Abstract
This experiment examined the effects of diazepam (DZP) on acquisition and retention of an inhibitory avoidance response by rats with excitotoxic-induced lesions of central (CE), lateral (LAT), or basolateral (BL) amygdala nuclei. Sham-operated and lesioned rats received i.p. injections of DZP (2.0 mg per kg of body weight) 30 min before training in a continuous multiple-trial inhibitory avoidance task. Retention was tested 48 h later. Acquisition was not impaired by the lesions or the DZP. Retention was impaired in animals with CE and LAT lesions in comparison with sham-operated controls. DZP impaired retention in the sham-operated controls as well as CE- and LAT-lesioned animals but did not affect retention in animals with BL lesions. These findings indicate that the DZP-induced anterograde amnesia for inhibitory avoidance training is mediated through influences involving the BL amygdala nucleus.
Full text
PDF
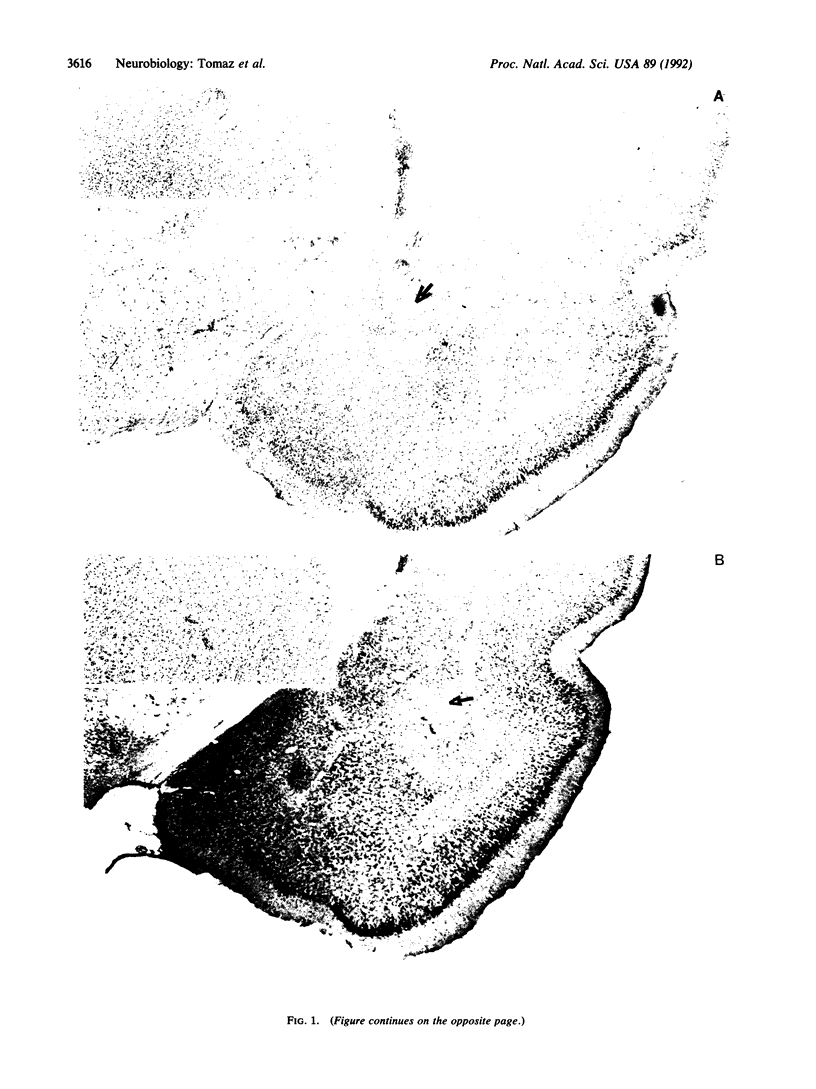

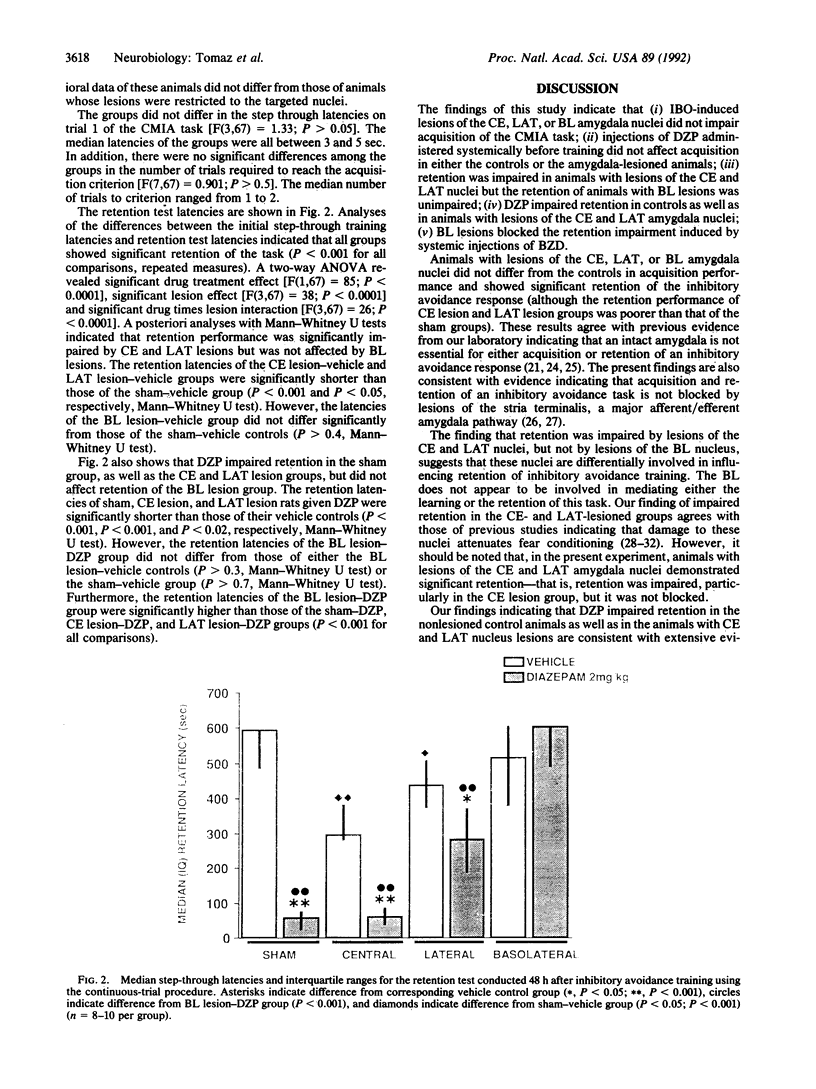

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammassari-Teule M., Pavone F., Castellano C., McGaugh J. L. Amygdala and dorsal hippocampus lesions block the effects of GABAergic drugs on memory storage. Brain Res. 1991 Jun 14;551(1-2):104–109. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90919-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arolfo M. P., Brioni J. D. Diazepam impairs place learning in the Morris water maze. Behav Neural Biol. 1991 Jan;55(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0163-1047(91)80133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brioni J. D., Nagahara A. H., McGaugh J. L. Involvement of the amygdala GABAergic system in the modulation of memory storage. Brain Res. 1989 May 15;487(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90945-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill L., Brioni J., Izquierdo I. Retrograde memory enhancement by diazepam: its relation to anterograde amnesia, and some clinical implications. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1986;90(4):554–556. doi: 10.1007/BF00174078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill L., McGaugh J. L. Amygdaloid complex lesions differentially affect retention of tasks using appetitive and aversive reinforcement. Behav Neurosci. 1990 Aug;104(4):532–543. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.104.4.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. R., Eccersley P. S., Frisby J. P., Thornton J. A. The amnesic effect of diazepam (Valium). Br J Anaesth. 1970 Aug;42(8):690–697. doi: 10.1093/bja/42.8.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. Diazepam and flurazepam: effects on conditioned fear as measured with the potentiated startle paradigm. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979 Mar 29;62(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00426027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker M. W., Tran T., McGaugh J. L. A comparison of the effects of scopolamine and diazepam on acquisition and retention of inhibitory avoidance in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1990;100(4):515–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02244005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamzu E. R. Animal model studies of benzodiazepine-induced amnesia. Psychopharmacol Ser. 1988;6:218–229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-73288-1_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock J. M., Sananes C. B., Davis M. Sensitization of the startle reflex by footshock: blockade by lesions of the central nucleus of the amygdala or its efferent pathway to the brainstem. Behav Neurosci. 1989 Jun;103(3):509–518. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.103.3.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock J., Davis M. Lesions of the amygdala, but not of the cerebellum or red nucleus, block conditioned fear as measured with the potentiated startle paradigm. Behav Neurosci. 1986 Feb;100(1):11–22. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.100.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges H., Green S. Are the effects of benzodiazepines on discrimination and punishment dissociable? Physiol Behav. 1987;41(3):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(87)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo I., Pereira M. E., Medina J. H. Benzodiazepine receptor ligand influences on acquisition: suggestion of an endogenous modulatory mechanism mediated by benzodiazepine receptors. Behav Neural Biol. 1990 Jul;54(1):27–41. doi: 10.1016/0163-1047(90)91221-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. A., Martinez J. L., Jr, Vasquez B. J., McGaugh J. L. Benzodiazepines alter acquisition and retention of an inhibitory avoidance response in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979 Jun 28;64(1):125–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00427358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp B. S., Frysinger R. C., Gallagher M., Haselton J. R. Amygdala central nucleus lesions: effect on heart rate conditioning in the rabbit. Physiol Behav. 1979 Dec;23(6):1109–1117. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(79)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDoux J. E., Cicchetti P., Xagoraris A., Romanski L. M. The lateral amygdaloid nucleus: sensory interface of the amygdala in fear conditioning. J Neurosci. 1990 Apr;10(4):1062–1069. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-04-01062.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang K. C., Juler R. G., McGaugh J. L. Modulating effects of posttraining epinephrine on memory: involvement of the amygdala noradrenergic system. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 12;368(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang K. C., McGaugh J. L., Yao H. Y. Involvement of amygdala pathways in the influence of post-training intra-amygdala norepinephrine and peripheral epinephrine on memory storage. Brain Res. 1990 Feb 5;508(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90400-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister R. G. The amnesic action of benzodiazepines in man. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1985 Spring;9(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(85)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh J. L., Introini-Collison I. B., Nagahara A. H., Cahill L., Brioni J. D., Castellano C. Involvement of the amygdaloid complex in neuromodulatory influences on memory storage. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1990 Winter;14(4):425–431. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh J. L., Introini-Collison I. B., Nagahara A. H. Memory-enhancing effects of posttraining naloxone: involvement of beta-noradrenergic influences in the amygdaloid complex. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 12;446(1):37–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J., Zámbó K., Decsi L. Anti-anxiety action of diazepam after intra-amygdaloid application in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Jun;18(6):573–576. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J. Benzodiazepine receptors: localization in rat amygdala. J Neurosci. 1983 Oct;3(10):2091–2097. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-10-02091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen E. N., Braestrup C., Scheel-Krüger J. Evidence that the anticonflict effect of midazolam in amygdala is mediated by the specific benzodiazepine receptors. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Feb 4;53(3):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90552-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roozendaal B., Koolhaas J. M., Bohus B. Differential effect of lesioning of the central amygdala on the bradycardiac and behavioral response of the rat in relation to conditioned social and solitary stress. Behav Brain Res. 1990 Dec 7;41(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(90)90052-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata K., Kataoka Y., Gomita Y., Ueki S. Localization of the site of the anticonflict action of benzodiazepines in the amygdaloid nucleus of rats. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 25;234(2):442–446. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90884-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiébot M. H. Some evidence for amnesic-like effects of benzodiazepines in animals. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1985 Spring;9(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0149-7634(85)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. R., Lewis M. E., Iversen S. D. Correlation of [3H]diazepam binding density with anxiolytic locus in the amygdaloid complex of the rat. Brain Res. 1985 Sep 2;342(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91355-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomaz C., Dickinson-Anson H., McGaugh J. L. Amygdala lesions block the amnestic effects of diazepam. Brain Res. 1991 Dec 24;568(1-2):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91382-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venault P., Chapouthier G., Simiand J., Dodd R. H., Rossier J. Enhancement of performance by methyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate, in learning and memory tasks. Brain Res Bull. 1987 Sep;19(3):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(87)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. Radiohistochemical localization of benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Feb;212(2):337–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]