Cystic carcinoid tumors of the pancreas represent a subgroup of malignant potential and difficult diagnosis.(1,2)
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) is an effective tool to evaluate these lesions.(1–4)
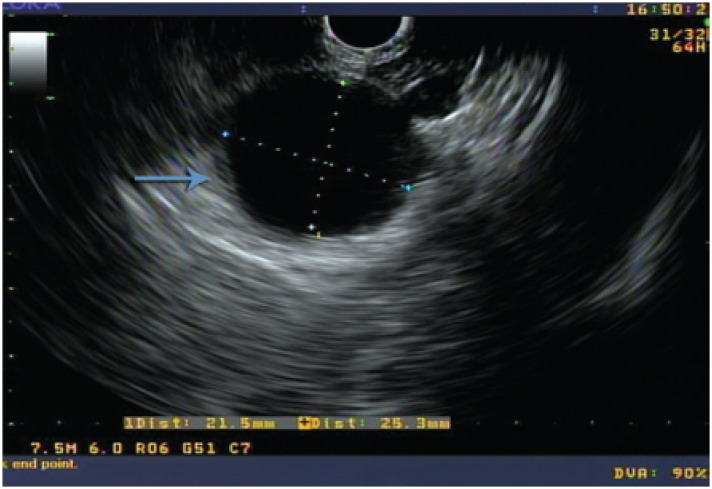
A 52-year old man was referred to the Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein to investigate a pancreatic cyst. Endoscopic ultrasound revealed a cystic lesion, measuring 2cm in the pancreatic tail, without septations and communication with the pancreatic duct (Figures 1 and 2). The FNA fluid showed normal amylase (67U/L) and low CEA (11,2ng/mL) levels.
Figure 1. Neuroendocrine cyst.
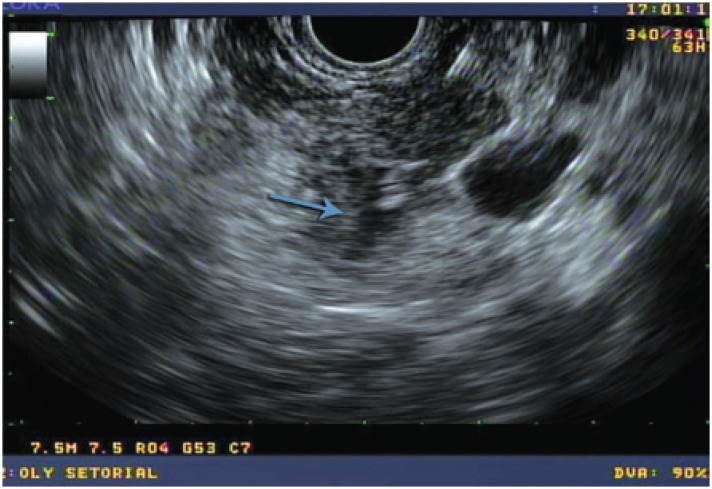
Figure 2. After fine needle aspiration.
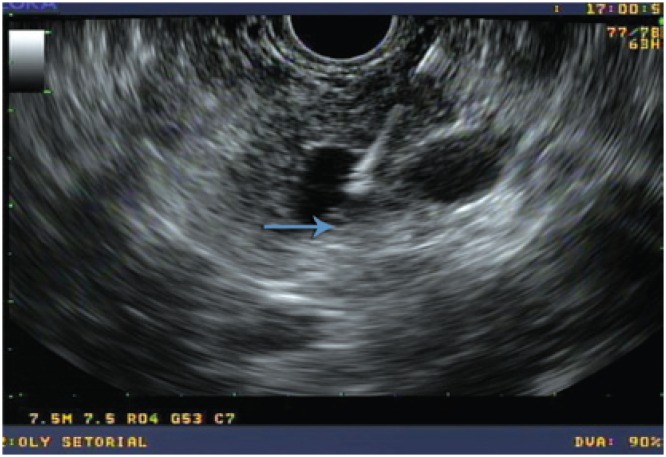
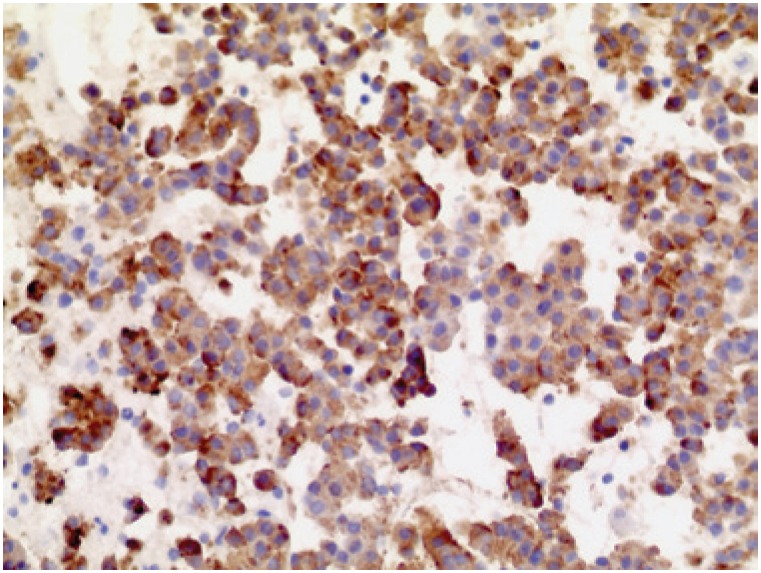
Histological examination of fragments of the cystic wall obtained by FNA (Figure 3) revealed a carcinoid tumor, confirmed by chromogranin and synaptofisin immunohistochemistry analyses (Figure 4).
Figure 3. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of the cyst wall.
Figure 4. Cell-block of the pancreas shows numerous epithelial cells with rounded nucleus, “salt and pepper” chromatin and eosinophilic cytoplasm (Hematoxylin and eosin stain, 10x). Immunohistochemistry positive for neuroendocrine tumor.
DISCUSSION
The preoperative diagnosis of cystic pancreatic carcinoid tumor is important due to their malignant potential and possibility of ressection.(5)
Computed tomography (CT) and EUS may not help making diagnosis, since the radiological aspect is often interpreted as a pancreatic mucinous cystadenoma, such as in this report.
EUS-FNA is a highly accurate method to diagnose pancreatic carcinoid tumors.(2–4) The few studies available show a high agreement between cytology and pathology.(2–4)
In this report a rare lesion is described, and the diagnosis was possible only after the histological study of the cystic wall fragments obtained by EUS-FNA.
This case report shows the efficacy of EUS-FNA in an unusual diagnosis.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ballarin R, Masetti M, Losi L, Di Benedetto F, Di Sandro S, De Ruvo N, et al. Cystic pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms with uncertain malignant potential: report of two cases. Surg Today. 2009;39(2):162–167. doi: 10.1007/s00595-008-3806-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Charfi S, Marcy M, Bories E, Pesanti C, Caillol F, Giovannini M, et al. Cystic pancreatic endocrine tumors: an endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy study with histologic correlation. Cancer Cytopathol. 2009;117(3):203–210. doi: 10.1002/cncy.20024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Raddaoui E. Clinical utility and diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of pancreatic lesions: Saudi Arabian experience. Acta Cytol. 2011;55(1):26–29. doi: 10.1159/000320908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Figueiredo FA, Giovannini M, Monges G, Charfi S, Bories E, Pesenti C, et al. Pancreatic endocrine tumors: a large single-center experience. Pancreas. 2009;38(8):936–940. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181b365db. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Patel KK, Kim MK. Neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas: endoscopic diagnosis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2008;24(5):638–642. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e32830bf7fb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]