Abstract
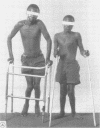
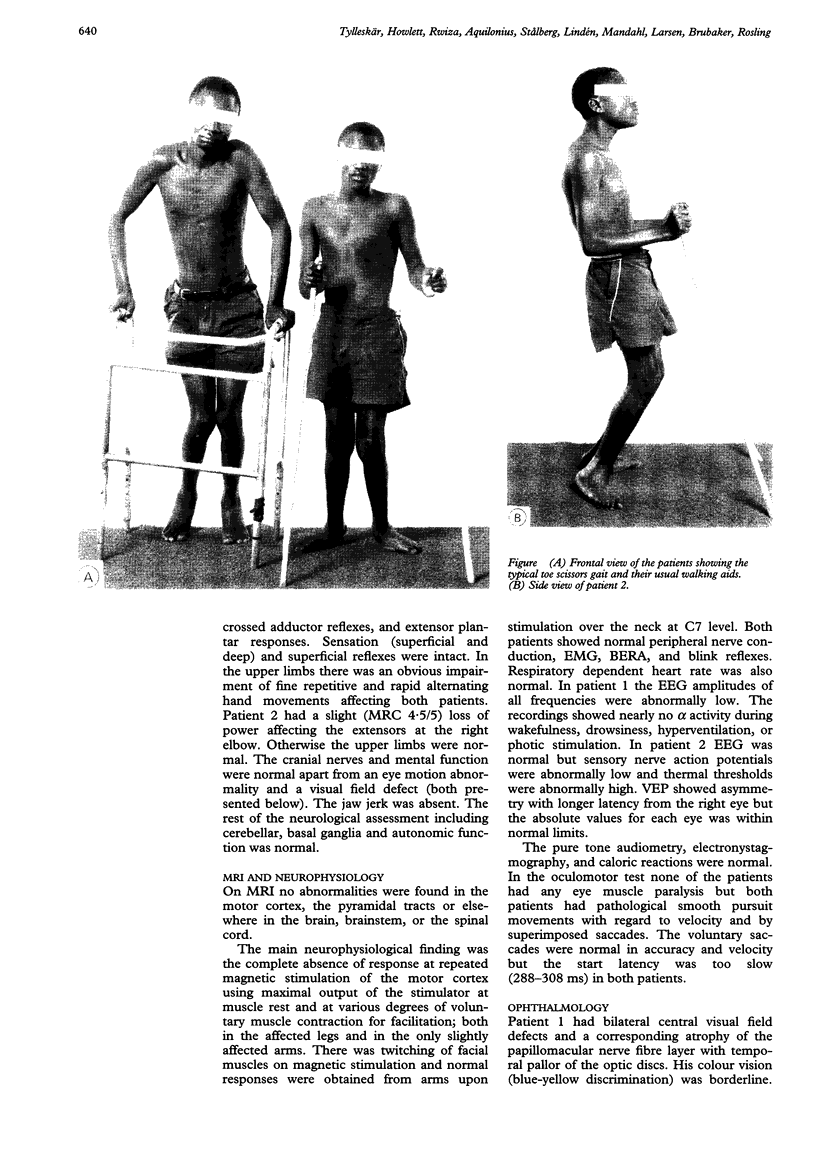
Two Tanzanian patients with konzo were severely disabled by a non-progressive spastic paraparesis, since the sudden onset during an epidemic six years earlier. At the time of onset they had a high dietary intake of cyanide from exclusive consumption of insufficiently processed bitter cassava roots. MRI of brain and spinal cord were normal but motor evoked potentials on magnetic brain stimulation were absent, even in the only slightly affected upper limbs. Other neurophysiological investigations were largely normal but the more affected patient had central visual field defects. Konzo is a distinct disease entity with selective type upper motor neuron damage.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergenius J. Computerized analysis of voluntary eye movements. A clinical method for evaluation of smooth pursuit and saccades in oto-neurological diagnosis. Acta Otolaryngol. 1984 Nov-Dec;98(5-6):490–500. doi: 10.3109/00016488409107590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carella F., Grassi M. P., Savoiardo M., Contri P., Rapuzzi B., Mangoni A. Dystonic-Parkinsonian syndrome after cyanide poisoning: clinical and MRI findings. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Oct;51(10):1345–1348. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.10.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carton H., Kayembe K., Kabeya, Odio, Billiau A., Maertens K. Epidemic spastic paraparesis in Bandundu (Zaire). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Jun;49(6):620–627. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.6.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett W. P., Brubaker G. R., Mlingi N., Rosling H. Konzo, an epidemic upper motor neuron disease studied in Tanzania. Brain. 1990 Feb;113(Pt 1):223–235. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.1.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hufnagel A., Elger C. E., Marx W., Ising A. Magnetic motor-evoked potentials in epilepsy: effects of the disease and of anticonvulsant medication. Ann Neurol. 1990 Nov;28(5):680–686. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugon J., Lubeau M., Tabaraud F., Chazot F., Vallat J. M., Dumas M. Central motor conduction in motor neuron disease. Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):544–546. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayembe K., Goubau P., Desmyter J., Vlietinck R., Carton H. A cluster of HTLV-1 associated tropical spastic paraparesis in Equateur (Zaire): ethnic and familial distribution. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Jan;53(1):4–10. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.1.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kira J., Fujihara K., Itoyama Y., Goto I., Hasuo K. Leukoencephalopathy in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: MRI analysis and a two year follow-up study after corticosteroid therapy. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Nov;106(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90192-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link H., Tibbling G. Principles of albumin and IgG analyses in neurological disorders. II. Relation of the concentration of the proteins in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 Sep;37(5):391–396. doi: 10.1080/00365517709091497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludolph A. C., Hugon J., Dwivedi M. P., Schaumburg H. H., Spencer P. S. Studies on the aetiology and pathogenesis of motor neuron diseases. 1. Lathyrism: clinical findings in established cases. Brain. 1987 Feb;110(Pt 1):149–165. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luís M. L., Hormigo A., Maurício C., Alves M. M., Serrão R. Magnetic resonance imaging in motor neuron disease. J Neurol. 1990 Dec;237(8):471–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00314764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan D. E., Geevarghese P. J. Dietary cyanide and tropical malnutrition diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1979 Mar-Apr;2(2):202–208. doi: 10.2337/diacare.2.2.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton M., Cruickshank K., Miller D., Dalgleish A., Rudge P., Clayden S., Moseley I. Antibody to human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 in West-Indian-born UK residents with spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1987 Feb 21;1(8530):415–416. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuntokun B. O. Cassava diet, chronic cyanide intoxication and neuropathy in the Nigerian Africans. World Rev Nutr Diet. 1981;36:141–173. doi: 10.1159/000393156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. M. Neuropathology of cyanate toxicity in rhesus monkeys. Preliminary report. Pharmacology. 1974;12(3):166–176. doi: 10.1159/000136535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E. V., Nogués M. A. Automatic analysis of heart rate variation: I. Method and reference values in healthy controls. Muscle Nerve. 1989 Dec;12(12):993–1000. doi: 10.1002/mus.880121207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E., Chu J., Bril V., Nandedkar S., Stålberg S., Ericsson M. Automatic analysis of the EMG interference pattern. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1983 Dec;56(6):672–681. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(83)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. D., Day B. L., Rothwell J. C., Dick J. P., Cowan J. M., Asselman P., Griffin G. B., Sheehy M. P., Marsden C. D. The interpretation of electromyographic responses to electrical stimulation of the motor cortex in diseases of the upper motor neurone. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;80(1):91–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truyen L., Gheuens J., Parizel P. M., Van de Vyver F. L., Martin J. J. Long term follow-up of multiple sclerosis by standardized, non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Nov;106(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tylleskär T., Banea M., Bikangi N., Cooke R. D., Poulter N. H., Rosling H. Cassava cyanogens and konzo, an upper motoneuron disease found in Africa. Lancet. 1992 Jan 25;339(8787):208–211. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90006-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugawa Y., Shimpo T., Mannen T. Central motor conduction in cerebrovascular disease and motor neuron disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 1988 Oct;78(4):297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1988.tb03660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]