1, but inhibited IGF-1/insulin-stimulated transport by 50% in 243-6 cells. The effect of cAMP was investigated further by using Chinese hamster ovary cells transiently expressing GLUT1 and GLUT4. Bt2cAMP inhibited glucose transport only in Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing GLUT4. These results indicate that cAMP-mediated inhibition of glucose transport is dependent on expression of the GLUT4 isozyme.
Full text
PDF
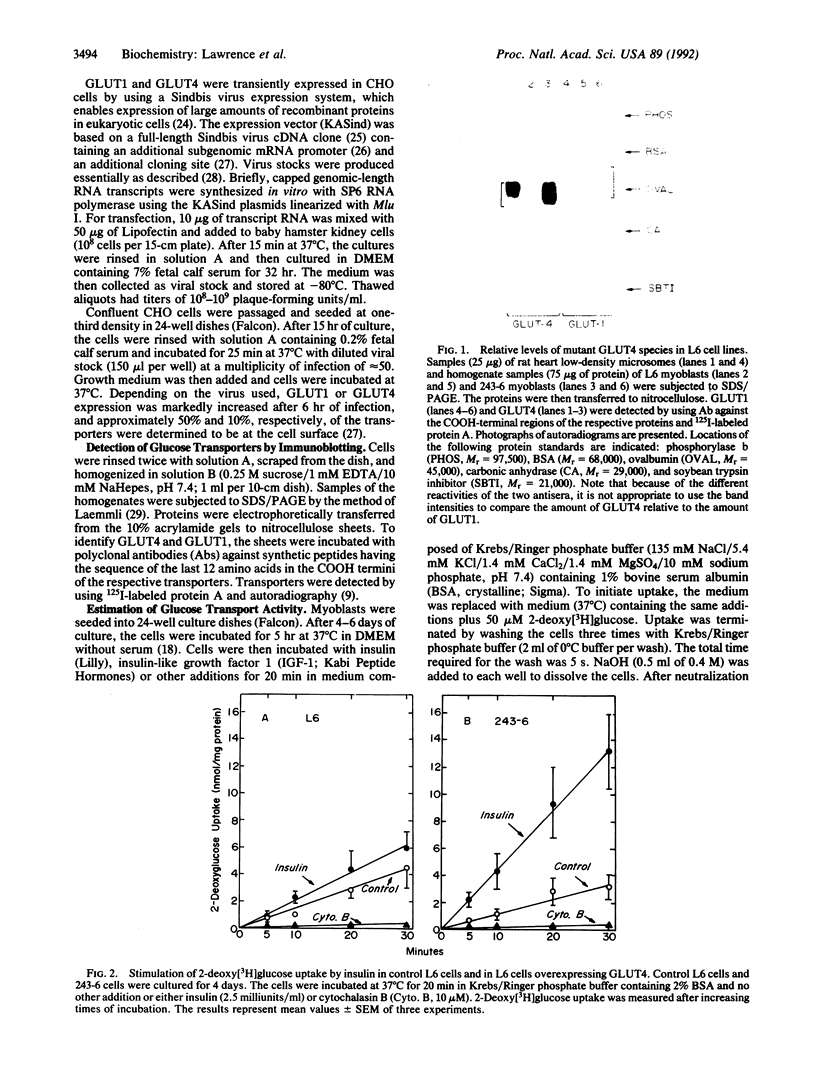
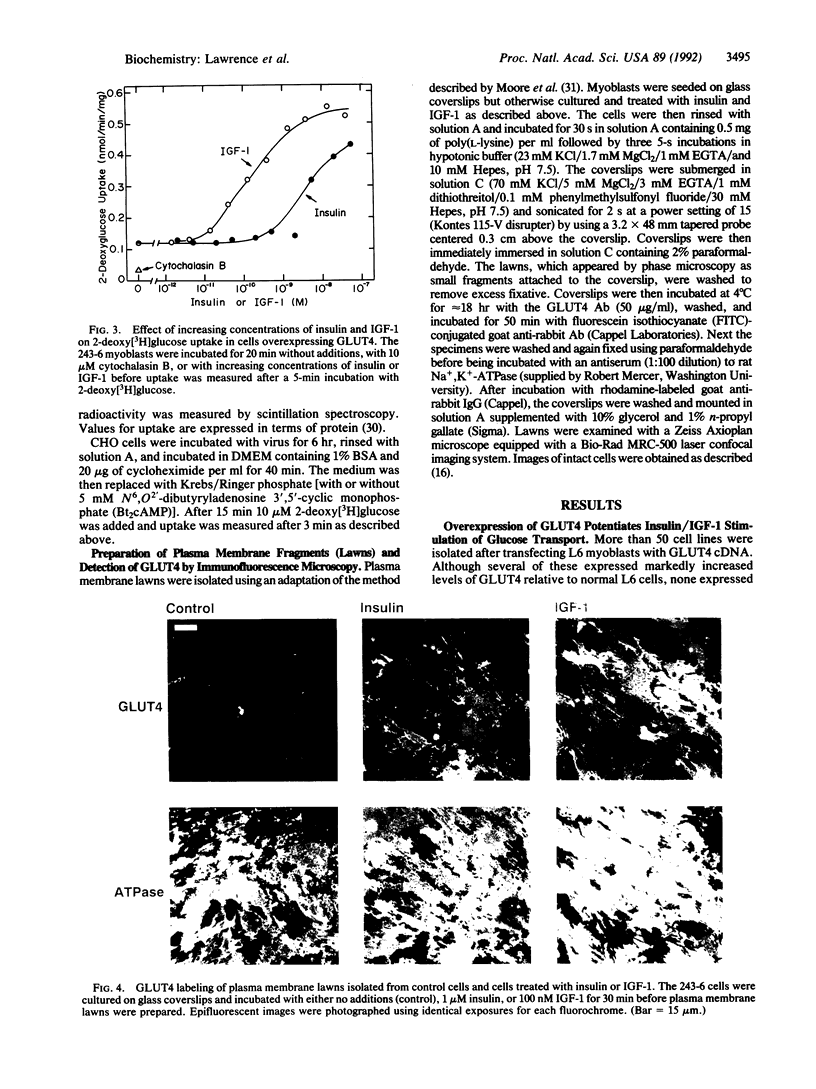

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beguinot F., Kahn C. R., Moses A. C., Smith R. J. Distinct biologically active receptors for insulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and insulin-like growth factor II in cultured skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15892–15898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Burant C. F., Takeda J., Lin D., Fukumoto H., Seino S. Molecular biology of mammalian glucose transporters. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):198–208. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok J., Gibbs E. M., Lienhard G. E., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters from post-Golgi compartments to the plasma membrane of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):69–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderhead D. M., Kitagawa K., Tanner L. I., Holman G. D., Lienhard G. E. Insulin regulation of the two glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13801–13808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Structural and functional homologies in the receptors for insulin and the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbrink J., Bihler I. Membrane transport: its relation to cellular metabolic rates. Science. 1975 Jun 20;188(4194):1177–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.1096301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs E. M., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E. The glucose transporter in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is phosphorylated in response to phorbol ester but not in response to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16597–16603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grakoui A., Levis R., Raju R., Huang H. V., Rice C. M. A cis-acting mutation in the Sindbis virus junction region which affects subgenomic RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5216–5227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5216-5227.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney P. M., Slot J. W., Piper R. C., James D. E., Mueckler M. Intracellular targeting of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter (GLUT4) is isoform specific and independent of cell type. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):689–699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Hiken J., Lawrence J. C., Jr Isoproterenol stimulates phosphorylation of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter in rat adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8368–8372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Weber T. M., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Activity and phosphorylation state of glucose transporters in plasma membranes from insulin-, isoproterenol-, and phorbol ester-treated rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11261–11267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Li G., Logan W. J. Induction of sugar uptake response to insulin by serum depletion in fusing L6 myoblasts. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 1):E291–E296. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.3.E291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivisto U. M., Martinez-Valdez H., Bilan P. J., Burdett E., Ramlal T., Klip A. Differential regulation of the GLUT-1 and GLUT-4 glucose transport systems by glucose and insulin in L6 muscle cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2615–2621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda M., Honnor R. C., Cushman S. W., Londos C., Simpson I. A. Regulation of insulin-stimulated glucose transport in the isolated rat adipocyte. cAMP-independent effects of lipolytic and antilipolytic agents. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):245–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. C., Catterall W. A. Tetrodotoxin-insensitive sodium channels. Ion flux studies of neurotoxin action in a clonal rat muscle cell line. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6213–6222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Schlesinger S., Huang H. V. Promoter for Sindbis virus RNA-dependent subgenomic RNA transcription. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1726–1733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1726-1733.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Mahaffey D. T., Brodsky F. M., Anderson R. G. Assembly of clathrin-coated pits onto purified plasma membranes. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):558–563. doi: 10.1126/science.2883727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Hess L. J., James D. E. Differential sorting of two glucose transporters expressed in insulin-sensitive cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):C570–C580. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.3.C570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Levis R., Strauss J. H., Huang H. V. Production of infectious RNA transcripts from Sindbis virus cDNA clones: mapping of lethal mutations, rescue of a temperature-sensitive marker, and in vitro mutagenesis to generate defined mutants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3809–3819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3809-3819.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan M. F., Edwards B. M., Ruoho A. E. Interactions of insulin, catecholamines and adenosine in the regulation of glucose transport in isolated rat cardiac myocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 16;887(1):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M. Structure and function of hexose transporters. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:757–794. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., James D. E., Lienhard G. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac myocytes of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., Lienhard G. E., James D. E. Immuno-localization of the insulin regulatable glucose transporter in brown adipose tissue of the rat. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):123–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. S., Ramlal T., Sarabia V., Koivisto U. M., Bilan P. J., Pessin J. E., Klip A. Glucose transport activity in L6 muscle cells is regulated by the coordinate control of subcellular glucose transporter distribution, biosynthesis, and mRNA transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1516–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong C., Levis R., Shen P., Schlesinger S., Rice C. M., Huang H. V. Sindbis virus: an efficient, broad host range vector for gene expression in animal cells. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1188–1191. doi: 10.1126/science.2922607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A., Wallberg-Henriksson H., Cranshaw J., Chen M., Holloszy J. O. Effect of catecholamines on glucose uptake and glycogenolysis in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):C406–C409. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Froesch E. R., Humbel R. E. The insulin-like growth factors (IGF) of human serum: chemical and biological characterization and aspects of their possible physiological role. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;19:257–309. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152819-5.50024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]