The authors would like to correct Figs 6 and 8, as errors were introduced in the preparation of these figures for publication. In Figs 4A and 6A, the same image was used to represent the MS control in both figures. The authors have provided a corrected Fig 6 here with a new MS image from another biological replicate. In Fig 8A, the same image was inadvertently used to represent both the WT Control and OE2 Control conditions. The authors have provided a corrected Fig 8 here with the correct OE2 Control image. The authors confirm that these changes do not alter their findings and have provided the underlying images for Fig 8 as Supporting Information.
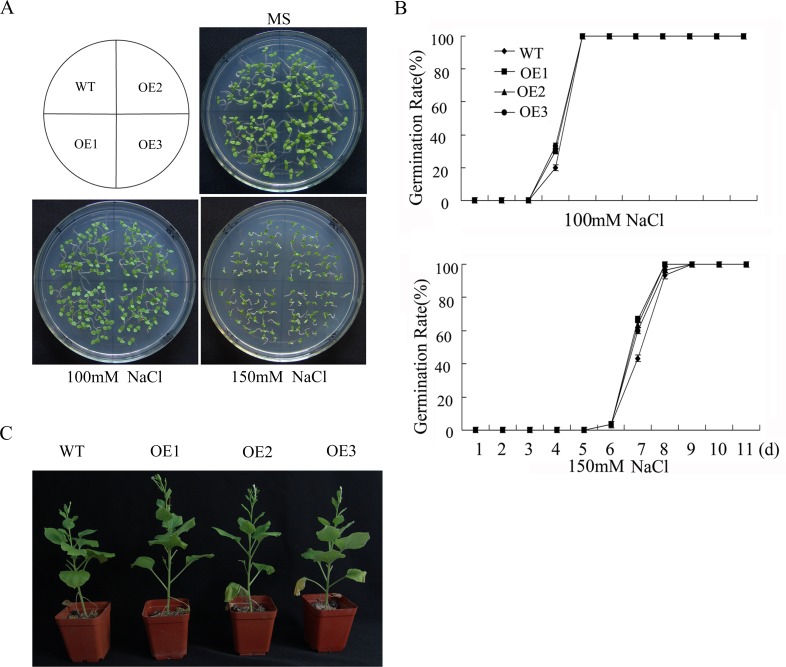
Fig 6. Salt tolerance of WT and GhWRKY41-overexpressing N. benthamiana plants.
(A, B) Seed germination assay. (C) Photograph of representative 8-week-old WT and OE plants watered with 200 mM NaCl for 1 month.
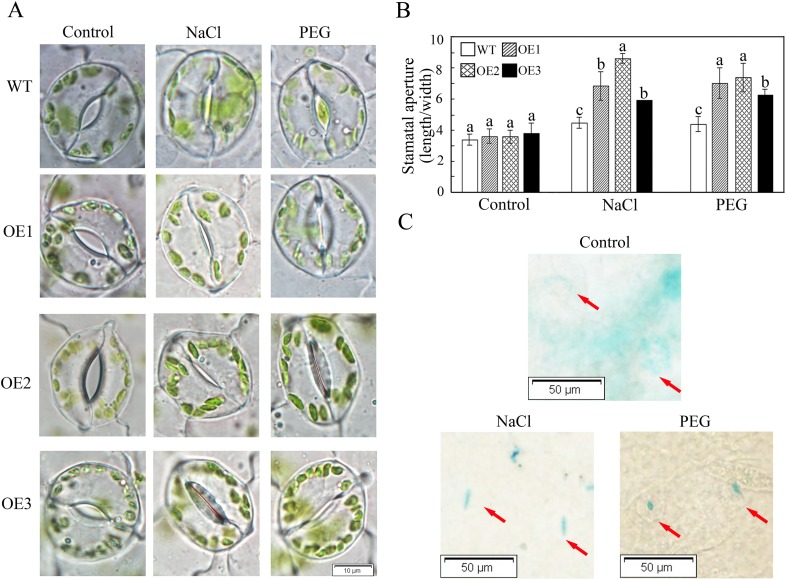
Fig 8. GhWRKY41 regulates stomatal movement.
(A) Comparison of stomatal aperture in response to salt and drought. (B) Stomatal aperture data were calculated from 50 stomata from the leaves of three different plants. Values are the mean ± SD. (C) GUS staining of leaves from transgenic Arabidopsis exposed to salt and drought treatments.
Supporting Information
(ZIP)
Reference
- 1.Chu X, Wang C, Chen X, Lu W, Li H, Wang X, et al. (2015) The Cotton WRKY Gene GhWRKY41 Positively Regulates Salt and Drought Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana. PLoS ONE 10(11): e0143022 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(ZIP)