Abstract
Fentanyl is the most commonly used opioid analgesic in intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (IV PCA) in Korea. IV oxycodone was approved for postoperative IV PCA by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of Korea in 2013. The approved dosage regimen for postoperative pain relief with IV oxycodone is IV bolus loading of 2 mg followed by PCA composed of demand boluses of 1 mg and no background infusion with an oxycodone concentration of 1 mg/ml. However, a simulation study indicated that the minimum effective analgesic concentration (MEAC, as indicated by relief of pain by administering rescue analgesics) of oxycodone was reached most quickly with a higher loading dose of 0.1 mg/kg and IV PCA with background infusion. Oxycodone is a therapeutic option as an analgesic for postoperative pain management. It is necessary to reduce the analgesic dose of oxycodone in elderly patients because metabolic clearance decreases with age.
Keywords: Patient-controlled analgesia, Postoperative pain
Introduction
Oxycodone is a µ-opioid receptor agonist and is generally indicated for the relief of moderate to severe pain [1,2]. In recent years, the use of intravenous (IV) oxycodone has increased markedly [2]. As a result, it has replaced morphine as the first choice opioid in several countries [2]. In Korea, IV oxycodone was approved for postoperative IV patient-controlled analgesia (IV PCA) by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) in 2013. The approved dosage regimen for postoperative pain relief with IV oxycodone is IV bolus loading of 2 mg followed by PCA composed of demand boluses of 1 mg and no background infusion with an oxycodone concentration of 1 mg/ml. In Korea, the most common opioid analgesic used in IV PCA is fentanyl, and clinical experience of IV PCA with oxycodone is extremely limited. Although developed in an attempt to improve on the existing opioids, oxycodone has similar adverse effects to those typically found with opioids. An earlier study showed that intermittent administration of IV oxycodone up to 15 mg provided better analgesia than fentanyl at a dose of 200 µg, but caused more side effects [3]. Moreover, previous studies of postoperative pain management with IV oxycodone were limited in sample size, mostly to less than 100 patients, which may not be large enough to assess the safety of IV oxycodone [3,4]. This review discusses the pharmacokinetic characteristics of oxycodone and appropriate regimens of patient-controlled oxycodone. In addition, the analgesic effects of patient-controlled oxycodone for postoperative pain management are compared with those of patient-controlled fentanyl.
Clinical Pharmacology of Oxycodone
Oxycodone is a semisynthetic opioid synthesized from poppy-derived thebaine [1]. This agent was developed in 1916 in Germany as one of several new semisynthetic opioids in an attempt to improve on the existing opioids [1]. It is a narcotic analgesic generally indicated for relief of moderate to severe pain.
Mechanism of Action
Oxycodone is a semisynthetic, µ-opioid receptor agonist with analgesic effects in several pain conditions [1]. Ross and Smith [5] proposed that oxycodone acts on κ-opioid receptors. They also suggested that oxycodone may be a κ2b-opioid agonist [6]. Nozaki et al. [7] suggested that the effect of oxycodone is mediated by different receptors in different situations. Specifically, in diabetic mice, the κ-opioid receptor appears to be involved in the antinociceptive effects of oxycodone, while in nondiabetic mice, the µ1-opioid receptor seems to be primarily responsible for its effects [8].
Potency
Oxycodone and morphine are presumed to have a 1 : 1 ratio of analgesic potency in postoperative pain after surgery, with mixed somatic and visceral pain components [9,10]. In Korea, fentanyl is the most commonly used opioid for PCA-based postoperative pain management. However, no safe recommendations concerning the direct conversion factor of IV oxycodone and fentanyl dosage have yet been reported. In a previous study, the median consumption levels of oxycodone and fentanyl were 15 mg and 200 µg, respectively, and the intensity of abdominal pain was significantly lower in the oxycodone group, indicating that the potency ratio of oxycodone to fentanyl was less than 75 : 1 [2,3]. In a recent pilot study, the potency ratio was 60 : 1 in patients undergoing laparoscopic gynecological surgery [11].
Minimum Effective Concentration (MEC) and Minimum Effective Analgesic Concentration (MEAC)
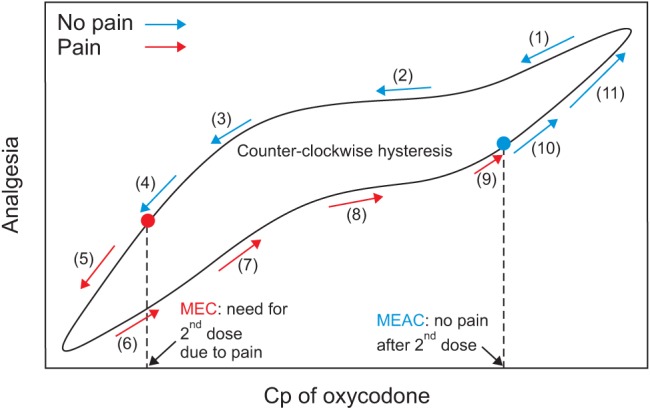
The analgesic effects of opioids are related to their plasma concentration. Either mean effective concentration (MEC) or minimum effective analgesic concentration (MEAC) is used to assess concentration–effect relationships. MEC is the concentration at the time re-medication is required. MEAC can be determined by constant-rate infusions of the opioid until steady-state concentrations are reached, at which time the drug concentration will have equilibrated between plasma and effect-site compartments containing its receptors, and the drug concentration eliciting analgesia can be determined (Fig. 1). The MEC and MEAC of IV oxycodone were reported as 20–35 ng/ml and 45–50 ng/ml in patients with laparoscopic cholecystectomy, respectively [12]. In cardiac surgical patients, MEC and MEAC of oxycodone are 6–12 ng/ml and 15–25 ng/ml, respectively [12,13]. These observations suggest that the MEC and MEAC of oxycodone may differ between different types of surgery. Moreover, oxycodone has not been evaluated for MEC and MEAC in major intraabdominal surgery. The MEC and MEAC of fentanyl in such surgery are 0.63 ng/ml and 0.6–1.0 ng/ml, respectively [14,15].
Fig. 1. Minimum effective concentration (MEC) and minimum effective analgesic concentration (MEAC) of intravenous (IV) oxycodone. Cp: plasma concentration.
Metabolism by the Cytochrome P450 Enzyme System
Oxycodone is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system in the liver with the major metabolic pathway, CYP3A4, and the minor metabolic pathway, CYP2D6 [16,17]. Oxycodone metabolism through the CYP3A pathway should represent well over half of the metabolism of this drug in most patients. The importance of the CYP3A pathway for oxycodone metabolism was demonstrated by the estimated 2- to 14-fold higher in vitro intrinsic clearance for N-dealkylation as compared to O-demethylation through CYP2D6 [18]. Urinary metabolites derived from CYP3A-mediated N-demethylation of oxycodone (noroxycodone, noroxymorphone, and α- and α-noroxycodol) accounted for 45% ± 21% of the dose, whereas CYP2D6-mediated O-demethylation (oxymorphone and α- and β-oxymorphol) and 6-keto-reduction (α- and β-oxycodol) accounted for 11% ± 6% and 8% ± 6% of the dose, respectively. Noroxycodone and noroxymorphone were the major metabolites in the circulation with elimination half-lives longer than that of oxycodone, but their uptake into rat brain was significantly lower compared with the parent drug [19]. Oxymorphone is a more potent opioid agonist with stronger and higher binding affinity to µ-opioid receptors than oxycodone [20]. However, the central opioid effects of oxycodone are governed by the parent drug, with a negligible contribution from its circulating oxidative and reductive metabolites [19]. CYP3A4-mediated N-demethylation makes oxycodone vulnerable to drug interaction, e.g., decreased or increased systemic exposure of oxycodone by rifampin, a CYP3A inducer, or itraconazole, a CYP3A4 inhibitor [21,22]. CYP2D6 has been reported to be unimportant for the clinical effect of oxycodone, despite great interindividual variation of the metabolism of CYP2D6 substrates due to differences in allele functionality [18,23]. Poor metabolizers (PM) have two nonfunctional alleles, while extensive metabolizers (EM) are homozygous with two functional alleles or heterozygous with one functional allele, and ultrarapid metabolizers (UM) have more than two functional alleles. There are pronounced interethnic differences in the allele distribution. Previous studies indicated that oxycodone concentrations are similar in CYP2D6 PM and reduced in CYP2D6 UM in comparison with CYP2D6 EM [18]. There are no clinically relevant drug interactions between IV oxycodone and inhibitors of CYP2D6, such as paroxetine [16]. However, Stamer et al. [24] demonstrated that the oxymorphone/oxycodone ratio was lowest, and oxycodone consumption up to the 12th hour was highest, in CYP2D6 PM in the setting of postoperative IV patient-controlled analgesia. The PM phenotype is attributed mainly to the CYP2D6*3, *4, *5, and *6 alleles, which predict 93%–98% of PMs in whites [25,26]. In contrast, certain nonfunctional allelic variants (CYP2D6*3, *4, and *6) have not been observed in Asians, including Koreans [27,28,29,30]. The CYP2D6*10 allele, the most common allele in Asians, including Koreans, at frequencies of up to 60% (45.58% in Koreans), is a reduced function allele and contributes to intermediate metabolism in a large number of Asian subjects [29,31]. Phenotypic studies have revealed that approximately 5%–10% of whites are PM [32,33,34], while the proportion is less than 1% in Asian populations [25,30,35]. Therefore, CYP2D6 genotyping to characterize the pharmacokinetics of oxycodone in Koreans is not likely to produce clinically significant results. If both oxidative metabolic pathways via CYP3A4 and 2D6 are inhibited, exposure to IV oxycodone increases substantially [16]. A similar effect is to be expected with use of a CYP3A inhibitor in CYP2D6 PM [18].
Age and Clearance of Oxycodone
Previous studies indicated the age dependency of oxycodone pharmacokinetics [36,37]. The pharmacokinetics of 5 mg of IV oxycodone in four groups of 10–11 patients, aged 20–40, 60–70, and 70–90 years, were evaluated by non-compartmental analysis [36]. In the oldest group, the mean AUCinf (area under the concentration- time curve from time zero to infinity) of oxycodone was 80% greater and the metabolic clearance was 34% lower than in the youngest group (both P < 0.05) [36]. In addition, age was a significant covariate on metabolic clearance of a pharmacokinetic model of oxycodone, and simulations of repetitive bolus administration showed a 20% increase in oxycodone concentration in the elderly [37]. Therefore, it is important to titrate the analgesic dose of oxycodone individually, particularly in the elderly.
Adverse Drug Reactions
Oxycodone shows the same adverse effects as those typically found for opioids, with constipation (25%–30%), nausea (25%–30%), and drowsiness (25%) being the three most common symptoms [38]. Vomiting, pruritus, and dizziness occur in 5%–15% of patients taking oxycodone. Other effects, such as loss of appetite, nervousness, abdominal pain, diarrhea, urine retention, dyspnea, hiccups, headaches, dry mouth, hallucinations, and bronchospasm present in less than 5% of patients.1) In high doses, overdoses, or in patients not tolerant to opiates, oxycodone can cause shallow breathing, bradycardia, cold clammy skin, apnea, hypotension, miosis, circulatory collapse, respiratory arrest, and death.1)
Pharmacokinetic Simulation of Intravenous PCA Regimen with Oxycodone
Saari et al. [37] characterized the population pharmacokinetics of oxycodone using pharmacokinetic data from patients and healthy volunteers (Table 1). The results showed that central volume and metabolic clearance of oxycodone are increased with increasing lean body mass. With increasing age, metabolic clearance is decreased, which is consistent with the non-compartmental pharmacokinetic analysis of Liukas et al. [36]. This simulation study was based on pharmacokinetic parameters and values of MEC, as indicated by the need to administer IV opioid due to pain, and MEAC, as indicated by relief of pain by administering opioid for oxycodone determined in previous studies [12,37,39]. Deterministic simulations that did not consider either interindividual or intraindividual random variability were performed using Asan Pump software (ver. 2.1.3; Bionet Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea, http://www.fit4nm.org/download, last accessed: Aug 27, 2012).
Table 1. Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Intravenous Oxycodone [37].
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| V1, L | 161 + 5.0 × (LBM − 54.58) |
| V2, L | 124 |
| Cl, L/h | 48.1 + 0.547 × (LBM − 54.58) − 0.1777 × (age − 44.81) |
| Q, L/h | 982 |
LBM: lean body mass (calculated by the James formula).
Bolus Loading
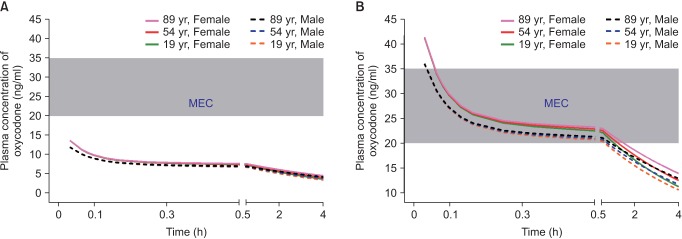
When administered at the end of surgery, oxycodone at a dose of 2 mg produced plasma concentrations over time less than the MEC (Fig. 2A). However, oxycodone at a dose of 0.1 mg/kg (6 mg in a 60-kg subject) produced concentrations higher than MEC for 1 hour after the end of surgery (Fig. 2B). As lean body mass (LBM) was shown to be a significant covariate for central volume of oxycodone in the pharmacokinetic model of Saari et al. [37] (Table 1), plasma concentrations of oxycodone for approximately 1 hour after the end of surgery were higher in female patients with lower LBM, calculated by the James formula. Therefore, the loading dose of oxycodone administered at the end of surgery should be 0.1 mg/kg, rather than 2 mg, to relieve immediate postoperative pain in the postanesthetic care unit.
Fig. 2. Predicted concentration of oxycodone in the plasma over time after IV administration of a bolus of 2 mg (A) or 0.1 mg/kg (B). The body weights and heights of all individuals were 60 kg and 165 cm, respectively. MEC: minimum effective concentration.
Background Infusion
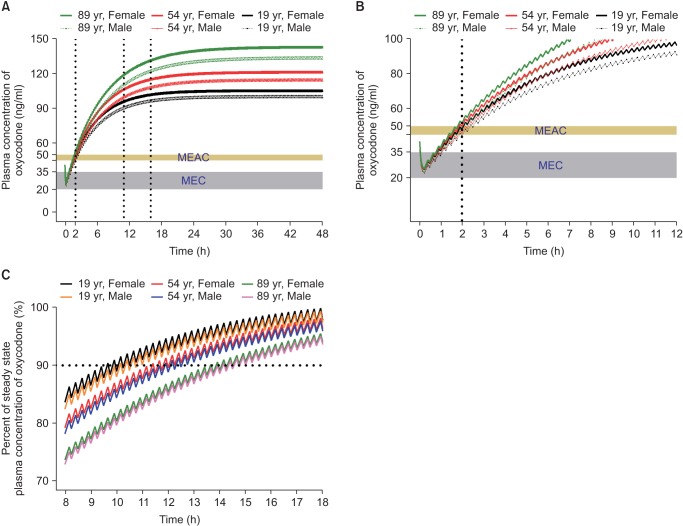
In another simulation, an IV oxycodone loading dose of 2 mg or 0.1 mg/kg was administered at the end of surgery and IV PCA with or without 1 mg/h background infusion was started 5 minutes later. Table 2 summarizes the time to reach MEAC, the time to reach 90% steady-state concentration, and the steady-state concentration of oxycodone. During the immediate postoperative period, MEAC was reached most quickly with a higher loading dose (0.1 mg/kg) and IV PCA with background infusion. Even with this regimen, rescue analgesic may be required to relieve pain for at least 2 hours after the end of surgery (Fig. 3). Time to 90% steady-state was shorter with a higher loading dose of oxycodone (0.1 mg/kg, 6 mg) compared to loading dose of 2 mg, while unaffected by background infusion of 1 mg/h. The steady-state concentration achieved was higher with the IV PCA regimen with background infusion, regardless of the loading dose. As LBM and age are significant covariates for metabolic clearance of oxycodone (Table 1), steady-state concentrations tended to be higher with increasing age and decreasing LBM. Steady-state concentrations for the dosage regimens in this simulation were approximately two to three times higher than the MEAC of oxycodone.
Table 2. Time to Minimum Effective Analgesic Concentration and 90% Steady-state, and Plasma Concentration at Steady-state in Intravenous (IV) Patient-controlled Analgesia with Oxycodone.
| Loading dose | 2 mg | 0.1 mg/kg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background infusion of 1 mg/h | − | + | − | + |
| Time to MEAC, h | 4 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 2 |
| Time to 90% SS, h | 11–16 | 11–16 | 9–14 | 9–14 |
| Cp at SS, ng/ml | 79–113 | 99–142 | 79–113 | 99–142 |
The data show the predicted oxycodone concentration in the plasma over time in hypothetical male and female subjects aged 19, 54, and 89 years after receiving an IV bolus of 2 mg or 0.1 mg/kg followed by demand boluses of 1 mg every 15 minutes with or without background infusion at 1 mg/h. The body weights and heights of all subjects were 60 kg and 165 cm, respectively. MEAC: minimum effective analgesic concentration, SS: steady-state, Cp at SS: plasma concentration at steady-state.
Fig. 3. Predicted concentration of oxycodone in the plasma over time after IV administration of a bolus of 0.1 mg/kg followed by demand boluses of 1 mg every 15 minutes and background infusion of 1 mg/h. (A) The entire time–concentration curve. (B) Time–concentration curve of time to reach MEAC. (C) Time–concentration curve of time to reach 90% steady-state concentration of oxycodone. Body weights and heights of all individuals were 60 kg and 165 cm, respectively. MEAC: minimum effective analgesic concentration, MEC: minimum effective concentration. Demand bolus, background infusion rate, and lock-out time of postoperative IV patient-controlled analgesia (IV PCA) were set at 1 ml, 1 ml/h, and 15 minutes, respectively. The concentration of oxycodone in IV PCA was 1 mg/ml. The pharmacokinetic model of Saari et al. was applied to this simulation [37]. Vertical dotted lines indicate time to reach MEAC (2 hours) and 90% steady-state concentration (9–14 hours). Time 0 indicates the end of surgery.
The dosage regimen for postoperative pain relief with IV oxycodone approved by MFDS is an IV bolus loading of 2 mg followed by patient-controlled analgesia with demand bolus of 1 mg and no background infusion. Earlier studies on IV PCA with oxycodone did not include background infusion [4,24,40]. However, the pharmacokinetic simulation demonstrated that MEAC of oxycodone was reached most quickly with higher loading dose (0.1 mg/kg) and IV PCA with background infusion, which may reduce the necessity of rescue analgesic during the immediate postoperative period.
Comparison of Analgesic Effects with Fentanyl
When comparing the analgesic effects of two patient-controlled opioids, it is important to determine the PCA dosage regimens of the two opioids because they affect the efficacy of analgesia. Previous studies have shown that the potency ratio of oxycodone to morphine is 1 : 1, whereas that of morphine to fentanyl is 100 : 1 [9,41]. Two studies comparing patient-controlled oxycodone and fentanyl in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy and hysterectomy showed that the cumulative oxycodone dose was lower than that of fentanyl [42,43]. Moreover, a study comparing patient-controlled oxycodone and fentanyl in patients undergoing laparoscopic hysterectomy or myomectomy showed that, with a potency ratio of oxycodone to fentanyl of 60 : 1, the two opioids had similar analgesic effects [11]. Thus, Koch et al. showed that in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy, intermittent administration of IV oxycodone up to 15 mg yielded better analgesia than fentanyl at 200 µg, indicating that the potency ratio of oxycodone to fentanyl was less than 75 : 1 [2,3]. Similarly, a pilot study by Park et al. [11] showed that oxycodone was more effective than fentanyl after laparoscopic gynecological surgery at a ratio of 100 : 1, and that the two analgesics were equipotent at 60 : 1. However, the sample sizes of these studies were relatively small, which may limit their reliability. Studies testing various potency ratios in a large cohort are needed to determine the appropriate potency ratio of oxycodone to fentanyl. Moreover, previous studies for postoperative pain management with IV oxycodone were limited in sample size, mostly to less than 100 patients, which may not be large enough to assess the safety of IV oxycodone [3,4]. Therefore, the effectiveness and tolerability of IV PCA with oxycodone should be evaluated in large-scale clinical trials in Korean surgical populations. In addition, the population pharmacokinetics of oxycodone should also be characterized in Korean surgical patients to further adjust the optimal dosage regimen.
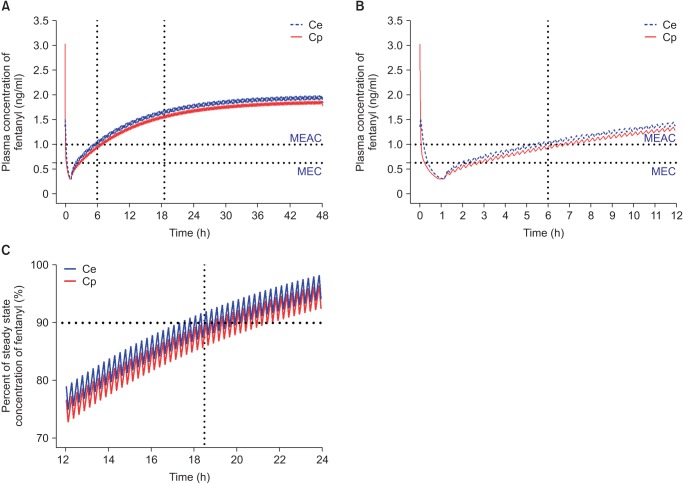
Based on population pharmacokinetic models of fentanyl reported by Scott et al. [44] (Table 3), plasma and effect-site concentrations of fentanyl were simulated using an Asan pump for comparison with oxycodone. The fentanyl PCA regimen for simulation consisted of 15 µg/ml fentanyl that was administered according to the standard clinical practice guidelines at the author's institution, i.e., IV bolus loading of 2 µg/kg followed by demand boluses of 15 µg with 15 µg/h background infusion. The lockout interval was 15 minutes. In this simulation, a loading dose of IV fentanyl was administered 1 hour before the end of surgery and IV PCA was started from the end of surgery. With this regimen of fentanyl, MEAC was reached 5 hours after the end of surgery. The 90% steady-state concentration was achieved 17.5 hours after the end of surgery, and steady-state concentration (1.8 ng/ml) was double the MEAC (1 ng/ml) of fentanyl (Fig. 4). MEAC and 90% steady-state concentration were reached more quickly with IV PCA with oxycodone compared to fentanyl.
Table 3. Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Intravenous Fentanyl [44].
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| V1, L | 13.0 |
| k10, (/min) | 0.0492 |
| k12, (/min) | 0.380 |
| k13, (/min) | 0.179 |
| k21, (/min) | 0.0960 |
| k31, (/min) | 0.0077 |
| ke0, (/min) | 0.147 |
Fig. 4. Predicted concentration of fentanyl in the plasma over time after administration of an IV bolus of 2 µg/kg followed by demand boluses of 15 µg every 15 minutes and background infusion of 15 µg/h. (A) The entire time–concentration curve. (B) Time–concentration curve of time to reach MEAC. (C) Time–concentration curve of time to reach 90% steady-state concentration of fentanyl. MEAC: minimum effective analgesic concentration, MEC: minimum effective concentration. Demand bolus, background infusion rate, and lock-out time of postoperative IV patient-controlled analgesia (IV PCA) were set at 1 ml, 1 ml/h, and 15 minutes, respectively. The concentration of fentanyl in IV PCA was 15 µg/ml. The pharmacokinetic model of Scott et al. was applied to this simulation [44]. Vertical dotted lines indicated time to reach MEAC (6 hours) and 90% steady-state concentration (18.5 hours). Time 0 indicates 1 hour before the end of surgery.
Summary
Since the approval of IV oxycodone as a patient-controlled analgesic, the use of IV patient-controlled analgesia with oxycodone is increasing gradually in Korea. Although the approved dosage regimen for postoperative pain relief with IV oxycodone involves IV bolus loading of 2 mg followed by patient-controlled analgesia with demand bolus of 1 mg and no background infusion, the MEAC of oxycodone was reached most quickly with a higher loading dose (0.1 mg/kg) and IV PCA with background infusion. When a potency ratio of morphine to fentanyl of 100 : 1 was applied, oxycodone showed similar, and sometimes better, effects on postoperative analgesia compared with fentanyl. Oxycodone is a good alternative to fentanyl in postoperative pain management. However, it is necessary to reduce the analgesic dose of oxycodone in elderly patients because metabolic clearance decreases with age.
References
- 1.Kalso E. Oxycodone. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2005;29(5 Suppl):S47–S56. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2005.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sjövall S, Kokki M, Kokki H. Laparoscopic surgery: a narrative review of pharmacotherapy in pain management. Drugs. 2015;75:1867–1889. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0482-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Koch S, Ahlburg P, Spangsberg N, Brock B, Tønnesen E, Nikolajsen L. Oxycodone vs. fentanyl in the treatment of early post-operative pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomised double-blind study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2008;52:845–850. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lenz H, Sandvik L, Qvigstad E, Bjerkelund CE, Raeder J. A comparison of intravenous oxycodone and intravenous morphine in patient-controlled postoperative analgesia after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:1279–1283. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e3181b0f0bb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ross FB, Smith MT. The intrinsic antinociceptive effects of oxycodone appear to be kappa-opioid receptor mediated. Pain. 1997;73:151–157. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3959(97)00093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Smith MT. Differences between and combinations of opioids re-visited. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2008;21:596–601. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e32830a4c4a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nozaki C, Saitoh A, Kamei J. Characterization of the antinociceptive effects of oxycodone in diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;535:145–151. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nozaki C, Kamei J. Involvement of mu1-opioid receptor on oxycodone-induced antinociception in diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;560:160–162. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Silvasti M, Rosenberg P, Seppälä T, Svartling N, Pitkänen M. Comparison of analgesic efficacy of oxycodone and morphine in postoperative intravenous patient-controlled analgesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1998;42:576–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1998.tb05169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brittain GJ. Dihydrohydroxycodeinone pectinate. Lancet. 1959;2:544–546. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91781-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Park JH, Lee C, Shin Y, An JH, Ban JS, Lee JH. Comparison of oxycodone and fentanyl for postoperative patient-controlled analgesia after laparoscopic gynecological surgery. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015;68:153–158. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2015.68.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kokki M, Broms S, Eskelinen M, Rasanen I, Ojanperä I, Kokki H. Analgesic concentrations of oxycodone--a prospective clinical PK/PD study in patients with laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012;110:469–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2011.00839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pesonen A, Suojaranta-Ylinen R, Hammarén E, Tarkkila P, Seppälä T, Rosenberg PH. Comparison of effects and plasma concentrations of opioids between elderly and middle-aged patients after cardiac surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009;53:101–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Camu F, Vanlersberghe C. Pharmacology of systemic analgesics. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2002;16:475–488. doi: 10.1053/bean.2002.0262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gourlay GK, Kowalski SR, Plummer JL, Cousins MJ, Armstrong PJ. Fentanyl blood concentration-analgesic response relationship in the treatment of postoperative pain. Anesth Analg. 1988;67:329–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Grönlund J, Saari TI, Hagelberg NM, Neuvonen PJ, Laine K, Olkkola KT. Effect of inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes 2D6 and 3A4 on the pharmacokinetics of intravenous oxycodone: a randomized, three-phase, crossover, placebo-controlled study. Clin Drug Investig. 2011;31:143–153. doi: 10.2165/11539950-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Korjamo T, Tolonen A, Ranta VP, Turpeinen M, Kokki H. Metabolism of oxycodone in human hepatocytes from different age groups and prediction of hepatic plasma clearance. Front Pharmacol. 2012;2:87. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2011.00087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Söderberg Löfdal KC, Andersson ML, Gustafsson LL. Cytochrome P450-mediated changes in oxycodone pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics and their clinical implications. Drugs. 2013;73:533–543. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lalovic B, Kharasch E, Hoffer C, Risler L, Liu-Chen LY, Shen DD. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral oxycodone in healthy human subjects: role of circulating active metabolites. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;79:461–479. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2006.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kalso E. How different is oxycodone from morphine? Pain. 2007;132:227–228. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.09.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nieminen TH, Hagelberg NM, Saari TI, Pertovaara A, Neuvonen M, Laine K, et al. Rifampin greatly reduces the plasma concentrations of intravenous and oral oxycodone. Anesthesiology. 2009;110:1371–1378. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31819faa54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Saari TI, Grönlund J, Hagelberg NM, Neuvonen M, Laine K, Neuvonen PJ, et al. Effects of itraconazole on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intravenously and orally administered oxycodone. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;66:387–397. doi: 10.1007/s00228-009-0775-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zwisler ST, Enggaard TP, Mikkelsen S, Brosen K, Sindrup SH. Impact of the CYP2D6 genotype on post-operative intravenous oxycodone analgesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scan. 2010;54:232–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2009.02104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stamer UM, Zhang L, Book M, Lehmann LE, Stuber F, Musshoff F. CYP2D6 genotype dependent oxycodone metabolism in postoperative patients. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60239. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Droll K, Bruce-Mensah K, Otton SV, Gaedigk A, Sellers EM, Tyndale RF. Comparison of three CYP2D6 probe substrates and genotype in Ghanaians, Chinese and Caucasians. Pharmacogenetics. 1998;8:325–333. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199808000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xie HG, Kim RB, Wood AJ, Stein CM. Molecular basis of ethnic differences in drug disposition and response. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:815–850. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.41.1.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Heim MH, Meyer UA. Evolution of a highly polymorphic human cytochrome P450 gene cluster: CYP2D6. Genomics. 1992;14:49–58. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Garcia-Barceló M, Chow LY, Lam KL, Chiu HF, Wing YK, Waye MM. Occurrence of CYP2D6 gene duplication in Hong Kong Chinese. Clin Chem. 2000;46:1411–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kubota T, Yamaura Y, Ohkawa N, Hara H, Chiba K. Frequencies of CYP2D6 mutant alleles in a normal Japanese population and metabolic activity of dextromethorphan O-demethylation in different CYP2D6 genotypes. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2000;50:31–34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2000.00209.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee SJ, Lee SS, Jung HJ, Kim HS, Park SJ, Yeo CW, et al. Discovery of novel functional variants and extensive evaluation of CYP2D6 genetic polymorphisms in Koreans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37:1464–1470. doi: 10.1124/dmd.108.022368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bertilsson L, Dahl ML, Dalén P, Al-Shurbaji A, et al. Molecular genetics of CYP2D6: clinical relevance with focus on psychotropic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;53:111–122. doi: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.01548.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Marez D, Legrand M, Sabbagh N, Lo Guidice JM, Spire C, Lafitte JJ, et al. Polymorphism of the cytochrome P450 CYP2D6 gene in a European population: characterization of 48 mutations and 53 alleles, their frequencies and evolution. Pharmacogenetics. 1997;7:193–202. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199706000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gaedigk A, Gotschall RR, Forbes NS, Simon SD, Kearns GL, Leeder JS. Optimization of cytochrome P4502D6 (CYP2D6) phenotype assignment using a genotyping algorithm based on allele frequency data. Pharmacogenetics. 1999;9:669–682. doi: 10.1097/01213011-199912000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bradford LD. CYP2D6 allele frequency in European Caucasians, Asians, Africans and their descendants. Pharmacogenomics. 2002;3:229–243. doi: 10.1517/14622416.3.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lennard MS, Iyun AO, Jackson PR, Tucker GT, Woods HF. Evidence for a dissociation in the control of sparteine, debrisoquine and metoprolol metabolism in Nigerians. Pharmacogenetics. 1992;2:89–92. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199204000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Liukas A, Kuusniemi K, Aantaa R, Virolainen P, Neuvonen M, Neuvonen PJ, et al. Elimination of intravenous oxycodone in the elderly: a pharmacokinetic study in postoperative orthopaedic patients of different age groups. Drugs Aging. 2011;28:41–50. doi: 10.2165/11586140-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Saari TI, Ihmsen H, Neuvonen PJ, Olkkola KT, Schwilden H. Oxycodone clearance is markedly reduced with advancing age: a population pharmacokinetic study. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108:491–498. doi: 10.1093/bja/aer395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ordóñez Gallego A, González Barón M, Espinosa Arranz E. Oxycodone: a pharmacological and clinical review. Clin Transl Oncol. 2007;9:298–307. doi: 10.1007/s12094-007-0057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kokki M, Broms S, Eskelinen M, Neuvonen PJ, Halonen T, Kokki H. The analgesic concentration of oxycodone with co-administration of paracetamol -- a dose-finding study in adult patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012;111:391–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2012.00916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tanskanen P, Kyttä J, Randell T. Patient-controlled analgesia with oxycodone in the treatment of postcraniotomy pain. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1999;43:42–45. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-6576.1999.430110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pereira J, Lawlor P, Vigano A, Dorgan M, Bruera E. Equianalgesic dose ratios for opioids. a critical review and proposals for long-term dosing. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2001;22:672–687. doi: 10.1016/s0885-3924(01)00294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hwang BY, Kwon JY, Kim E, Lee DW, Kim TK, Kim HK. Oxycodone vs. fentanyl patient-controlled analgesia after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Int J Med Sci. 2014;11:658–662. doi: 10.7150/ijms.8331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kim NS, Kang KS, Yoo SH, Chung JH, Chung JW, Seo Y, et al. A comparison of oxycodone and fentanyl in intravenous patient-controlled analgesia after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015;68:261–266. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2015.68.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Scott JC, Stanski DR. Decreased fentanyl and alfentanil dose requirements with age. A simultaneous pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987;240:159–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]