Abstract
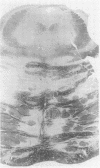
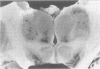
The treatment of hyponatraemia is controversial because of the risk of causing central or extrapontine myelinolysis (EPM). Rapid correction with hypertonic saline to a low normal sodium level has its proponents; others feel that slow correction to below normal sodium values is preventative. Most investigators feel that overcorrection should be avoided. It is not known whether the magnitude of serum sodium change is more important than the actual rate of correction. We present three patients with hyponatraemia ranging from 103 to 105 mmol/l who were corrected slowly with normal saline, corrected quickly with hypertonic saline, or rapidly overcorrected with hypertonic saline. All became comatose and died; all had EPM with or without central pontine myelinolysis (CPM). The rate of correction, the solution used, or the magnitude of correction did not seem to protect against demyelination. In a review of 67 reported CPM cases since 1983, no patients documented as having CPM or EPM by radiological studies or necropsy were treated with water restriction only. A group of 27 hyponatraemic patients treated only with water restriction and 35 with diuretic cessation alone did not develop CPM or EPM. This may be a reasonable approach to patients with symptomatic hyponatraemia and normal renal function.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS R. D., VICTOR M., MANCALL E. L. Central pontine myelinolysis: a hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1959 Feb;81(2):154–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALEU F. P., TERRY R. D. CENTRAL PONTINE MYELINOLYSIS. A REPORT OF TWO CASES. Arch Pathol. 1963 Aug;76:140–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arieff A. I. Hyponatremia, convulsions, respiratory arrest, and permanent brain damage after elective surgery in healthy women. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 12;314(24):1529–1535. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606123142401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arieff A. I. Hyponatremia. Mt Sinai J Med. 1990 May;57(3):125–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayus J. C., Krothapalli R. K., Arieff A. I. Changing concepts in treatment of severe symptomatic hyponatremia. Rapid correction and possible relation to central pontine myelinolysis. Am J Med. 1985 Jun;78(6 Pt 1):897–902. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayus J. C., Krothapalli R. K., Arieff A. I. Treatment of symptomatic hyponatremia and its relation to brain damage. A prospective study. N Engl J Med. 1987 Nov 5;317(19):1190–1195. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198711053171905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon A. P., Potter A. E. Extensive extrapontine and central pontine myelinolysis associated with correction of profound hyponatraemia. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;13(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1987.tb00166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burcar P. J., Norenberg M. D., Yarnell P. R. Hyponatremia and central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology. 1977 Mar;27(3):223–226. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.3.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo R. A., Ray R. A., Yaghmai F. Central pontine myelinolysis and pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1989 Mar;73(3 Pt 2):459–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifford D. B., Gado M. H., Levy B. K. Osmotic demyelination syndrome. Lack of pathologic and radiologic imaging correlation. Arch Neurol. 1989 Mar;46(3):343–347. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520390109028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluitmans F. H., Meinders A. E. Management of severe hyponatremia: rapid or slow correction? Am J Med. 1990 Feb;88(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90467-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conger J. D., McIntyre J. A., Jacoby W. J., Jr Central pontine myelinolysis associated with inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Am J Med. 1969 Nov;47(5):813–817. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt L. D., Buonanno F. S., Kistler J. P., Zeffiro T., DeLaPaz R. L., Brady T. J., Rosen B. R., Pykett I. L. Central pontine myelinolysis: demonstration by nuclear magnetic resonance. Neurology. 1984 May;34(5):570–576. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.5.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Oda M., Hara M. Central pontine myelinolysis. A study of 37 cases in 1,000 consecutive autopsies. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53(2):145–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00689995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estol C. J., Faris A. A., Martinez A. J., Ahdab-Barmada M. Central pontine myelinolysis after liver transplantation. Neurology. 1989 Apr;39(4):493–498. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson M. H., Snider S., Oliva L. A., Gault M. H. Cerebral and pontine myelinolysis. Two cases with fluid and electrolyte imbalance and hypotension. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Apr;18(4):399–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber O., Geller M., Stiller J., Yang W. Central pontine myelinolysis. Resolution shown by computed tomography. Arch Neurol. 1983 Feb;40(2):116–118. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04050020078019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocht A., Colmant H. J. Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: a report of 58 cases. Clin Neuropathol. 1987 Nov-Dec;6(6):262–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazratji S. M., Kim R. C., Lee S. H., Marasigan A. V. Evolution of pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1983 Apr;7(2):356–361. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198304000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illowsky B. P., Laureno R. Encephalopathy and myelinolysis after rapid correction of hyponatraemia. Brain. 1987 Aug;110(Pt 4):855–867. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.4.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalnins R. M., Berkovic S. F., Bladin P. F. Central pontine myelinolysis with widespread extrapontine lesions: a report of two cases. Clin Exp Neurol. 1984;20:189–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandt R. S., Heldrich F. J., Moser H. W. Recovery from probably central pontine myelinolysis associated with Addison's disease. Arch Neurol. 1983 Feb;40(2):118–119. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04050020080020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt-DeMasters B. K., Norenberg M. D. Rapid correction of hyponatremia causes demyelination: relation to central pontine myelinolysis. Science. 1981 Mar 6;211(4486):1068–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.7466381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kold A., Johansen O., Reintoft I., Reske-Nielsen E. Central pontine myelinolysis. A case report with typical neuropathological findings. Acta Neurol Scand. 1986 Mar;73(3):260–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1986.tb03272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laureno R. Central pontine myelinolysis following rapid correction of hyponatremia. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):232–242. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laureno R., Karp B. I. Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis following rapid correction of hyponatraemia. Lancet. 1988 Jun 25;1(8600):1439–1441. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra T. R. Hemiparesis apparently due to central pontine myelinolysis following hyponatremia. Ann Neurol. 1983 Dec;14(6):687–688. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick W. F., Danneel C. M. Central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Intern Med. 1967 May;119(5):444–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee A. C., Winkelman M. D., Banker B. Q. Central pontine myelinolysis in severely burned patients: relationship to serum hyperosmolality. Neurology. 1988 Aug;38(8):1211–1217. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.8.1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messert B., Orrison W. W., Hawkins M. J., Quaglieri C. E. Central pontine myelinolysis. Considerations on etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurology. 1979 Feb;29(2):147–160. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro L. La myélinolyse du centre du pont dans le cadre d'un nouveau syndrome histopathologique de topographie systématisée. A propos d'un cas anatomo-clinique. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Jul;13(3):293–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narins R. G. Therapy of hyponatremia: does haste make waste? N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 12;314(24):1573–1575. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606123142409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. M. Central pontine myelinolysis complicating hyponatraemia. Med J Aust. 1987 May 4;146(9):492-3, 496. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1987.tb120366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norenberg M. D. A hypothesis of osmotic endothelial injury. A pathogenetic mechanism in central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol. 1983 Feb;40(2):66–69. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04050020028004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norenberg M. D., Leslie K. O., Robertson A. S. Association between rise in serum sodium and central pontine myelinolysis. Ann Neurol. 1982 Feb;11(2):128–135. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh M. S., Uribarri J., Barrido D., Landman E., Choi K. C., Carroll H. J. Danger of central pontine myelinolysis in hypotonic dehydration and recommendation for treatment. Am J Med Sci. 1989 Jul;298(1):41–43. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198907000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okeda R., Kitano M., Sawabe M., Yamada I., Yamada M. Distribution of demyelinating lesions in pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis--three autopsy cases including one case devoid of central pontine myelinolysis. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;69(3-4):259–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00688302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peces R., Ablanedo P., Alvarez J. Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis following correction of severe hyponatremia. Nephron. 1988;49(2):160–163. doi: 10.1159/000185044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. H., Mesulam M. M. Behavioral manifestations of central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol. 1987 Jun;44(6):671–673. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520180085025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. B., Kramer J., Hotson G. C., Loh J. P. Central pontine myelinolysis: report of a case with distinctive appearance on MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1987 May-Jun;8(3):576–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippe D. J., Edwards M. K., D'Amour P. G., Holden R. W., Roos K. L. MR imaging of central pontine myelinolysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1987 Jul-Aug;11(4):724–726. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198707000-00037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez M. L., Hankey G. J. The "locked-in" syndrome and alcoholism--a preventable complication. Med J Aust. 1987 May 4;146(9):487-90, 492. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1987.tb120365.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbloom S., Buchholz D., Kumar A. J., Kaplan R. A., Moses H., 3rd, Rosenbaum A. E. Evolution of central pontine myelinolysis on CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1984 Jan-Feb;5(1):110–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaumburg H. H., Spencer P. S. Recognizing neurotoxic disease. Neurology. 1987 Feb;37(2):276–278. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.2.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam J., van Oers M. H., Verbeeten B., Jr Recovery after central pontine myelinolysis. J Neurol. 1984;231(1):52–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00313654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Schneck S. A., Mazzoni G., Aldrete J. A., Porter K. A., Schröter G. P., Koep L. J., Putnam C. W. Acute neurological complications after liver transplantation with particular reference to intraoperative cerebral air embolus. Ann Surg. 1978 Mar;187(3):236–240. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197803000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinsapir K. D., Vinters H. V. Central pontine myelinolysis in a child with the Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1985 Jul;16(7):741–743. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterns R. H., Riggs J. E., Schochet S. S., Jr Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 12;314(24):1535–1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606123142402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Sakuta M., Saeki F. Central pontine myelinolysis diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1985 Mar;17(3):310–311. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telfer R. B., Miller E. M. Central pontine myelinolysis following hyponatremia, demonstrated by computerized tomography. Ann Neurol. 1979 Nov;6(5):455–456. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. D., Gledhill R. F., Quinn N. P., Rossor M. N., Stanley P., Coomes E. N. Neurological complications associated with parenteral treatment: central pontine myelinolysis and Wernicke's encephalopathy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 8;292(6521):684–685. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6521.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Pierides A. M., Bradley W. G. Central pontine myelinolysis. Two cases with associated electrolyte disturbance. Q J Med. 1976 Jul;45(179):373–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. V., Englander R. N. Central pontine myelinolysis following rapid correction of hyponatremia in an alcoholic. Am J Kidney Dis. 1988 Dec;12(6):531–533. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(88)80106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman J. D., Weissman B. M. Pontine myelinolysis and delayed encephalopathy following the rapid correction of acute hyponatremia. Arch Neurol. 1989 Aug;46(8):926–927. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520440122030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthley L. I., Thomas P. D. Treatment of hyponatraemic seizures with intravenous 29.2% saline. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Jan 18;292(6514):168–170. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6514.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Laureno R., Victor M. Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Brain. 1979 Jun;102(2):361–385. doi: 10.1093/brain/102.2.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zegers Beyl D., Flament-Durand J., Borenstein S., Brunko E. Ocular bobbing and myoclonus in central pontine myelinolysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Jun;46(6):564–565. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.6.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Cunha C., Bertorini T. E., Lawrence J., Witherington J. M. Central pontine myelinolysis--a preventable condition. Two case reports and review of the literature. J Tenn Med Assoc. 1986 Aug;79(8):469–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]