Abstract
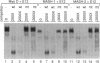
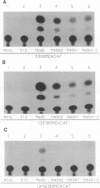
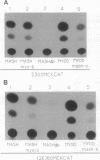
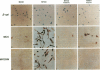
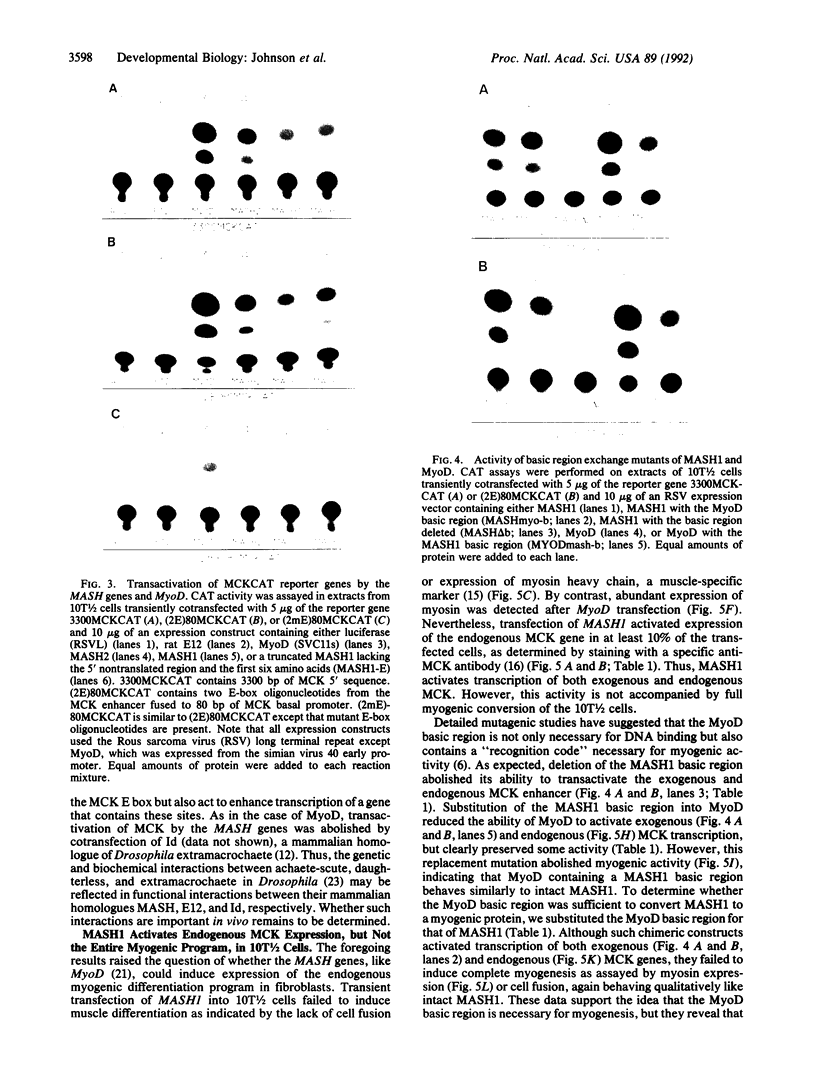
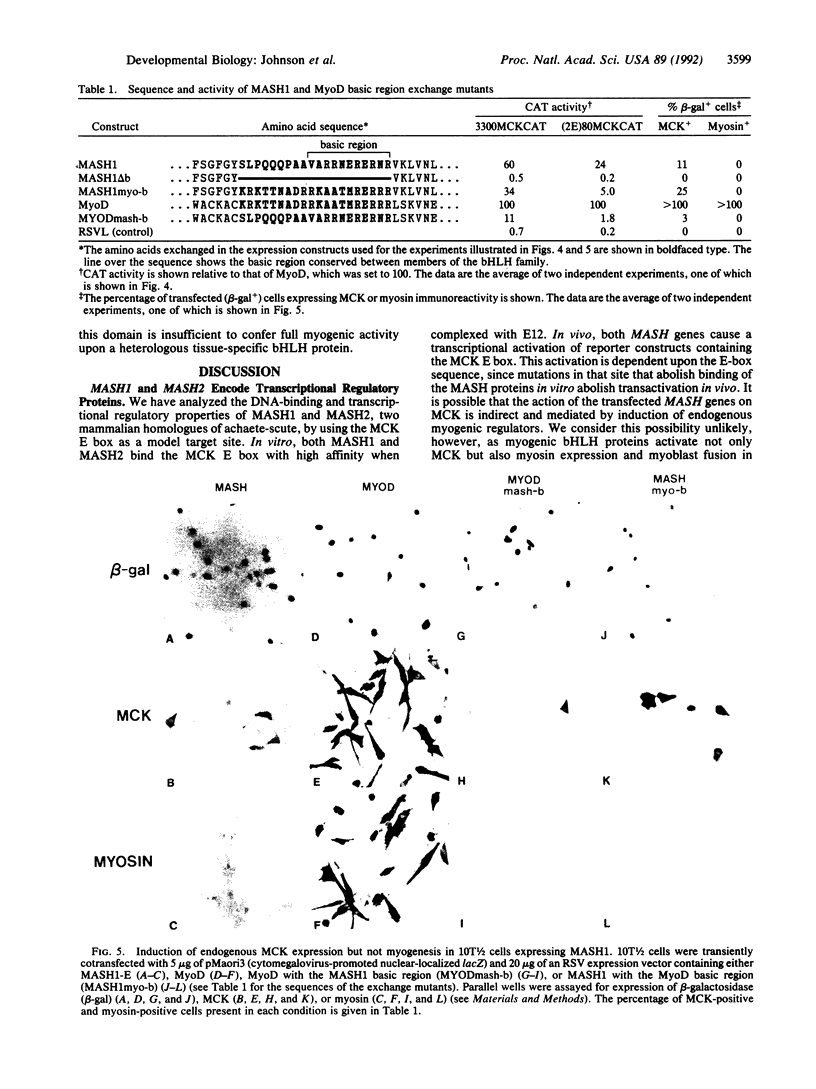
The MASH genes are vertebrate homologues of achaete-scute, genes required for neuronal determination in Drosophila. The sequence of MASH1 and MASH2 contains a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) motif that is present in other transcriptional regulators such as MyoD and E12. In the absence of an authentic target for the MASH proteins, we examined their DNA binding and transcriptional regulatory activity by using a binding site (the E box) from the muscle creatine kinase (MCK) gene, a target of MyoD. Like myogenic bHLH proteins, the MASH proteins form heterooligomers with E12 that bind the MCK E box with high affinity in vitro. Unexpectedly, however, MASH1 and MASH2 also activate transcription of both exogenous and endogenous MCK in transfected C3H/10T1/2 fibroblasts. However, they do not induce myogenesis. Myogenic activity is not exclusively a property of the MyoD basic region, as substitution of this domain fails to confer myogenic activity on MASH1. These data suggest that different bHLH proteins may activate overlapping but distinct sets of target genes in the same cell type.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader D., Masaki T., Fischman D. A. Immunochemical analysis of myosin heavy chain during avian myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):763–770. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Weintraub H. Differences and similarities in DNA-binding preferences of MyoD and E2A protein complexes revealed by binding site selection. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1104–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2174572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Winter B., Bober E., Arnold H. H. Transcriptional activation domain of the muscle-specific gene-regulatory protein myf5. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):663–665. doi: 10.1038/346663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Olson E. N. Myogenin resides in the nucleus and acquires high affinity for a conserved enhancer element on heterodimerization. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):582–595. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Brennan T. J., Li L., Edmondson D., Olson E. N. Inefficient homooligomerization contributes to the dependence of myogenin on E2A products for efficient DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3633–3641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Jaynes J. B., Hauschka S. D. Regulation of creatine kinase induction in differentiating mouse myoblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):484–492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., Johnson J. E., Buskin J. N., Gartside C. L., Hauschka S. D. The muscle creatine kinase gene is regulated by multiple upstream elements, including a muscle-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Birren S. J., Anderson D. J. Two rat homologues of Drosophila achaete-scute specifically expressed in neuronal precursors. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):858–861. doi: 10.1038/346858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Zimmerman K., Saito T., Anderson D. J. Induction and repression of mammalian achaete-scute homologue (MASH) gene expression during neuronal differentiation of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Development. 1992 Jan;114(1):75–87. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Kadesch T., Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D., Weintraub H. Functional activity of myogenic HLH proteins requires hetero-oligomerization with E12/E47-like proteins in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90620-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo L. C., Johnson J. E., Wuenschell C. W., Saito T., Anderson D. J. Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is transiently expressed by spatially restricted subsets of early neuroepithelial and neural crest cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1524–1537. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. M-CAT binding factor, a novel trans-acting factor governing muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4271–4283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. J. c-myc inhibition of MyoD and myogenin-initiated myogenic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2842–2851. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. Herculin, a fourth member of the MyoD family of myogenic regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Turner D., Cepko C. Lineage analysis in the vertebrate nervous system by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren M., Ellis H. M., Posakony J. W. The Drosophila extramacrochaetae protein antagonizes sequence-specific DNA binding by daughterless/achaete-scute protein complexes. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):245–255. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Dwarki V. J., Verma I., Davis R., Hollenberg S., Snider L., Lassar A., Tapscott S. J. Muscle-specific transcriptional activation by MyoD. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1377–1386. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]