Abstract
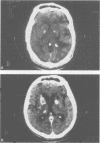
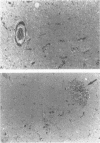
In a prospective study pallidal calcification was detected in 30 of 1478 (2%) adult patients, on CT brain scans. In 8 cases (26%), the calcifications were detected either years after, or during the course of, conditions known to cause basal ganglia calcification, including AIDS in four cases. Eight patients (three with AIDS) had disturbances of calcium and phosphorus metabolism. It was concluded that: a) pallidal calcification is not uncommon and aetiological factors may be recognised more often than previously reported; b) AIDS is emerging as a significant cause of pallidal calcification in young adults, and c) in AIDS and other conditions, abnormal calcium and phosphate metabolism may act in conjunction with local vascular changes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belman A. L., Lantos G., Horoupian D., Novick B. E., Ultmann M. H., Dickson D. W., Rubinstein A. AIDS: calcification of the basal ganglia in infants and children. Neurology. 1986 Sep;36(9):1192–1199. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.9.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannan T. S., Burger A. A., Chaudhary M. Y. Bilateral basal ganglia calcifications visualised on CT scan. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 May;43(5):403–406. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.5.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. R., Duchesneau P. M., Weinstein M. A. Calcification of the basal ganglia as visualized by computed tomography. Radiology. 1980 Jan;134(1):97–99. doi: 10.1148/radiology.134.1.7350641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray F., Gherardi R., Keohane C., Favolini M., Sobel A., Poirier J. Pathology of the central nervous system in 40 cases of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1988 Sep-Oct;14(5):365–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1988.tb01139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray F., Lescs M. C., Keohane C., Paraire F., Marc B., Durigon M., Gherardi R. Early brain changes in HIV infection: neuropathological study of 11 HIV seropositive, non-AIDS cases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Mar;51(2):177–185. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199203000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington M. G., Macpherson P., McIntosh W. B., Allam B. F., Bone I. The significance of the incidental finding of basal ganglia calcification on computed tomography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Dec;44(12):1168–1170. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.12.1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illum F., Dupont E. Prevalences of CT-detected calcification in the basal ganglia in idiopathic hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism. Neuroradiology. 1985;27(1):32–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00342514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazis A. D. Contribution of CT scan to the diagnosis of Fahr's syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand. 1985 Mar;71(3):206–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1985.tb03190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller W. C., Cochran J. W., Klawans H. L. Calcification of the basal ganglia: computerized tomography and clinical correlation. Neurology. 1979 Mar;29(3):328–333. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.3.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller W., Graner D., Mlcoch A. Essential voice tremor: treatment with propranolol. Neurology. 1985 Jan;35(1):106–108. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. M., Rosenbloom S., Perrett L. V. Neuroradiologic findings in AIDS: a review of 200 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986 Nov;147(5):977–983. doi: 10.2214/ajr.147.5.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin D., Hammerstad J., Orwoll E., McClung M., Calhoun D. Intracranial calcification in hyperparathyroidism associated with gait apraxia and parkinsonism. Neurology. 1980 Sep;30(9):1005–1007. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.9.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgante L., Vita G., Meduri M., Di Rosa A. E., Galatioto S., Coraci M. A., Di Perri R. Fahr's syndrome: local inflammatory factors in the pathogenesis of calcification. J Neurol. 1986 Feb;233(1):19–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00313985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A., Winickoff R. N., Heinz E. R. Familial calcification of the basal ganglions: a metabolic and genetic study. N Engl J Med. 1971 Jul 8;285(2):72–77. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197107082850202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenter M. D., Whisnant J. P. Basal ganglia calcification, hypoparathyroidism, and extrapyramidal motor manifestations. Neurology. 1968 Nov;18(11):1075–1083. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.11.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. J. Clinical correlations of CT scan-detected calcifications of the basal ganglia. Ann Neurol. 1979 Dec;6(6):507–511. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom D. M., West S. G., Andersen P. A. Basal ganglia calcifications in central nervous system lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Dec;28(12):1412–1416. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. K., Harding A. E., Morgan-Hughes J. A. The clinical features of mitochondrial myopathy. Brain. 1986 Oct;109(Pt 5):915–938. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.5.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes P. F., Gonzalez C. F., Zalewska M. K., Besarab A. Intracranial calcification in adults with chronic lead exposure. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986 Feb;146(2):267–270. doi: 10.2214/ajr.146.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs C., Ericson K., Erasmie U., Bergström M. Incidence of basal ganglia calcifications on computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1979 Jun;3(3):339–344. doi: 10.1097/00004728-197906000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selekler K. Calcification of the basal ganglia on computed tomography. Schweiz Arch Neurol Neurochir Psychiatr. 1982;131(2):187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima S., Becker L. E. Basal ganglia calcification in Down's syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985 Jan;48(1):61–64. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.48.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vles J. S., Lodder J., van der Lugt P. J. Clinical significance of basal ganglia calcifications detected by ct (a retrospective study of 33 cases). Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1981;83(4):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0303-8467(81)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]