Abstract
PIM1 is a proto-oncogene encoding the serine/threonine PIM1 kinase. PIM1 kinase plays important roles in regulating aspects of cell cycle progression, apoptosis resistance, and has been implicated in the development of such malignancies as prostate cancer and acute myeloid leukemia among others. Knockout of PIM1 kinase in mice has been shown to be non-lethal without any obvious phenotypic changes, making it an attractive therapeutic target. Our investigation of anthraquinones as kinase inhibitors revealed a series of quinone analogs showing high selectivity for inhibition of the PIM kinases. Molecular modeling studies were used to identify key interactions and binding poses of these compounds within the PIM1 binding pocket. Compounds 1, 4, 7 and 9 inhibited the growth of DU-145 prostate cancer cell lines with a potency of 8.21 μM, 4.06 μM, 3.21 μM and 2.02 μM.
Graphical abstract
Three isoforms (PIM-1, -2 and -3) of PIM kinases are encoded in the gene. The three members of the PIM family are serine/threonine kinases that exhibit very high homology and hence a certain amount of functional redundancy is found. These enzymes have little homology with the other members of protein kinase family. The PIM1 gene was initially identified as a proviral integration site in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced mouse T-cell lymphomas1, 2. PIM kinases are implicated in the development of solid tumors. DNA microarray analyses showed the overexpression of PIM1 in human prostate cancer in relation to the grade of the prostate cancer3. PIM kinases are critical mediators of hematopoeitic cell survival in both immunology and oncology4, 5. PIM kinases potently cooperate with Myc, block apoptosis, and induce oncogenic transformation6–8. Sustained PIM1 expression is induced by many cytokines, mitogens and growth factors and PIM1 has been shown to be a major downstream target of the STATs (signal transducer and activator of transcription)9, 10. PIM proteins role in human cancers such as prostate, pancreatic, colon, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and multiple myeloma is well established10–15. It has been found that the knockout of PIM1 in mice is not lethal and its absence does not induce any immediately obvious phenotype16. This makes PIM1 an attractive target for chemotherapy.
Many classes of ATP competitive small molecule PIM1 inhibitors have been recently reported such as the pan-kinase inhibitor staurosporine and its related bisindolylmalemides17, imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazines18, pyridones19, 20, flavonoids21, 22, benzoisoxazoles23, cinnamic acids24, thiazolidinones25, etc. Most of these molecules inhibit a variety of protein kinases, leading to questionable therapeutic value. Only SGI-1776 has been shown to fairly selective inhibitor of PIM kinases and demonstrated to effectively induce apoptosis in lymphocytic leukemia cells26, 27. Given the prominent role of PIM kinases in numerous types of cancers, there is an urgent need to find more lead compounds to be developed as PIM kinase inhibitors that can exhibit good kinase selectivity profile.
Recently several reports have been published solving the crystal structure of PIM1 revealing several interesting features that is unique to PIM kinases24, 28–32. The PIM1 protein has the typical secondary structural architecture with two domains connected by the hinge region apart from a distinctive N-terminal peptide sequence. The PIM kinases contain the unique consensus sequence ERPXPX in the hinge region. The hinge region is atypical due to presence of a proline residue, Pro123, capable of making only a single hydrogen bond to the natural substrate ATP. Of the five kinases that share such a characteristic, three of them belong to the PIM kinase family. The P-loop of PIM1 is glycine rich containing residues GSGGFG. These aspects could play an important role in determining the potency and specificity of inhibitors. Our searches for lead molecules as kinase inhibitors lead us to quinolines and anthraquinones. Emodin a natural anthraquinone isolated from Rheum emodi, is a Traditional Chinese Medicine. Emodin is an established tyrosine kinase inhibitor33 and has been shown to inhibit several kinases such as HER233, Pim134, Casein Kinase 235, DYRK1a36, SGK36, JAK237, etc.
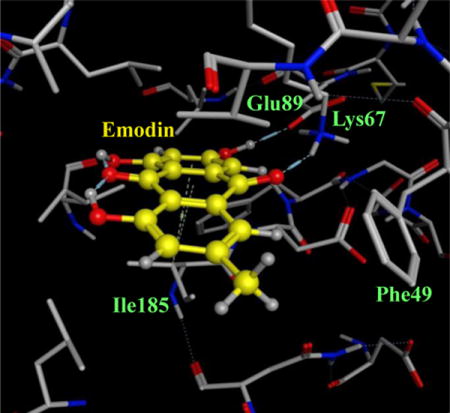
Emodin was docked into the crystal structure of Pim1 kinase to understand the interactions and the features of emodin responsible for these interactions (Figure 1). The consensus docking postures revealed that the Emodin did not make any hydrogen bonds with the hinge region residues. Emodin made two hydrogen bonds with the residues Lys67 and Glu89. Additional π-alkyl interaction of the emodin aromatic rings with the residue Ile185 was also evidenced. Many groups have solved the crystal structure of Pim1 and a total of 53 crystal structures were found deposited on the RCSB PDB website (http://www.rcsb.org)38. All the ligands in the crystal structures were ATP-competitive or ATP-mimetic. A study of the interactions of the numerous ligands to the Pim1 protein revealed that only on hydrogen bond was made by the ligands with the hinge region to the residue Glu121. Other hydrogen bonds that were made by the ligands involved the residues Gly45, Asp128, Glu171, Asn172, Asp186. Additionally, hydrophobic interactions and π-methyl interactions were found for these ligands with the Pim1 residues Phe49, Ile185 and Leu174. These insights helped during the search for Emodin analogs that could act as potential inhibitors of Pim1 kinase.
Figure 1.
(A) Binding mode of emodin to the ATP binding site of Pim1 kinase (PDB ID: 2O64.pdb). The protein residues are shown as stick models and the emodin moecule is shown as yellow ball & stick model. (C) The interactions depicted by emodin to the protein residues of Pim1
A 2D-pharmacophore involving the key functional groups of Emodin was designed and Sybyl-UNITY search was performed of the PUBCHEM and ZINC databases. The hitlist obtained was subjected to docking studies and based on the docking scores, a total of ~40 emodin analogues were chosen. The compounds 10, 12 and 14 were synthesized.
The precursor compound in the synthesis of compound 10, 2-formyl-1,4,5,8-tetramethoxynaphthalene, was synthesized through known literature procedure39. Compound 11 was obtained through a double Friedel-Crafts acylation using 1,4-dimethoxybenzene and 2-methylmaleic anhydride at high temperatures. Demethoxylation using HCl gave the desired product 11 (55%). (Figure 2-Scheme I). Reported attempts using radical initiator catalysts in the bromination of compound i resulted in no desired product formation40. Two 120W tungsten lamps were used to initiate hemolytic bond cleavage of NBS by placing the lamps close to the flask and allowing a vigorous reflux over 2h. Compound 12 was obtained after purification (32%) (Figure 2-Scheme I). Formation of the trimethylsilyl diene 13 (74%) in the synthesis of 14 proceeded through an LDA enolate reduction41. (Figure 2-Scheme II). The Diels-Alder cycloaddition between 13 and 1,4-quinone occurred slowly over 20h at 0°C. The corresponding hydroxynaphthoquinone 14 (37%) was obtained through hydrolysis using HCl (Figure 2-Scheme II). The synthesized compounds were characterized by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and Mass spectroscopies. All compounds had characteristic peaks with appropriate spectroscopic values (The experimental methods and spectroscopic charaterizations are detailed in Supporting information). An initial high-throughput in-vitro screen at 10μM concentration of all of the compounds and emodin showed that eight compounds exhibited perceptible inhibition of Pim1 kinase (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
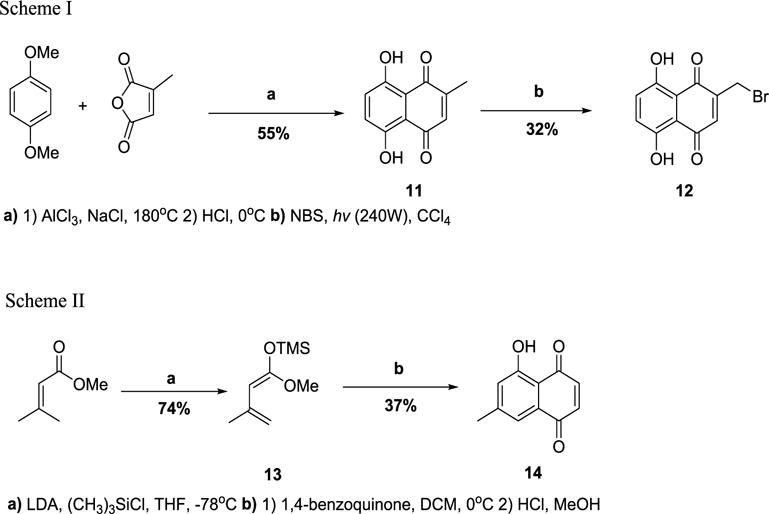
Schemes I and II outline the synthesis of compounds 12 and 14.
Figure 3.
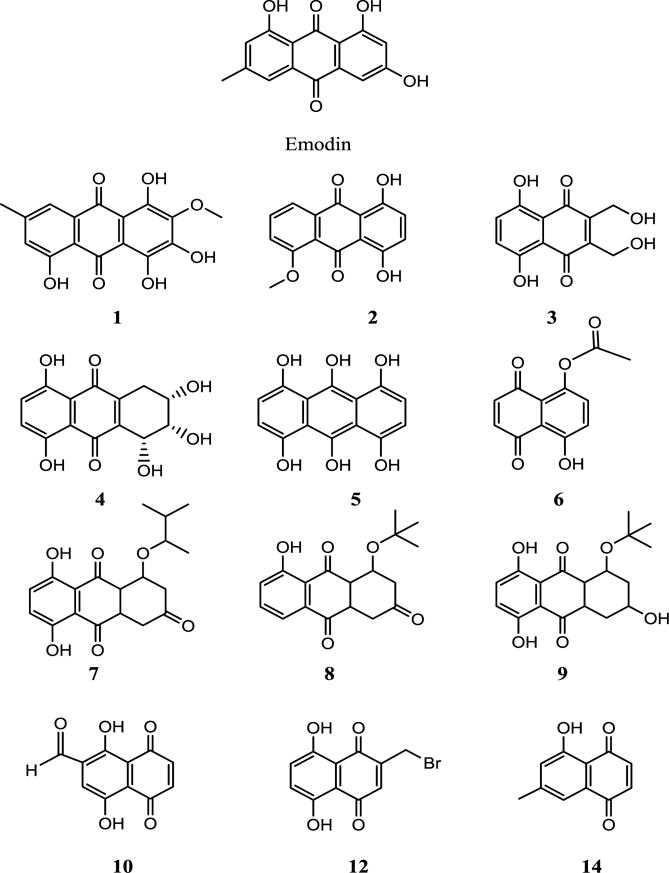
Structures of Emodin and compounds 1–10, 12 and 14 investigated for inhibition of Pim1 kinase.
Since Emodin inhibited numerous kinases, the selectivity of the analogues chosen needed to be evaluated first. At this time Chemical Computing group (CCG) introduced a new module in MOE for kinase search. The kinase search module uses a database of kinases aligned globally. The kinase detection algorithm employed in MOE is based on the alignments with the kinase reference collections within the Hank’s regions. Additionally a database containing a broad collection of chemical scaffolds or building blocks of available kinase inhibitors has been compiled in MOE. This database contains structures belonging to 10 classes of inhibitors (adenosines, staurosporines, oxoindoles, purines, isoquinolines, quinazlines, ureas, imidazoles, aminopyrimidines, and anthraquinones) along with the SMARTS strings that can be used for substructure search. The kinase search module had the option of ligand similarity search using tanimoto distance cutoff property to identify kinases that could be the potential target of the compound under study. Compound 4 was used as the study compound and an initial tanimoto cutoff value of 0.80 was specified. The results displayed only those structures that belonged to casein kinase II. This could have been the due of the presence of a crystal structure of casein kinase II with Emodin as the bound ligand. The stringent tanimoto distance cutoff value was relaxed to 0.60 for the next kinase search. The results (Figure 4) presented 5 protein kinases that could be the potential target for inhibition- CK2 (43%), Pim kinases (29%), SRC kinase (14%), CDK (7%) and DAPK (7%). These five kinases belonged to the three families CMGC (50%), CAMK (36%) and TK (14%).
Figure 4.
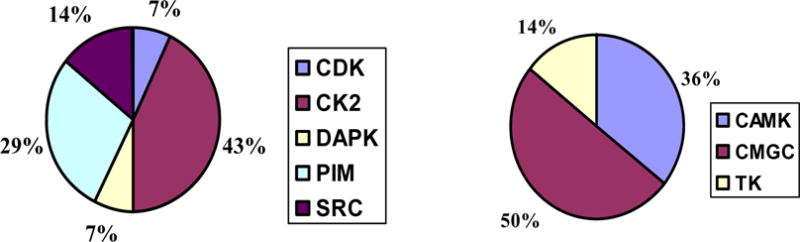
The results of kinase search in MOE using the 2D structure of compound 4. The pie charts represent the identity of kinase structure hits for each family of kinases and the group for which these kinases belong.
To understand the significance of the kinase selectivity search using MOE computing program, compound 4 was evaluated against a panel of 100 kinases at KINOMEscan (www.kinomescan.com). The compound(s) were screened at the 10 μM concentration, and results for primary screen binding interactions are reported as ‘% Ctrl’, where lower numbers indicate stronger hits.
The results presented in supporting information table 1 show that compound 4 that the only protein kinases strongly inhibited are CSNK1D (30% control at 10μM), Pim1 (34% control at 10μM) and Pim3 (36% control at 10μM). The selectivity score S(35) was calculated as 0.022. The KINOMEscan results were in excellent agreement with the kinase search performed in MOE with casein kinase and Pim kinases being the main protein kinases to be targeted by compound 4.
The dose response curves were performed for the inhibition of Pim1 kinase by Emodin, the eight compounds identified in the initial high-throughput screening (compounds 1–9) and three synthesized compounds (compounds 10, 12 and 14) (Table 1). Emodin exhibited an IC50 value of 2.5 μM in the in-vitro assay. Compounds 3, 6, 7 and 9 showed IC50 values of 7.4 μM, 3.0 μM, 3.6 μM and 3.5 μM which were equivalent to that of Emodin. Compound 2 and 4 presented IC50 values of 11.6 μM and 19.2 μM which were in the low micro molar range and close to that of Emodin. Only compound 5 showed poor inhibition potency for Pim1 kinase with an IC50 value of 57.1 μM. Compounds 10, 12, and 14 were found to have IC50 values of 28 μM, 27 μM, and 28 μM, respectively.
Table 1.
Inhibition of Pim1 kinase by emodin and compounds 1 to 10, 12 and 14.
| Compound | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|
| Emodin | 2.5 |
| 1 | 21.4 |
| 2 | 11.6 |
| 3 | 7.4 |
| 4 | 19.2 |
| 5 | 57.1 |
| 6 | 3.0 |
| 7 | 3.6 |
| 8 | 23.8 |
| 9 | 3.5 |
| 10 | 28.0 |
| 11 | 27.0 |
| 12 | 28.0 |
Pim1 is highly expressed in a significant fraction of human prostate cancer in which c-MYC was also overexpressed. It was determined that synergistic interaction of Pim1 and c-MYC was critically dependent on Pim1 kinase activity implying that inhibition of Pim1 kinase activity should be effective in cancer treatment. To determine whether these compounds were effective in-vivo, we tested the growth inhibitory properties of Emodin and compounds 1, 4, 7 and 8 on the human prostate cancer cell line DU-145 that is known to express PIM-142. Figure 5 shows that compounds 1, 4, 7, 9 and Emodin inhibit the growth of DU-145 cells with an IC50 of 3.93 μM, 8.21 μM, 4.06 μM, 3.21 μM and 2.02 μM. These data show that the Emodin and its analogs show good promise in anticancer activities on prostate cancer cell lines.
Figure 5.
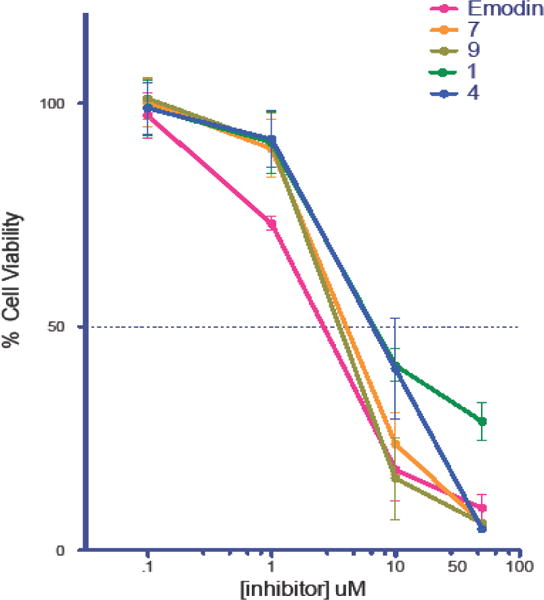
Growth inhibition curve for DU-145 cells treated with compounds 1, 4, 7, 9 and Emodin.
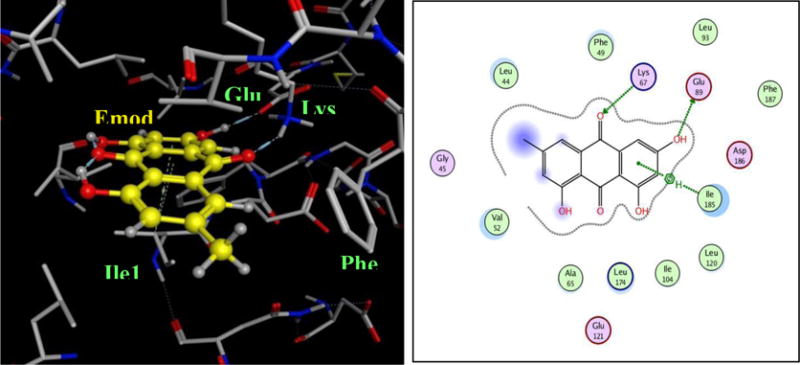
Docking studies of Emodin and compounds 1–6 were performed on the known crystal structure of Pim1 kinase protein (PDB ID: 2O64.pdb). The binding modes of compounds 1–6 to Pim1 protein were similar to that of Emodin in that they occupied the ATP-binding pocket, but did not show any hydrogen bonding interaction with the hinge region residues (Figure 5). One of the carbonyl groups and its adjacent hydroxyl group of the compounds makes hydrogen bonds to the side chains of two highly conserved residues, Lys67 and/or Glu89. The binding interactions of the compounds with the best inhibition potency are shown in figure 5A for compound 3 and figure 5B for compound 6. The binding postures show the planar portion of the molecules aligned in the cavity in such a way that π-alkyl group interactions could be maximized with the numerous hydrophobic residues lining the top and bottom regions of the binding site. From a study of all the available crystal structures and the co-crystallography study by the Bremer group29, it is evident that all of the small molecule inhibitors bind in the ATP binding site of Pim1, and most of them are localized near the hinge and the conserved Lys67/Glu89/Phe187 region. The fact that our compounds bind to Lys67 and/or Glu89, demonstrates that they satisfy the requirements of hydrogen bonding to Lys67/Glu89 region as exemplified by the previous studies Pim1. The docking scores of the compounds had a trend similar to that of their inhibition potency with the more potent compounds having lower scores indicating more favorable poses (supporting document, table 2).
In conclusion, a new series of compounds have been identified as inhibitors of Pim1 kinase. They have excellent effect on the arrest of growth in the prostate cancer cells DU145. The selectivity of the representative compound 4 for the Pim1, Pim2 and CSNK1D was discovered by the KINOMEscan assay against a panel of 100 kinases. Docking studies have revealed the binding orientations of these molecules in the ATP-binding cavity of the Pim1 protein. The insights obtained from the docking studies will help us to design and develop new Pim1 inhibitors with improved potency while maintaining the selectivity for Pim kinases.
Supplementary Material
Figure 6.
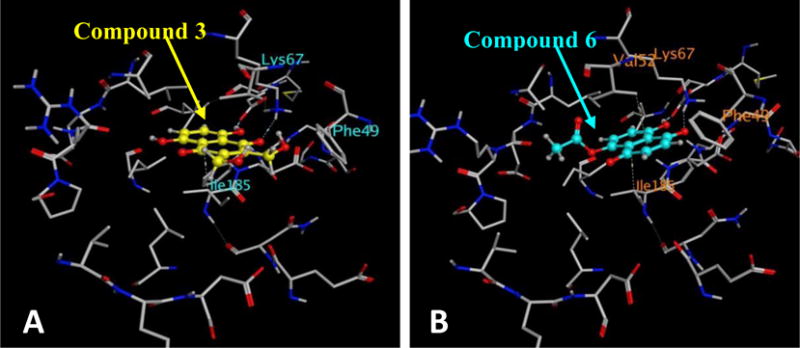
Binding mode of compounds 3 (A) and 6 (B) to the ATP-binding pocket of Pim1 kinase (PDB ID: 2O64.pdb). The protein is shown as stick model and the ligands are shown as ball
Acknowledgments
This research work was funded by the NIH-RCMI (2G12MD007595-06) from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities and the startup grant by the Louisiana Cancer Research Consortium. Additional support from the Department of Defense Award (W81XWH-11-1-0105), the Louisiana Biomedical Research Network (LBRN-P20GM103424) is greatfully acknowledged. We thank the NIH-BUILD Grant—TL4MD009607 and the Center for Undergraduate Research at Xavier University of Louisiana for supporting the students who worked on this project. The contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not represent the official views of NIH.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Supplementary data
Supplementary data (synthetic protocols, compound characterization data, assay details, and supplementary figures) associated with this article can be found in the online version.
References
- 1.Cuypers HT, Selten G, Quint W, Zijlstra M, Maandag ER, Boelens W, van Wezenbeek P, Melief C, Berns A. Cell. 1984;37:141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Selten G, Cuypers HT, Berns A. EMBO J. 1985;4:1793. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dhanasekaran SM, Barrette TR, Ghosh D, Shah R, Varambally S, Kurachi K, Pienta KJ, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM. Nature. 2001;412:822. doi: 10.1038/35090585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Domen J, van der Lugt NM, Laird PW, Saris CJ, Berns A. Leukemia. 1993;7(Suppl 2):S108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.van der Lugt NM, Domen J, Verhoeven E, Linders K, van der Gulden H, Allen J, Berns A. EMBO J. 1995;14:2536. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07251.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Allen JD, Verhoeven E, Domen J, van der Valk M, Berns A. Oncogene. 1997;15:1133. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.van Lohuizen M, Verbeek S, Krimpenfort P, Domen J, Saris C, Radaszkiewicz T, Berns A. Cell. 1989;56:673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90589-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Verbeek S, van Lohuizen M, van der Valk M, Domen J, Kraal G, Berns A. Mol Cell Biol. 1991;11:1176. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Matikainen S, Sareneva T, Ronni T, Lehtonen A, Koskinen PJ, Julkunen I. Blood. 1999;93:1980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang Z, Bhattacharya N, Weaver M, Petersen K, Meyer M, Gapter L, Magnuson NS. J Vet Sci. 2001;2:167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Grundler R, Brault L, Gasser C, Bullock AN, Dechow T, Woetzel S, Pogacic V, Villa A, Ehret S, Berridge G, Spoo A, Dierks C, Biondi A, Knapp S, Duyster J, Schwaller J. J Exp Med. 2009;206:1957. doi: 10.1084/jem.20082074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li YY, Popivanova BK, Nagai Y, Ishikura H, Fujii C, Mukaida N. Cancer Res. 2006;66:6741. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pasqualucci L, Neumeister P, Goossens T, Nanjangud G, Chaganti RS, Kuppers R, Dalla-Favera R. Nature. 2001;412:341. doi: 10.1038/35085588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Popivanova BK, Li YY, Zheng H, Omura K, Fujii C, Tsuneyama K, Mukaida N. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:321. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Valdman A, Fang X, Pang ST, Ekman P, Egevad L. Prostate. 2004;60:367. doi: 10.1002/pros.20064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Laird PW, van der Lugt NM, Clarke A, Domen J, Linders K, McWhir J, Berns A, Hooper M. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993;21:4750. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.20.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bullock AN, Debreczeni JE, Fedorov OY, Nelson A, Marsden BD, Knapp S. J Med Chem. 2005;48:7604. doi: 10.1021/jm0504858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pogacic V, Bullock AN, Fedorov O, Filippakopoulos P, Gasser C, Biondi A, Meyer-Monard S, Knapp S, Schwaller J. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6916. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cheney IW, Yan S, Appleby T, Walker H, Vo T, Yao N, Hamatake R, Hong Z, Wu JZ. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007;17:1679. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.12.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Knight ZA, Shokat KM. Chem Biol. 2005;12:621. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2005.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Holder S, Lilly M, Brown ML. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15:6463. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.06.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Holder S, Zemskova M, Zhang C, Tabrizizad M, Bremer R, Neidigh JW, Lilly MB. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:163. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pierce AC, Jacobs M, Stuver-Moody C. J Med Chem. 2008;51:1972. doi: 10.1021/jm701248t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Qian K, Wang L, Cywin CL, Farmer BT, 2nd, Hickey E, Homon C, Jakes S, Kashem MA, Lee G, Leonard S, Li J, Magboo R, Mao W, Pack E, Peng C, Prokopowicz A, 3rd, Welzel M, Wolak J, Morwick T. J Med Chem. 2009;52:1814. doi: 10.1021/jm801242y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xia Z, Knaak C, Ma J, Beharry ZM, McInnes C, Wang W, Kraft AS, Smith CD. J Med Chem. 2009;52:74. doi: 10.1021/jm800937p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Magnuson NS, Wang Z, Ding G, Reeves R. Future Oncol. 2010;6:1461. doi: 10.2217/fon.10.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mumenthaler SM, Ng PY, Hodge A, Bearss D, Berk G, Kanekal S, Redkar S, Taverna P, Agus DB, Jain A. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:2882. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jacobs MD, Black J, Futer O, Swenson L, Hare B, Fleming M, Saxena K. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:13728. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413155200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kumar A, Mandiyan V, Suzuki Y, Zhang C, Rice J, Tsai J, Artis DR, Ibrahim P, Bremer R. J Mol Biol. 2005;348:183. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.02.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Qian KC, Wang L, Hickey ER, Studts J, Barringer K, Peng C, Kronkaitis A, Li J, White A, Mische S, Farmer B. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:6130. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409123200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schulz MN, Fanghanel J, Schafer M, Badock V, Briem H, Boemer U, Nguyen D, Husemann M, Hillig RC. Acta Crystallogr, Sect D. 2011;67:156. doi: 10.1107/S0907444910054144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Xiang Y, Hirth B, Asmussen G, Biemann HP, Bishop KA, Good A, Fitzgerald M, Gladysheva T, Jain A, Jancsics K, Liu J, Metz M, Papoulis A, Skerlj R, Stepp JD, Wei RR. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011;21:3050. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang L, Lau YK, Xi L, Hong RL, Kim DS, Chen CF, Hortobagyi GN, Chang C, Hung MC. Oncogene. 1998;16:2855. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cozza G, Mazzorana M, Papinutto E, Bain J, Elliott M, di Maira G, Gianoncelli A, Pagano MA, Sarno S, Ruzzene M, Battistutta R, Meggio F, Moro S, Zagotto G, Pinna LA. Biochem J. 2009;421:387. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yim H, Lee YH, Lee CH, Lee SK. Planta Med. 1999;65:9. doi: 10.1055/s-1999-13953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sarno S, de Moliner E, Ruzzene M, Pagano MA, Battistutta R, Bain J, Fabbro D, Schoepfer J, Elliott M, Furet P, Meggio F, Zanotti G, Pinna LA. Biochem J. 2003;374:639. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Muto A, Hori M, Sasaki Y, Saitoh A, Yasuda I, Maekawa T, Uchida T, Asakura K, Nakazato T, Kaneda T, Kizaki M, Ikeda Y, Yoshida T. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:987. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:235. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tanoue YT. A Bull Chem Soc Jpn. 1988;61:2039. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dessolin J, Biot C, Davioud-Charvet E. J Org Chem. 2001;66:5616. doi: 10.1021/jo010137n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tietze LF, Gericke KM, Singidi RR, Schuberth I. Org Biomol Chem. 2007;5:1191. doi: 10.1039/b700838d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hu XF, Li J, Vandervalk S, Wang Z, Magnuson NS, Xing PX. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:362. doi: 10.1172/JCI33216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


