Abstract
Congress grass, Parthenium hysterophorus L., of the family Asteraceae (tribe: Heliantheae), is an erect and much branched annual or ephermeral herb, known for its notorious role as environmental, medical, and agricultural hazards. It is believed to have been introduced into India and Australia from North America and in the last few years the weed has emerged as the seventh most devastating weed in Africa, Asia, and Australia. The aim of this review is to provide general information about the physiology, distribution, ill effects, and management of parthenium. Control of parthenium has been tried by various methods, but no single management option would be adequate to manage parthenium, and there is a need to integrate various management options. Successful management of this weed can only be achieved by an integrated approach with biological control as the key element.
1. Introduction
Parthenium hysterophorus L. (Asteraceae), a noxious plant, inhabits many parts of the world, in addition to its native range in North and South America and the West Indies [1]. According to Holm et al. [2] this noxious invasive species is considered to be one of the worst weeds currently known. This is a weed of global significance responsible for severe human and animal health issues, such as dermatitis, asthma and bronchitis, and agricultural losses besides a great problem for biodiversity. It is a widely held belief that the seeds of this weed came to India with grains imported from USA under the US PL 480 scheme, also known as “Food for Peace” which is a food assistance programme of the US government, and spread alarmingly like a wild blaze to almost all the states in India and were established as a naturalized weed. In India, the weed was first pointed out in Poona (Maharashtra) by Professor Paranjape, 1951, as stray plants on rubbish heaps and was reported by Rao [3] as a new species in India, but the earliest record of this species in India goes back to 1814 by Roxburgh, the father of Indian Botany, in his book Hortus Bengalensis [3, 4]. Ever since the weed became a menace around the globe including India, efforts have been made to manage the weed employing different methods such as mechanical, competitive replacement (allelopathy), chemical, and biological control methods. However, the weed has defied all human efforts to control it due to one or other disadvantages. Biological control, the intentional manipulation of natural enemies, insects, bioherbicides, nematodes, snails, and competitive plants to control harmful weeds, is gaining momentum as it is an effective and ecofriendly alternative to conventional methods of weed control [5].
2. Distribution and Biology of Parthenium Weed
2.1. Distribution
Parthenium is native to the area surrounding the Gulf of Mexico, Central America, southern North America, West Indies, and central South America [1, 6]. The weed has now invaded more than 20 countries around the globe, including five continents and numerous islands. Recent developments have indicated that African countries are at high risk of invasion. It is now also present in eight provinces of China and spreading at an alarming rate. Partheniumprobably entered India before 1910 (through contaminated cereal grain) but went unrecorded until 1956. Since 1956, the weed has spread like wildfire throughout India [7].
2.2. Name
The genus name Parthenium is derived from the Latin word parthenice—a reference to the plant now known as Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Bernh. or “feverfew;” hysterophorus was derived from the Greek hystera (womb) and phoros (bearing), referring to the prolific seeding habit of the plant [8]. It is commonly called as bitter weed, carrot weed, broom bush, and congress grass (India); whitetop, escobar amarga, and feverfew (Caribbean) and; false ragweed and ragweed parthenium (USA). Parthenium hysterophorus L. (parthenium weed) is a member of the tribe Heliantheae of the family Asteraceae, an extremely diverse family with a cosmopolitan distribution [6].
2.3. Morphology of the Plant
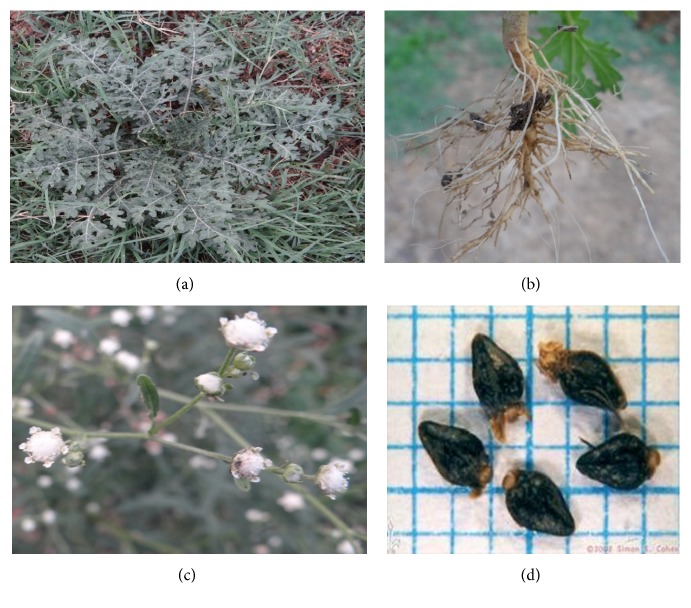
P. hysterophorus L. of the family Asteraceae (tribe: Heliantheae) is fast maturing, erect, and much branched annual or ephemeral herb. It shows two distinct phases in life: juvenile, rosette, or the vegetative stage and adult, mature, or the reproductive stage. The juvenile stage exhibits a rosette with large, dark green, simple, radicle, and pinnatisect small leaves lacking flowering (Figure 1(a)). The large lower leaves are spread on the ground like a carpet, without allowing any vegetation underneath it [9]. The adult stage is erect, much branched with deep tap root system that reaches up to 2 m in height (Figure 1(b)). The stem is hairy, octangular, longitudinally grooved and becomes tough and woody as the plant matures into a hardy bush. Leaves are simple, alternate, pinnately or bipinnately dissected (Figure 1(a)), 20–30 × 12–25 cm, becoming smaller towards the apex of the branches. The stem and leaf surface is covered with four types of glandular and nonglandular, multicellular white trichomes. The flowers are creamy white, about 4 mm across, arising from the leaf forks. Enormous number of pollen grains, 624 millions/plant, are produced which are anemophilous, that is, wind pollinated. Each flower produces four to five black wedge shaped seeds (Figures 1(c) and 1(d)) that are 2 mm long with thin white scales and difficult to see by the naked eye. It is a very prolific seed producer, producing up to 25,000 seeds/plant, leading to large seed bank in the soil [10].
Figure 1.
Parthenium weed; (a) rosette stage of parthenium plant; (b) tap root system of parthenium;(c) capitula; and (d) black wedge shaped seeds.
2.4. Habitat
Parthenium grows luxuriantly in wastelands, public lawns, orchards, forestlands, flood plains, agricultural areas (Figure 2(a)), urban areas, overgrazed pastures, industrial areas, playgrounds, roadsides, railway tracks, and residential plots (Figure 2(b)). Drought and subsequent reduced pasture cover create the ideal situation for the parthenium weed to establish itself. Although parthenium weed is capable of growing in most soil types, it is most dominant in alkaline, clay loam soils.
Figure 2.
Area of infestation of parthenium; (a) crop field infestation; (b) residential plot infestation.
2.5. Dispersal and Germination of Seeds
The seeds are mainly dispersed through water currents, animals, movement of vehicles, machinery, grains, stock feed and to a lesser extent by the wind. Most of the long distance spread is through vehicles, farm machinery, and flooding. The spread of seeds plus their ability to remain viable in the soil for many years pose one of the most complex problems for control [11]. Seeds do not have a dormancy period and are capable of germinating anytime when moisture is available. Seeds germinate within a week with the onset of monsoon and flowering starts after a month and continues up to another three months. In northwest India, parthenium germinates mainly in the months of February-March, attaining peak growth after rains in June-July and produces seeds in September-October. It normally completes its life cycle within 180–240 days. Its growth remains less and stunted from November to January due to severe cold [7, 12].
3. Harmful Effects
Parthenium is considered as the number one dangerous terrestrial weed because of its harmful effects both to humans and to biodiversity which are discussed below.
3.1. Effects on Ecosystem
Parthenium has been reported to be causing a total habitat change in native Australian grasslands, open woodlands, river banks, and flood plains [9]. It is an aggressive colonizer of wasteland, road sides, railway sides, water courses, cultivated fields, and overgrazed pastures and has invaded 14.25 million hectares of farm land during 2001–2007, compared to 2 million hectares in 1991–2000 [10].
3.2. Effects on Crops
Parthenium plant contains chemicals, like parthenin, hysterin, hymenin, and ambrosin, and due to the presence of these chemicals, the weed exerts strong allelopathic effects on different crops. Parthenin has been reported as a germination and radical growth inhibitor in a variety of dicot and monocot plants [13]. The weed affects nodulation in legumes due to inhibition of activity of nitrogen fixing and nitrifying bacteria, namely, Rhizobium, Actinomycetes, Azotobacter, and Azospirillum. Parthenium produces enormous numbers of pollens (on an average 624 million/plant), which are carried away at least to short distance in clusters of 600–800 grains, and settles on the vegetative and floral parts, including stigmatic surface, inhibiting fruit setting in crops like tomato, brinjal, beans, capsicum, and maize. In India, P. hysterophorus causes a yield decline of up to 40% in agricultural crops, Khosla and Sobti [14]. Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) grain yield losses between 40 and 97% have been reported in Ethiopia if parthenium is left uncontrolled throughout the season [7, 15]. In Australia, P. hysterophorus infests around 170000 km2 of prime grazing country in Queensland, causing economic losses of around $16.8 million per year to the pasture industry [16]. On cracking clay soils with an annual rainfall between 600 and 800 mm, P. hysterophorus was estimated to reduce the carrying capacity of affected farms in Australia by about 40% [17, 18]. The weed also acts as a collateral host for many diseases caused by viruses in crop plants.
3.3. Effects on Animals
Parthenium weed is toxic to animals causing dermatitis with pronounced skin lesions on various animals including horses and cattles. If eaten, it is responsible for mouth ulcers with excessive salivation. Significant amount (10–50%) of this weed in the diet can kill cattle [19]. In addition, it causes anorexia, pruritus, alopecia, diarrhea, and eye irritation in dogs. It also causes acute illness, when bittermilk and tainted meat from buffaloes, cows and goats, are fed on grass mixed with parthenium [12]. The parthenium extract results in significant reduction of rat WBC count which signifies its immune system weakening ability [20].
3.4. Effects on Human Beings
The pollen grains, airborne dried plant parts, and roots of parthenium cause various allergies like contact dermatitis, hay fever, asthma, and bronchitis in human beings. The common allergens found in this weed are parthenin, coronopilin, tetraneuris, and ambrosin. Pollens of parthenium cause asthma (allergic bronchitis), especially in children playing outdoors and in adults and old-age persons. Contact of plant with the body causes dermatitis and the spread of the problem all over the body causes great discomfort [21]. Clinically the parthenium dermatitis is of five types, as discussed below.
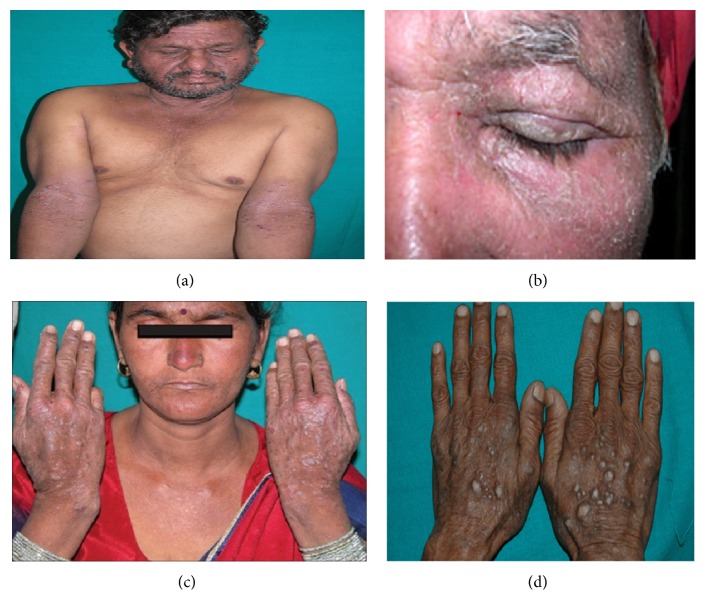
(1) The classical pattern also known as airborne contact dermatitis (ABCD) (Figures 3(a) and 3(b)) affects the face, especially eyelids and/or neck, V of chest, cubital, and popliteal fossae; (2) the chronic actinic dermatitis (CAD) (Figure 3(c)) pattern involves the exposed areas such as forehead, rim of ears, cheeks, nape of neck, dorsae of forearms, and hands as lichenified papules, plaques, or papulonodules with relative sparing of nonsun exposed areas such as eyelids, retroauricular areas and undersurface of chin and depth of the skin folds; (3) the mixed pattern (combination of classical and CAD pattern) manifests as scattered infiltrated scaly papules over the exposed parts and dermatitis over eyelids, flexures of extremities and neck; (4) the photosensitive lichenoid eruption pattern presents with pruritic, discrete, flat, violaceous papules, and plaques over sun-exposed parts such as forehead, ears, cheek, upper chest, and back, extensor aspect of forearms and dorsae of hands stimulating photosensitive lichenoid eruptions; (5) and the prurigo nodularis-like pattern presents as multiple hyperkeratotic papules and nodules over extremity with characteristic histopathologic features similar to prurigo nodularis (Figure 3(d)) [12, 22].
Figure 3.
Four of the five types ofsymptoms of commonly known parthenium dermatitis; (a, b) airborne contact dermatitis; (c) chronic actinic dermatitis in a female; and (d) prurigo-like lesions over dorsa of hands.
4. Control of Parthenium
Singh (1997) considered use of biocontrol agents (insects and fungal pathogens) and exploitation of competitive plants (allelopathy), the most economic and practical way of managing parthenium. But the weed has not been managed below the threshold level and is threatening biodiversity and posing ill problems for the humanity and animals. Various methods, for example, physical, chemical, bioherbicidal, and integrated, are being practiced to manage this weed around the globe and are discussed.
4.1. Physical Control
Manual uprooting of parthenium before flowering and seed setting is the most effective method. Uprooting the weed after seed setting will increase the area of infestation. Some landholders have achieved success in ploughing the parthenium weed in the rosette stage before it seeds, but this must be followed up by sowing a crop or direct seeding the perennial pasture. Physical control involves hand weeding, a time consuming and unpleasant job, made worse by the health hazards involved with handling parthenium weed.
Burning, another strategy employed to manage weed, is not a useful control strategy for parthenium. However, research suggests that burning for other purposes (e.g., woody weed control) will not result in an increased infestation of parthenium as long as the pasture is allowed to recover before stock is introduced. This too has proved to be inadequate due to two reasons; it requires large quantity of fuel and burning destroys all other economically important plants growing in its vicinity [23, 24].
4.2. Chemical Control
Chemical control is an effective method to control parthenium in the areas where its natural enemies are absent. Use of chemical herbicides, such as chlorimuron ethyl, glyphosate, atrazine, ametryn, bromoxynil, and metsulfuron, are known to be very effective in controlling this weed. References [25–27] reported that the application of 2,4-D EE (0.2%) and metribuzin (0.25 and 0.50%) were found more effective for controlling parthenium at 15 days after spraying (DAS), causing complete kill of parthenium population, and did not allow any emergence of weed. Khan et al. [28] reported that the stage/time of parthenium weed for herbicidal control is important and the weed was effectively controlled at rosette stage in wasteland, noncropped areas, along railway tracks, water channels, and roadsides. The most effective treatments for parthenium weed control were glyphosate and metribuzin, having higher mortality at 4 weeks after treatment (WAT) at both rosette and bolted stages than 2, 4-D, triasulfuron + terbutryn, bromoxynil + MCPA and atrazine + s-metolachlor, atrazine, s-metolachlor. Pendimethalin was the least effective treatment for both growth stages. Overall, the efficacy of herbicides was promising on rosette parthenium plants than bolted plants. The mortality rate by different herbicides at rosette and bolted stages is given in Table 1. In open wasteland, noncropped areas and along railway tracks and roadsides, the spraying of a solution of common salt (Sodium chloride) at 15–20% concentration has been found to be effective.
Table 1.
Parthenium weed control at rosette and bolted stages with different herbicidal application at 4 weeks after treatment (WAT).
| Serial number | Herbicides | % Mortality at rosette stage | % Mortality at bolted stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Glyphosate | 96 | 91 |
| 2 | Metribuzin | 87 | 75 |
| 3 | 2,4-D | 71–80 | 43 |
| 4 | Bromoxynil + MCPA | 57–79 | 50–61.5 |
| 5 | Atrazine | 56.5 | 36.5 |
| 6 | S-metolachor | 57.5 | 41 |
| 7 | Pendimethalin | 42.5 | 30 |
4.2.1. Disadvantages of Herbicides
There are several disadvantages of using the chemical herbicides, such as the environmental hazards and the development of resistance against many herbicides, like atrazine 2, 4-D, metribuzin, paraquat (Gramoxone), trifluralin, diphenamid, and glyphosate [29–31]. Glyphosate is one of the most toxic herbicides, with many species of wild plants being damaged or killed by applications of less than 10 micrograms per plant. Moreover, glyphosate can be more damaging to wild flora than many other herbicides. Atrazine has been found to be highly persistent in soil and has been classified as a restricted use pesticide (RUP) in the USA due to its potential for groundwater contamination [32].
4.3. Allelopathic Control
The term allelopathy was coined by Molisch (1937), which generally refers to the detrimental effect of one plant species on seed germination, growth, and reproduction of another plant species. Numerous plants are reported to possess allelopathic potential and efforts have been made to use them in weed control [33]. Competitive replacement of parthenium can be achieved by planting plants like Cassia sericea, C. tora, C. auriculata, Croton bonplandianum, Amaranthus spinosus, Tephrosia purpurea, Hyptis suaveolens, Sida spinosa, and Mirabilis jalapa which are capable of effectively suppressing partheniumin natural habitats [34]. A study in India revealed that Cassia sericea reduces the accumulation of parthenium by 70% and parthenium population by 52.5% [35]. Another study showed that aqueous extracts from Imperata cylindrica, Desmostachya bipinnata, Otcantium annulatum, and Sorghum halepense markedly suppressed seedling growth and germination of parthenium [36]. In India, crop rotation using Marigold (Tagetes spp.) during the rainy season, instead of the usual crop, has been found effective in reducing parthenium infestation in cultivated areas.
Both the root and shoot extracts of three allelopathic grasses, namely, Dicanthium annulatum, Cenchrus pennisetiformis, and Sorghum halepense, reduce germination and suppress early seedling growth of exotic weed P. hysterophorus. Aqueous foliar extracts of Azadirachta indica, Aegle marmelos, and Eucalyptus tereticornis totally inhibited the seed germination of partheniumand may be exploited for controlling parthenium weed.
4.4. Biological Control
Biological control is an environmentally sound and effective means of reducing or mitigating pests and pest effects through the use of natural enemies. In the last three to four decades, a great deal of emphasis has been given to control parthenium through various biocontrol agents like microbial pathogens, insects, and botanicals [24, 37]. Of the various biocontrol strategies, biological control of weeds by plant pathogens has gained acceptance as a practical, safe, and environmentally beneficial method applicable to agroecosystem [38]. There are two basic strategies to implement the biological control of weeds: the introduction of foreign pathogenic organisms, called the “classical approach,” and the “augmentative” or “bioherbicidal approach,” where the pathogenic organisms are already present (native or introduced) and their population is increased by mass rearing. In epidemiological terms, these approaches are described as “inoculative” and “inundative strategy,” respectively [39].
4.4.1. Classical Strategy
The “inoculative” or “classical approach” implies the control of invasive weeds by introduction of suitable, exotic bioagent from the weed's natural habitat. The main objective of classical biological weed control is restoring balance between target alien weed and its natural enemies in the ecosystem. Successful bioagent reduces the weed population first then the bioagent population dies due to starvation of food. This process continues in cyclic fashion until the bioagent and weed population get established at a low level. A successful control strongly depends on favourable conditions for the bioagent, which effectively increase the population of the controlling organism [40]. This method is a slow operation and currently used in noncropped areas. The control of different weeds through the use of classical biological agents, insects, and fungal plant pathogen is given in Table 2 [30, 41].
Table 2.
Successful examples of control of weeds through classical biocontrol agents.
| Weed | Bioagent | Kind of bioagent | Reporting country |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chondrilla juncea | Puccina chondrillina | Rust | Australia |
| Cyperus rotundus | Bactra verutana | Shoot boring moth | India, Pakistan, USA |
| Eupatorium riparium | Entyloma compositarum | Plant pathogen | USA |
| Hydrilla verticillata | Hydrellia pakistanae | Shoot fly | USA |
| Orobanche cernua | Sclerotinia sp. | Plant pathogen | USA |
| Parthenium hysterophorus | Puccinia abrupta var. partheniicola | Rust | Mexico |
| Parthenium hysterophorus |
Zygogramma Bicolorata
Epiblema strenuana Conotrachels sp. |
Leaf eating bettle, Stem galling insect, Stem galling insect |
Mexico Australia Australia |
| Rumex spp. |
Uromyces rumicis
Gastrophysa viridula |
Plant pathogen Beetle |
USA USA |
| Tribulus terrestris | Microlarinus lareynii and M. lypriformis | Pod weevil | USA |
4.4.2. Bioherbicidal Approach
“Plant pathogenic fungi are developed and used in the inundative strategy to control weeds in the way chemical herbicides are used,” or as “living products that control specific weeds in agriculture as effectively as chemicals” [42]. Usually, they are applied in a manner similar to chemical herbicides (hence called bioherbicides) by periodic dispersals of distinct doses of the virulent inoculum [37, 43]. The concept of mycoherbicides was introduced by Daniel et al. [44], who demonstrated that an endemic pathogen might be rendered completely destructive to its weedy host by applying a massive dose of inoculum at a particularly susceptible growth stage. To achieve success, the pathogen must be culturable in artificial media; the inoculum must be capable of abundant production using conventional methods such as liquid fermentation; the final product must be genetically stable and specific to the target weed; storage (shelf-life), handling, and methods of application must be compatible with current agricultural practices; and the pathogen must be efficacious under sufficient different environment conditions to allow a feasible application window [44]. In the past, several attempts have been made to control weeds with fungal products or mycoherbicides [38] and several products of mycoherbicides are available in the market (Table 3) and many more are in the pipeline.
Table 3.
Examples of weed control using bioherbicidal approach (liquid and solid formulations).
| Serial number | Target weed | Fungus | Product name | Year of registration | Formulation type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid formulations | |||||
| 1. | Persimmon (Diospyros virginiana) trees in rangelands | Acremonium diospyri | Acremonium diospyri | 1960 | Conidial suspension |
| 2. | Dodder (Cuscuta chinesis and C. australis) in soybeans | Colletotrichum gloeosporioides f. sp. Cuscutae | Lubao | 1963 | Conidial suspension |
| 3. | Milkweed vine (Morrenia odorata) | Phytophthora palmivora (P. citrophthora) | DeVine | 1981 | Liquid spores suspension |
| 4. | Yellow nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus) | Puccinia canaliculata | Dr. Biosedge | 1987 | Emulsified suspension |
| 5. | Turf grass (Poa annua) in golf courses | Cylindrobasidium leave | Stumpout | 1997 | Liquid (oil) suspension |
| 6. | Woody plants Blackberry weed (Prunus serotina) | Chondrostereum purpureum | BioChon | 1997 | Mycelial suspension in water |
| 7. | Hakea gummosis and H. sericea in native vegetation | Colletotrichum acutatum | Hakatak | 1999 | Conidial suspension |
| 8. | Deciduous tree species | Chondrostereum purpureum | Mycotech Paste | 2004 | Paste |
| 9. | Alder, aspen, and other hardwoods | Chondrostereum purpureum | Chontrol (Ecoclear) |
2004 | Spray emulsion and paste |
| 10. | Dodder species | Alternaria destruens | Smolder | 2008 | Conidial suspension |
| 11. | Soda apple (Solanum viarum) | Tobacco mild green mosaic virus | Solvinix | 2009 | Foliar spray suspension |
|
| |||||
| Solid formulations | |||||
| 1. | Northern joint-vetch (Aeschynomene virginica) | Colletotrichum gloeosporioides f. sp. aeschynomene | Collego LockDown |
1982 | Wettable powder |
| 2. | Sickle-pod and coffee senna (Cassia spp.) | Alternaria cassia | Casst | 1983 | Solid |
| 3. | Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) | Cercospora rodmanii | ABG-5003 | 1984 | Wettable powder |
| 4. | Velvet leaf (Abutilon theophrastus) | Colletotrichum coccodes | Velgo | 1987 | Wettable powder |
| 5. | Round-leaved mallow (Malva pussila) | Colletotrichum gloeosporioides f. sp. malvae | BioMal | 1992 | Mallet wettable powder |
| 6. | Hakea gummosis and H. sericea in native vegetation | Colletotrichum acutatum | Hakatak | 1999 | Granular (dry conidia) |
| 7. | Dyers woad (Isastis tinctoria) in farms, rangeland, waste areas, and roadsides | Puccinia thlaspeos | Woad Warrior |
2002 | Powder |
| 8. | Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) in lawns/turf | Sclerotinia minor | Sarritor | 2007 | Granular |
5. Biological Control of Parthenium
5.1. Classical Biological Control
(a) Insects as Classical Biocontrol Agents. Several insects have been tried to control parthenium weed in the different countries (Table 4). Of the various insects, the leaf-feeding beetle (Zygogramma bicolorata) (Figure 4) and the stem galling moth (Epiblema strenuana), both imported from Mexico, have shown good potential to control this weed. The beetle, Z. bicolorata, an effective leaf eater, was imported from Mexico for the management of parthenium in Australia in 1980, and in Indian Institute of Horticulture Research (IIHR) [45]. Both the adults and larvae of this insect feed on leaves. The early stage larvae feed on the terminal and auxiliary buds and move on to the leaf blades as they grow. The fully-grown larvae enter the soil and pupate. An insect density of one adult per plant caused skeletonization of leaves within 4–8 weeks but little success has been achieved as the weed has very high generative potential, and moreover the insect is not a species specific and is found to attack sunflower in India [41]. Attempts have also been made to introduce Epiblema strenuana—a stem galling moth, but as this moth lays eggs and develops on niger crops [45], so its cultures were destroyed.
Table 4.
Insect biocontrol agents released to control parthenium weed in different countries.
| Biological control agent | Feeding habits | Native country | Released country |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bucculatrix parthenica | (Leaf mining moth) | Mexico | Australia |
| Conotrachelus albocinereus | (Stem galling weevil) | Mexico | Australia |
| Epiblema strenuana | (Stem galling moth) | Mexico | Australia |
| Listronotus setosipennis | (Stem boring weevil) | Argentina and Brazil | Australia |
| Platphalonidia mystica | (Stem boring moth) | Argentina | Sri Lanka |
| Smicronyx lutulentus | (Seed feeding weevil) | Mexico | Pakistan, Australia |
| Stobaera concinna | (Parthenium sap feeder plant hopper) | Mexico | Australia |
| Zygogramma bicolorata | (Leaf feeding beetle) | Mexico | Australia, India |
Figure 4.
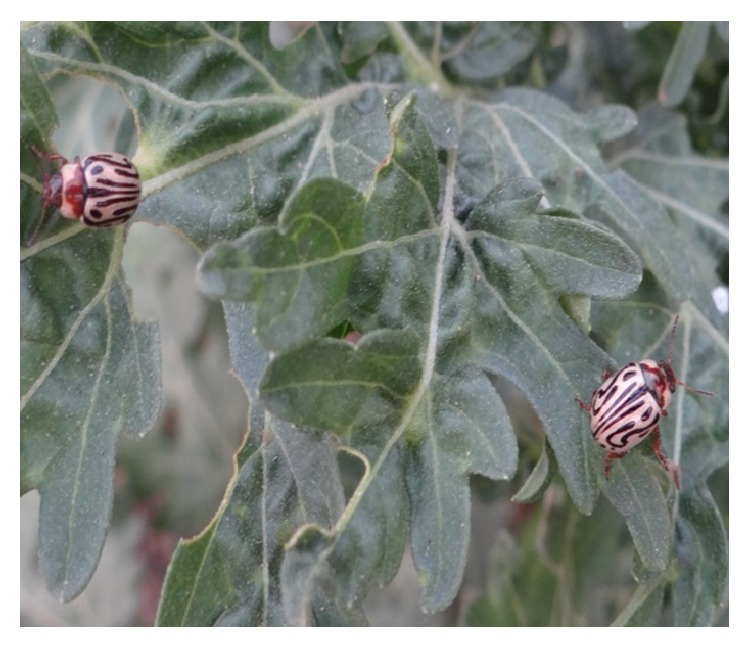

Zygogramma bicolorata feeding on parthenium weed.
(b) Classical Control by Fungal Plant Pathogens. In standard classical biological control strategy, obligate parasites, especially rust fungi, are the first choice because they exhibit narrow host ranges, high reproductive capacities, and efficient aerial dispersal [46]. The most promising fungal agents to manage parthenium are Puccinia abrupta var. partheniicola (Jackson) Parmelee, Puccinia xanthii var. parthenii-hysterophorae (previously known as P. melampodii Diet. and Holw.) (Uredinales), Entyloma compositarum De Bary (Ustilaginales), and Plasmopara halstedii (Farlow) Berl. and De Toni (Peronosporales). Of these, Puccinia abrupta var. partheniicola and Puccinia xanthii var. parthenii-hysterophorae originate from Mexico and have been fully screened and released in Australia; they are the most potential classical biocontrol fungal pathogens of this weed in Australia.
5.1.1. Puccinia abrupta var. partheniicola
A rust pathogen, Puccinia abrupta var. partheniicola, indigenous to Mexico, was introduced in 1999 to Australia to control parthenium, as a classical biocontrol agent. The rust is commonly found in high to mid altitude (1400–2500 m.a.s.l.) with disease incidence up to 100% in some locations. The incidence of the rust disease on parthenium in different locations under field conditions showed varied effects on morphological parameters of this weed, with seed production capacity reduced by 42%. Host specificity tests against the weed and crop hosts related to parthenium revealed that sporulation of P. abrupta were observed exclusively on parthenium, though limited number of poorly developed pustules were recorded on varieties of niger seeds (Guizotia abyssinica) [47, 48].
5.1.2. Puccinia xanthii var. parthenii-hysterophorae
Puccinia xanthii var. parthenium-hysterophorus is an autoecious, microcyclic rust fungus, producing both telia and basidiospores on one host [49]. The teliospores germinate over a wide temperature range (optimum being 25°C) and produce basidiospores (optimum at 22°C), which directly penetrate the host epidermis [50, 51]. Prior to the release of P. xanthii var. parthenii-hysterophorae in Australia and South Africa, host-specificity testing was conducted on over different plant species within the family Asteraceae. Limited infection was observed on a few plants, but in most cases the infection consisted of abnormal or abortive sporulation, and the level of sporulation was much less than those on parthenium weed [50, 52]. Since its release in Australia in 2000 there have been no reports of P. xanthii var. parthenii-hysterophorae infecting any plant other than Parthenium hysterophorus, and it is thought to be a promising pathogen for controlling this weed in Australia. It is expected that P. xanthii var. parthenii-hysterophorae will also contribute greatly to the management of parthenium weed infestations in the warm, lower-altitude regions of South Africa, where there are currently no biological control agents implemented against this weed.
5.2. Inundative Biological Control
A series of surveys have been carried out to search for naturally occurring fungal pathogens on parthenium to control it through the bioherbicidal strategy. The pathogens reported on parthenium from world are listed in Table 5.
Table 5.
| Fungus | Countries | References |
|---|---|---|
| Alternaria alternata | India | [61] |
| Alternaria alternata ITCC (LC#508) | India | [53] |
| Alternaria protenta | Mexico | [62] |
| Alternaria zinniae | Mexico, India | [63] |
| Cercospora parthenii | Cuba, Mexico, India | [64] |
| Colletotrichum dematium | India | [65] |
| Colletotrichum capsici | India | [66] |
| Colletotrichum gloeosporioide | India | [67] |
| Cladosporium sp. (MCPL-461) | India | [5] |
| Curvularia lunata | India | [68] |
| Curvularia palesens | India | [69] |
| Curvularia verruculsa | India | [69] |
| Dreshlera australiensis | India | [69] |
| Dreshlera hawaiiensis | India | [69] |
| Erysiphe cichoracearum | India | [56] |
| Exerohilum rostratum | Mexico | [70] |
| Fusarium semitectum | Mexico | [70] |
| Fusarium oxysporum | India | [71] |
| Fusarium pallidoroseum | India | [58] |
| Fusarium solani | India | [71] |
| Lasiodiplodia theobromae | India | [72] |
| Myrothecium roridum | India | [73] |
| Oidium parthenii | India | [57] |
| Phoma sorghina | India | [74] |
| Rhizoctonia solani | India | [75] |
| Sclerotinia sclerotiorum | India | [76, 77] |
| Sclerotium rolfsii | India | [78] |
| Sphaerotheca fuliginea | India | [79] |
| Syncephalastrum racemosum | India | [69] |
There is a long list of fungal pathogens recorded on parthenium around the globe, out of which six have been evaluated for their biocontrol potential which are discussed here.
Saxena and Kumar [53] worked on the mycoherbicidal potential of Alternaria alternata ITCC (LC#508) in northern India to control parthenium weed and reported 50% damage of plants in vitro detached leaf and whole plant bioassay at 96 hours after treatment at a concentration of 1 × 106 spores/mL. Sclerotium rolfsii (teleomorph: Athelia rolfsii) incites a severe collar rot disease on parthenium [54, 55]. Although, the pathogen is responsible for severe damage to the weed, but the wide host range of the species creates doubt about its suitability as mycoherbicides. Cercospora parthenophilia, a leaf spot pathogen isolated from parthenium at Kurukshetra, has shown several characteristics that make it a potential biological control agent of this weed in India such as wide natural distribution; it sporulates well on Czapek dox agar (a simple and cheap culture medium), within ten days, and can thus be mass produced in a short time and at low cost; it has narrow host range and capable of limiting populations of the weed under experimental conditions [56]. Cladosporium sp. (MCPL-461), a floral leaf pathogen of parthenium, produces symptoms on the flowers, buds, and inflorescences, and causes sterility and reduces seed viability. The severity of pathogen to the reproductive organs led to serious damages of the partheniumplants and may be used as a potential mycoherbicide against this weed [5]. Satyaprasad and Usharani [57] reported powdery mildew causing Oidium parthenii on parthenium at Hyderabad. The fungus appears as small, circular, white powdery spots on the surface of leaves and spreads over the entire lamina on both the surfaces giving a powdery appearance to the plant. Severe infection leads to defoliation. Kauraw et al. [58] reported Fusarium pallidoroseum, on parthenium from Jabalpur. It was found to reduce seed germination, seedling vigour, height of plant, number of branches, and number of flowers and reported as a potential biocontrol agent for parthenium management.
5.3. Integrated Weed Management
The classical and bioherbicidal strategies, when applied alone, are not able to suppress this weed. However, integrated pest management (IPM) has gained attention in recent years as a means of reducing losses due to pests, minimizing reliance on chemical pest control, therefore fostering the long-term sustainability of agricultural systems. In Australia, to complement the classical biological control approach with other management tactics, two selected suppressive plants, the native Mitchell grass (Astrebella squrossa) and the introduced legume, butterfly pea (Clitoria ternatea) along with two biological control agents, a leaf and a seed feeding beetle (Zygogramma bicolorata) and a stem galling moth (Epiblema strenuana), have been used to control parthenium weed under integrated weed management. The suppressive plants significantly suppressed weed growth in the absence of the biological control agents. However, this suppressive ability could be further enhanced in the presence of one of the either aforementioned biological agents. Work carried out in Australia has revealed that the parthenium weed can be more effectively managed by complementing presently existing biological control strategies with suppressive plants [52]. Shabbir [59] conducted another experiment in Australia for a two-year period to control parthenium weed. They used six suppressive plant species with biological control agents (Epiblema strenuana Walker, Zygogramma bicolorata Pallister, Listronotus setosipennis Hustache, and Puccinia abrupta var. partheniicola) in the field to reduce the growth of parthenium weed between 60–80% and 47–91% in the years 1 and 2, respectively. The biomass of the suppressive plants was between 6% and 23% greater when biological control agents were present than when the biological control agents had been excluded. This shows that parthenium weed can be more effectively managed by combining the current biological control management strategy with selected sown suppressive plant species.
6. Conclusions
The noxious P. hysterophorus grows in a wide variety of habitats and causes changes in above ground vegetation as well as in below ground soil nutrients. It is capable of out-competing native and nonnative palatable plants that are important to livestock. Furthermore, the changes in vegetation and soil nutrients could lead to ultimate changes in other trophic levels and alter the function of the ecosystem. Appropriate methods for the management of P. hysterophorus are necessary to avoid potential threats to biodiversity and economic losses. The efficient and environment-friendly alternative to other time-consuming, costly, toxic, physical, and chemical methods is the use of biological control through allelopathy, insects and fungal pathogens. Nine insect species and two rusts have been released in Australia to check this weed. Of these, two insects Z. bicolorata and E. stenuana, and two rust fungi, Puccinia abrupta var. partheniicola and Puccinia xanthii var. parthenii-hysterophorae, have shown potential and are being used to control this weed. Nevertheless the weed has not been completely checked and is still creating nuisance in both Australia and India, and more needs to be done by scientists, agriculturists, and government to work jointly for managing this troublesome weed.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- 1.Picman J., Picman A. K. Autotoxicity in Parthenium hysterophorus and its possible role in control of germination. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology. 1984;12(3):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0305-1978(84)90051-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Holm L., Doll J., Holm E., Pancho J. V., Herberger J. P. World Weeds: Natural Histories and Distribution. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rao R. S. Parthenium, a new record for India. Journal of Bombay Natural History Society. 1956;54:218–220. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Roxburg W. Hortus Bengalensis or a Catalogue of the Plants Growing in the Honourable East India Company’s Botanic Garden at Calcutta. Serampore, India: The Mission Press; 1814. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kumar S. Biological control of Parthenium in India: status and prospects. Indian Journal of Weed Science. 2009;41(1-2):1–18. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Navie S. C., McFadyen R. E., Panetta F. D., Adkins S. W. The biology of Australian Weeds Parthenium hysterophorus L. Plant Protection Quarantine. 1996;11:76–88. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Aneja K. R. From Ethnomycology to Fungal Biotechnology. London, UK: Plenum; 1999. Biotechnology for the production and enhancement of mycoherbicide potential; pp. 91–114. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Parsons W. T., Cuthbertson E. G. Noxious Weeds of Australia. Melbourne, Australia: Inkata Press; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lakshmi C., Srinivas C. R. Type I hypersensitivity to Parthenium hysterophorus in patients with parthenium dermatitis. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology. 2007;73(2):103–105. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.31895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Javaid A., Adrees H. Parthenium management by cultural filtrates of phytopathogenic fungi. Natural Product Research. 2009;23(16):1541–1551. doi: 10.1080/14786410902726167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Monaco J. T., Weller S. C., Ashton F. M. Weed Biology and Ecology. 4th. NewYork, NY, USA: Academic Publisher; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Aneja K. R. Botanical Researches in India. Udaipur, India: Himanshu Publications; 1991. Deadly weed Parthenium hysterophorus and its control-a review; pp. 258–269. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gunaseelan N. V. Impact of anaerobic digestion on inhibition potential of Parthenium solids. Biomass and Bioenergy. 1998;14(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/S0961-9534(97)10019-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Khosla S. N., Sobti S. N. Effective control of Parthenium hysterophorus L. Pesticides. 1981;15(4):18–19. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tamado T., Ohlander L., Milberg P. Interference by the weed Parthenium hysterophorus L. with grain sorghum: influence of weed density and duration of competition. International Journal of Pest Management. 2002;48(3):183–188. doi: 10.1080/09670870110101739. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chippendale J. F., Panetta F. D. The cost of Parthenium weeds to the Queensland cattle industry. Plant Protection Quarantine. 1994;9:73–76. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fessehaie R., Chichayibelu M., Giorgis M. H. Spread and ecological consequences of Parthenium hysterophorus in Ethiopia. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2005;6:11–21. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mcconnachie A. J., Strathie L. W., Mersie W., et al. Current and potential geographical distribution of the invasive plant Parthenium hysterophorus (Asteraceae) in eastern and southern Africa. Weed Research. 2011;51(1):71–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3180.2010.00820.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Narasimhan T. R., Ananth M., Swamy M. N., Babu M. R., Mangala A., Rao P. V. S. Toxicity of Parthenium hysterophorus L. to cattle and buffaloes. Experientia. 1977;33(10):1358–1359. doi: 10.1007/BF01920179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yadav N., Saha P., Jabeen S., et al. Effect of methanolic extract of Parthenium hysterophorus on haematological parameters in wistar albino rat. The Bioscan—International Journal of Life Sciences. 2010;2:357–363. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wiesner M., Tessema T., Hoffmann A., et al. Impact of the Pan-Tropical Weed Parthenium hysterophorus L. on Human Health in Ethiopia. Berlin, Germany: Institute of Horticultural Science, Urban Horticulture; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sharma V. K., Verma P., Maharaja K. Parthenium dermatitis. Photochemical and Photobiological Sciences. 2013;12(1):85–94. doi: 10.1039/c2pp25186h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kushwaha V. B., Maurya S. Biological utilities of Parthenium hysterophorus . Journal of Applied Natural Science. 2012;4(1):137–143. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ray P., Gour H. N. Integrated management of Parthenium hysterophorus L. (Asteraceae): a weed of worldwide significance. Indian Society of Mycology and Plant Pathology. 2012;5:605–632. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Javaid A. Efficacy of some chemical herbicides against Parthenium hysterophorus L. Pakistan Journal of Weed Science Research. 2007;13:93–98. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mishra J. S., Bhan V. M. Efficacy of sulfonyl urea herbicides against Parthenium hysterophorus. Weed News. 1994;1, article 16 [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gaikwad C. B., Kasture M. C., Lambade B. M. Evaluation of herbicides for control of Parthenium in waste land. Indian Journal of Weed Science. 2008;40(1-2):79–81. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Khan H., Khan B. M., Hassan G., Khan M. A. Chemical control of Parthenium hysterophorus L. at different growth stages in non-cropped area. Pakistan Journal of Botany. 2012;44(5):1721–1726. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Njoroge J. M. Tolerance of Bidens pilosa L. and Parthenium hysterophorus L. to parquat (Gramooxone) in Kenya. Kenya Coffee. 1991;56:999–1001. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Singh S., Yadav A., Balyan R. S., Malik R. K., Singh M. Control of ragweed parthenium (Parthenium hysterophorus) and associated weeds. Weed Technology. 2004;18(3):658–664. doi: 10.1614/WT-03-128R2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Vila-Aiub M. M., Vidal R. A., Balbi M. C., Gundel P. E., Trucco F., Ghersa C. M. Glyphosate-resistant weeds of South American cropping systems: an overview. Pest Management Science. 2008;64(4):366–371. doi: 10.1002/ps.1488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ware G. W. Fundamentals of Pesticides: A Self Instruction Guide. 2nd. Fresno, Calif, USA: Thomson Publications; 1986. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Knox J. An investigation on suppressing capabilities of some allelopathic plants against Parthenium hysterophorus L. [Ph.D. thesis] Agra, India: Dr. B. R. Ambedkar University; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wahab S. Management of Parthenium through an integrated approach initiatives, achievements and research opportunities in India. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Parthenium Management; 2005; Bangalore, India. University of Agricultural Sciences; pp. 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kandasamy O. S., Sankaran S. Biological suppression of parthenium weed using competitive crops and plants. Proceeding of the 1st International Conference on Parthenium Management; 1997; Dahrwad, India. University of Agricultural Sciences; pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Javaid A., Anjum T., Bajwa R. Biological control of Parthenium II: allelopathic effect of Desmostachya bipinnata on distribution and early seedling growth of Parthenium hysterophorus L. International Journal of Biology and Biotechnology. 2005;2(2):459–463. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Watson A. K., Wymore L. A. New Directions in Biological Control: Alternatives for Suppressing Agricultural Pests and Diseases. New York, NY, USA: Academic Press; 1990. Identifying limiting factors in the biocontrol of weeds; pp. 305–316. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Aneja K. R. Antimicrobial Resistance from Emerging Threats to Reality. New Delhi, India: Narosa Publishing House; 2009. Biotechnology: an alternative novel strategy in agriculture to control weeds resistant to conventional herbicides; pp. 160–173. [Google Scholar]
- 39.El-Sayed W. Review biological control of weeds with pathogens: current status and future trends. Journal of Plant Disease Protection. 2005;112(3):209–221. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Müller-Schärer H., Scheepens P. C. Biological control of weeds in crops: a coordinated European research programme (COST-816) Integrated Pest Management Reviews. 1997;2(2):45–50. doi: 10.1023/A:1018428412868. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dhileepan K. Effectiveness of introduced biocontrol insects on the weed Parthenium hysterophorus (Asteraceae) in Australia. Bulletin of Entomological Research. 2001;91(3):167–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.TeBeest D. O., Templeton G. E. Mycoherbicides: progress in the biological control of weeds. Plant Diseases. 1985;69:6–10. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Watson A. K. Current advances in bioherbicides research. Proceedings of the British Crop Protection Conference; 1989; Brighton, UK. pp. 987–996. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Daniel J. T., Templeton G. M., Smith R. J., Fox W. T. Biological control of northern jointvetch in rice with an endemic fungal disease. Weed Science. 1973;21(4):303–307. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jayanth K. P. Introduction and establishment of Zygogramma bicolorata on Parthenium hysterophorus at Bangalore, India. Current Science. 1987;40:568–569. doi: 10.1017/S000748530002928X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Evans H. C., Ellison C. A. Classical biological control of weeds with microorganisms: past, present, prospects. Aspects of Applied Biology. 1990;24:39–49. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fauzi M. T., Tomley A. J., Dart P. J., Ogle H. J., Adkins S. W. The rust Puccinia abrupta var. partheniicola, a potential biocontrol agent of parthenium weed: environmental requirements for disease progress. Biological Control. 1999;14(3):141–145. doi: 10.1006/bcon.1998.0680. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Parker A. Biological controls of Parthenium weed using two rust fungi. Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds; 1989; Rome, Italy. Instituto Sperimentala per la Pathologia Vegetale (MAF); pp. 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Parmelee J. A. The autoecious species of Puccinia on Heliantheae in North America. Canadian Journal of Botany. 1967;45:2267–2327. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Tomley A. J. Puccinia melampodii (summer rust), a new biocontrol agent for parthenium weed. Proceedings of the 6th Queensland Weed Symposium; 2000; Queensland, Australia. Weed Science Society of Queensland; pp. 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kelaniyangoda D. B., Ekanayake H. M. R. K. Puccinia melampodii Diet. and Hollow as a biological control agent of Parthenium hysterophorus . Journal of Food and Agriculture. 2008;1:13–17. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Seier M. K., Harvey J. L., Romero A., Kinnersley R. P. Safety testing of the rust Puccinia melampodii as a potential biocontrol agent of Parthenium hysterophorus L. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Parthenium Management; October 1997; Dharwad, India. University of Agricultural Sciences; pp. 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Saxena S., Kumar M. Evaluation of alternaria alternata ITCC4896 for use as mycoherbicide to control Parthenium hysterophorus . Journal of Plant Protection Research. 2010;47:213–218. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Pandey A. K., Mishra J., Hasija S. K. Effect of inoculum on mycoherbicidal potential of Sclerotium rolfsii against Parthenium. Journal of Mycology and Plant Pathology. 1998;28:284–287. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shukla R., Pandey A. K. Maximization of production of oxalic acid from Sclerotium rolfsii, a mycoherbicidal agent against Parthenium . Annals of Plant Protection Science. 2006;14(1):202–205. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Aneja K. R., Khan S. A. Powdery mildew disease of congress grass—a new disease record. Journal of Mycopathological Research. 2000;38(1):53–54. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Satyaprasad K., Usharani P. Occurrence of powdery mildew on Parthenium caused by Oidium parthenii . Current Science. 1981;24:1081–1082. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kauraw L. P., Chile A., Bhan V. M. Evaluation of Fusarium pallidoroseum (Cooke) Sacc. For the biocontrol of Parthenium hysterophorus L. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Parthenium Management; October 1997; Dharwad, India. pp. 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Shabbir A. Towards the improved management of Parthenium weed: complementing biological control with plant suppression [Ph.D. thesis] School of Agriculture and Food Sciences, University of Queensland; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Evans H. C. Parthenium hysterophorus: a review of its weed status and the possibilities for biological control. Biocontrol News and Information. 1997;18:89–98. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Dhawan S. R., Dhawan P. Phyllosphere mycoflora of Parthenium hysterophorus L. World Weeds. 1995;2(3-4):203–210. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Evans H. C. The potential of neotropical fungal pathogens as classical biological control agents for management of Parthenium hysterophorus . Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Parthenium Management; October 1997; Dahrwad, India. University of Agricultural Sciences; pp. 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rao V. G. The genus Alternaria Nees. In Bombay, Maharastra-I. Sydowia. 1964;18:46–64. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chupp C. A Monograph of the Fungus Genus Cercospora. New York, NY, USA: Itaca; 1956. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Gayathri S., Pandey A. K. Preliminary assessment of Colletotrichum dematium as a potential mycoherbicide against Parthenium hysterophorus . Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Parthenium Management; 1997; Dharwad, India. University of Agricultural Sciences; pp. 92–94. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Rao A. P., Rao A. S. A new leaf spot disease of Parthenium . Current Science. 1979;48:p. 456. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kumar V., Rao A. S. Two new leaf spot diseases. Indian Phytopathology. 1977;30:118–120. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Aneja K. R., Kaur M., Sharma A. B. Leaf-spot disease of Parthenium hysterophorus, a new disease record. National Academy Science Letters. 1994;17:179–180. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Jeyalakshmi C., Doraisamy S., Paridasan V. V. Selection of fungal pathogens for managing Parthenium weed. Journal of Mycology and Plant Pathology. 2004;34:492–496. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Rao A. P., Rao A. S. New fungal diseases of some weeds. Indian Botanical Reporter. 1987;6:p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pandey A. K., Farkya S., Rajak R. C. A preliminary evaluation of Fusarium spp. for biological control of Parthenium . Journal of Indian Botanical Society. 1992;71:103–105. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kumar P. S., Singh S. P. First report of Lasiodiplodia theobromae as a foliar pathogen of Parthenium hysterophorus . Plant Disease. 2000;84(12):p. 1343. doi: 10.1094/PDIS.2000.84.12.1343C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Rajak R. C., Farakya S., Hasija S. K., Pandey A. K. Fungi associated with congress weed. Proceedings of Natural Academy of Science. 1990;60:165–168. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kumar P. S., Kumar P. R. P. A new leaf spot disease of Parthenium hysterophorus caused by Phoma sorghina . Indian Phytopathology. 2000;53(1):p. 115. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kumar S., Jayaraj S., Muthukrishanan T. S. Natural enemies of Parthenium hysterophorus L. Journal of Entomological Research. 1979;3:32–35. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ghasolia R. P., Shivpuri A. Parthenium hysterophorus-a new host record for Sclerotinia sclerotiorum . Journal of Mycology and Plant Pathology. 2004;34:242–243. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Siddaramaiah A. L., Narendrappa T., Shivalingaradhya M. V. A new collar rot disease of Parthenium from India. Plant Pathology Newsletter. 1984;2(2):p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Pandey A. K., Mishra J., Rajak R. C., Hasija S. K. Herbal Medicines, Biodiversity and Conservation Strategies. Dehradun, India: International Book Distributors; 1996. Potential of indigenous strains of Sclerotium rolfsii Sacc . for the management of Parthenium hysterophorus L.: a serious threat to biodiversity in India; pp. 104–138. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Patwardhan P. G. Some new records of powdery mildews fungi. Plant Disease Reporter. 1966;50:709–710. [Google Scholar]