Abstract
Objective:
Objective platelet function assessment after cardiac surgery can predict postoperative blood loss, guide transfusion requirements and discriminate the need for surgical re-exploration. We conducted this study to assess the predictive value of point-of-care testing platelet function using the Multiplate® device.
Methods:
Patients undergoing isolated coronary artery bypass grafting were prospectively recruited (n = 84). Group A (n = 42) patients were on anti-platelet therapy until surgery; patients in Group B (n = 42) stopped anti-platelet treatment at least 5 days preoperatively. Multiplate® and thromboelastography (TEG) tests were performed in the perioperative period. Primary end-point was excessive bleeding (>2.5 ml/kg/h) within first 3 h postoperative. Secondary end-points included transfusion requirements, re-exploration rates, intensive care unit and in-hospital stays.
Results:
Patients in Group A had excessive bleeding (59% vs. 33%, P = 0.02), higher re-exploration rates (14% vs. 0%, P < 0.01) and higher rate of blood (41% vs. 14%, P < 0.01) and platelet (14% vs. 2%, P = 0.05) transfusions. On multivariate analysis, preoperative platelet function testing was the most significant predictor of excessive bleeding (odds ratio [OR]: 2.3, P = 0.08), need for blood (OR: 5.5, P < 0.01) and platelet transfusion (OR: 15.1, P < 0.01). Postoperative “ASPI test” best predicted the need for transfusion (sensitivity - 0.86) and excessive blood loss (sensitivity - 0.81). TEG results did not correlate well with any of these outcome measures.
Conclusions:
Peri-operative platelet functional assessment with Multiplate® was the strongest predictor for bleeding and transfusion requirements in patients on anti-platelet therapy until the time of surgery. Study registration: ISRCTN43298975 (http://www.controlled-trials.com/ISRCTN43298975/).
Keywords: Anti-platelet therapy, Bleeding, Coronary artery bypass grafting, Multiplate, Platelet Dysfunction, Platelet function assessment
INTRODUCTION
Patients suffering from coronary artery disease are usually advised to stop anti-platelet medication a few days prior to coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) to reduce the incidence of postoperative bleeding.[1] However, discontinuation of anti-platelet therapy increases the risk of early graft thrombosis after CABG and hence, anti-platelet therapy is often continued until the day of surgery.[2,3,4,5] Besides, patients who had recent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) need to continue anti-platelet medications until the day of surgery to prevent stent thrombosis.[2,3,4,5]
However, patients who are still on anti-platelet drugs are at an increased risk of postoperative bleeding.[2,6,7,8] Transfusions of blood and blood products have got deleterious effects, and hence efforts should be made to minimize transfusion.[9,10,11,12] Currently, the transfusion of blood and blood components to manage postoperative bleeding after CABG remains largely empirical, with considerable variation among institutions.[9,13]
Algorithm-based hemostatic therapy has been shown to be superior to empiric hemostatic therapy that is based on clinical judgment.[9,10,11,12,13] Hence, there is a need to have objective tests to demonstrate platelet dysfunction before platelet transfusion.[9,13] Several platelet function tests have been reported in clinical studies to evaluate platelet dysfunction and quantify the need for anti-platelet therapy.[2,9] The recently introduced point-of-care (POC) machine, the Multiplate® analyzer (Multiplate®, Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany), allows objective evaluation of platelet aggregation after using agonists by detecting changes in electrical resistance in whole blood.[14,15]
We hypothesized that objective measurement of platelet function after cardiac surgery can be useful in prediction of postoperative blood loss and in guiding postoperative transfusion requirements (blood and platelets) and the need for surgical re-exploration. Hence, the predictive accuracy of thromboelastography (TEG: Hemoscope Inc., Niles, IL, USA) and Multiplate® analyzer was compared.
METHODS
Patients undergoing 1st time isolated CABG on cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) (n = 84) were enrolled in the study. Group A (n = 42) included patients who were on anti-platelet drugs until the day of surgery. Patients in Group B (n = 42) stopped anti-platelet drugs at least 5 days preoperatively. This was a prospective, controlled, double-blind, single center trial. The trial was approved by the National Research Ethics Committee (NREC, 05/07/2011, Ref: 11/WM/0130). The trial was registered with the ISRCTN Register: ISRCTN43298975-http://www.controlled-trials.com/ISRCTN43298975/. The study was partly funded by the local cardiothoracic services charitable fund. Exclusion criteria included severe liver or renal dysfunction (altered liver function test, creatinine >200 μmol/L) and patients with known bleeding diathesis amongst others. All patients signed informed consent.
The primary endpoint was to correlate excessive postoperative bleeding defined as blood loss in excess of 2.5 ml/kg/h in the immediate 3 h, with the presence of platelet dysfunction as assessed by Multiplate® and TEG. The secondary outcome measures were transfusion requirements for blood and blood products, overall blood loss within 8 h of surgery, postoperative complications, intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay and hospital length of stay.
Patients enrolled in the study were managed according to institutional routine during the intra-operative and postoperative period. The latter included a blood-transfusion trigger set at 8 g/dl and transfusion of blood products based on the clinical picture, TEG results and clinician's decision. TEG is part of our routine practice. Aprotinin was not administered to any of the patients. Power calculations for this study confirmed that for a power of 0.9 and an alpha of 0.01, 40 patients were needed in each group.
Blood was sampled for Multiplate® (ASPI and adenosine diphosphate [ADP] tests) and TEG (R, MA) assessments before induction of anesthesia (preoperative) and after protamine administration after cessation of CPB (postoperative).
Multiple platelet function analyzer (Multiplate®) is whole blood test based on measurement of electrical impedance.[2,16,17,18,19,20] The method has been previously described.[19,20,21,22,23,24] It is a multiple electrode (five independent channels) platelet aggregation monitoring system with electronic pipetting and integrated computer analysis. Only 0.3 ml of whole blood is required per test. The Multiplate® machine has single use test cells with two sensor units. Adhesion and aggregation of platelets on the sensor surface enhances the electrical resistance between the two sensor wires and the increase of impedance is detected for each sensor unit separately and transformed to arbitrary aggregation units (AUs) that are plotted against time. The second sensor serves as an internal control.
Blood samples were collected into double walled Hirudin tubes (Roche Diagnostics, UK). Following a 3 min incubation adhesion and aggregation of platelets was measured for 6 min via the change of electrical resistance between two sensor wires.[15] Platelet aggregation was initiated by 32 μM thrombin receptor-activating peptide 6 (TRAP test), 0.5 mM arachidonic acid (ASPI test), or 6.4 μM ADP test using commercially available reagents (Roche Diagnostics, UK). Platelet aggregation in each test was quantified by the area under the aggregation curve (AUC) given in AUs (U). The units we used were U (not AU as reported by Weber et al.[9]), as recommended by the manufacturers in recent years (U = AU/10). The reference ranges for healthy subjects given by the manufacturer were 84-128 U for the TRAP test, 71–115 U for the ASPI test, and 57–113 U for the ADP test. Standard quality control procedures for each device were routinely performed as per the manufacturer's instructions. Since the change in impedance was measured simultaneously on two sensor units, the results of each test represented the mean value of the two aggregation curves obtained.[15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] Performance of POC testing required approximately 9 min. No additional manpower was required to perform these tests.
Statistical analysis
Patients’ demographics and clinical characteristics data, preoperative and postoperative laboratory data along with the POC tests data were prospectively collected. Data pertaining to the secondary outcome measures was also recorded. Anesthetists and surgeons (clinicians managing the patient on CICU) were blinded to the results of the Multiplate® measurements.
The data was analyzed using SPPS version 11.5 (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA). Continuous data is expressed as the mean (standard deviation) for Gaussian distributed data and median (range) for skewed data and any difference between the two groups was tested using the t-test and nonparametric test respectively. Nominal data is expressed as percentages, and any difference was assessed using the Chi-squared test. A P < 0.05 was considered significant.
RESULTS
Table 1 shows baseline demographic, clinical and laboratory tests data. There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of age and gender or risk stratification scores. There were more diabetics and “in-hospital urgent” patients in Group A. There were no significant differences in postoperative complications, e.g. atrial fibrillation, wound infection, renal and pulmonary complications [Table 2]. Median ICU stay was 2 (0, 9) days for Group A and 1 (1, 13) day for Group B (P = 0.002). Median in-hospital stay was 5.5 (3, 18) and 4 (3, 18) days, respectively (P = 0.02). There were no drop-outs in our study.
Table 1.
Pre-operative characteristics of patients from the two groups (Group A: continued anti-platelet medication until surgery, Group B: stopped anti-platelet medication at least five days prior to surgery)
| Group A (n=42) | Group B (n=42) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age* (years) | 62 (11) | 63 (10) | 0.7 |
| Pre-op Hb* (g/dl) | 13.7 (1.6) | 14.3 (1.3) | 0.06 |
| Log Euroscore* | 3.8 (3.5) | 3.2 (4.6) | 0.02 |
| Male (n, %) | 38, 91% | 36, 86% | 0.4 |
| Urgent surgery (n, %) | 29, 69% | 3, 7% | <0.01 |
| Diabetics (n, %) | 15, 36% | 10, 24% | <0.01 |
| PVD (n, %) | 10, 24% | 9, 21% | 0.1 |
*denotes mean (SD), PVD: Peripheral Vascular Disease Preop Hb: Preoperative Haemoglobin, Log Euroscore: Logistic Euroscore
Table 2.
Intra-op and post-op data for the two groups including post-op outcomes
| Group A (n=42) | Group B (n=42) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPB time* (minutes) | 98 (27) | 89 (20) | 0.08 |
| 8-hr blood loss* (ml/kg/hr) | 8.01 (6.9) | 4.98 (3.0) | 0.02 |
| CICU stay** (days) | 2 (0,9) | 1 (1,13) | <0.01 |
| In-hospital stay** (days) | 5.5 (3,18) | 4.0 (3,18) | 0.02 |
| Excessive bleeding (n, %) | 24, 59% | 14, 33% | 0.02 |
| Re-exploration (n, %) | 6, 14% | 0, 0% | 0.01 |
| Atrial Fibrillation (n, %) | 8, 19% | 9, 21% | 0.5 |
| Chest infection (n, %) | 1, 2% | 1, 2% | 0.7 |
| CVVHF (n, %) | 0, 0% | 1, 2% | 0.5 |
| Blood transfusion (n, %) | 17, 41% | 6, 14% | <0.01 |
| Platelet transfusion (n, %) | 6, 14% | 1, 2% | 0.05 |
| FFP transfusion (n, %) | 3, 7% | 0, 0% | 0.12 |
| Blood transfusion** (units) | 0 (0,15) | 0 (0,3) | <0.01 |
| Platelet transfusion** (units) | 0 (0,5) | 0 (0,1) | 0.04 |
| FFP transfusion** (units) | 0 (0,4) | 0 (0,0) | 0.08 |
*denotes mean (SD), **denotes median (range), Excessive bleeding = >2.5ml/kg/hr for first 3 hours post-op, CPB: Cardiopulmonary Bypass, CICU: Cardiac Intensive Care Unit, CVVHF: Continuous Veno-Venous Haemofiltration, FFP: Fresh Frozen Plasma
There were significant differences immediately postoperative with excessive bleeding (>2.5 ml/kg/h) (59% vs. 33%, P = 0.02), higher re-exploration rates (14% vs. 0%, P < 0.01) and a higher rate of blood (41% vs. 14%, P < 0.01) and platelet transfusion (14% vs. 2%, P = 0.05), in Group A.
All patients enrolled in this study were discharged and were alive at 30 days.
On multivariate analysis, preoperative platelet function testing was the most significant predictor of excessive bleeding (odds ratio [OR]: 2.3, P = 0.08), need for blood transfusion (OR: 5.5, P < 0.01) and platelet transfusion (OR: 15.1, P < 0.01). Factors included in the multivariate model included age, gender, diabetes, Log EuroScore, preoperative hemoglobin level, priority of surgery, CPB time, preoperative and postoperative TEG values (R, MA) and preoperative and postoperative ASPI values.
Preoperative “ASPI test” predicted the need for platelet transfusion (sensitivity - 0.86, negative predictive value - 0.98). Postoperative “ASPI test” best predicted the need for blood transfusion (sensitivity - 0.86) and excessive blood loss (sensitivity - 0.81). TEG results did not correlate well with any of these outcome measures. The AUC (receiver operating characteristic) for the TEG R value and MA value predicting the need for either blood transfusion or platelet transfusion was 0.53 and 0.51 respectively. TEG did not predict the need for platelet transfusion even in a single “excessive-bleeding” patient (>2.5 ml/kg/hr) and had a negative predictive value of 0.91. The ASPI and TEG data distributions are illustrated in Figures 1 and 2. Table 3 depicts the platelet function test results (both preoperatively and postoperatively) along with the TEG results.
Figure 1.
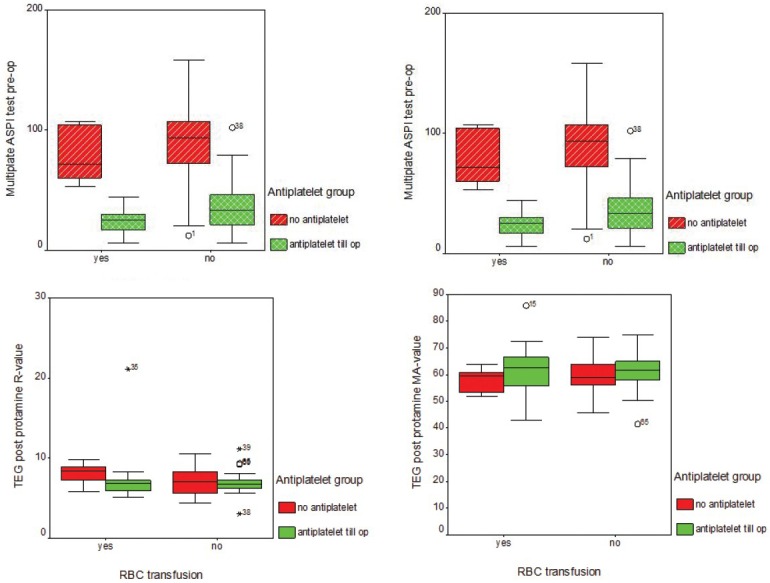
Box-plots for the data distribution in relation to need for blood transfusion. Multiplate analyser for ASPI (immediately pre-op and post protamine) showing significantly (p<0.01) low values for Group A (anti-platelet till day of surgery) TEG data (R and MA) post protamine demonstrating no significant differences (p=0.4) between the values for Groups A & B and hence non-predictive for the need for blood transfusion.
Figure 2.
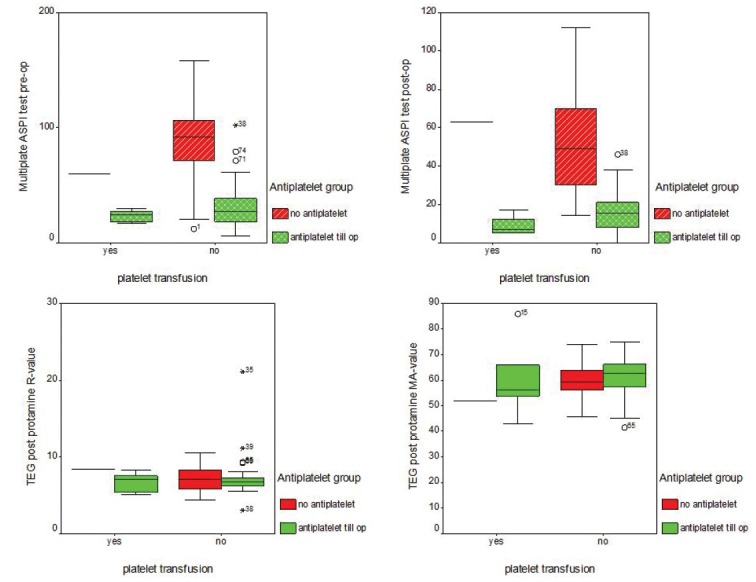
Box-plots for the data distribution in relation to need for platelet transfusion. Multiplate analyser for ASPI (immediately pre-op and post protamine) showing significantly (p<0.01) low values for Group A (anti-platelet till day of surgery) TEG data (R and MA) post protamine demonstrating no significant differences (p=0.2) between the values for Groups A & B and hence non-predictive for the need for platelet transfusion.
Table 3.
Platelet Function Test Results (Preoperatively and postoperatively) and TEG results
| Group A (n=42) | Group B (n=42) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-op data | |||
| ASPI | 30.8 (20) | 88.4 (30) | <0.01 |
| ADP | 68.6 (28) | 74.6 (27) | 0.6 |
| TEG - R value | 8.3 (2.3) | 7.4 (1.9) | 0.1 |
| TEG - MA value | 72.3 (7) | 68.9 (6) | 0.04 |
| TEG - Angle | 59.8 (10) | 60.1 (7) | 0.9 |
| Post-op data | |||
| ASPI | 15.4 (10) | 51.7 (26) | <0.01 |
| ADP | 37.2 (25) | 48.3 (25) | 0.01 |
| Plain samples | |||
| TEG - R value | 7.1 (3) | 7.2 (2) | 0.4 |
| TEG - MA value | 61.3 (9) | 59.3 (6) | 0.2 |
| TEG - Angle | 59.6 (10) | 58.2 (6) | 0.2 |
| Heparinase samples | |||
| TEG - R value | 6.6 (1) | 6.6 (2) | 0.9 |
| TEG - MA value | 60.7 (8) | 58.2 (6) | 0.08 |
| TEG - Angle | 62.0 (8) | 59.4 (9) | 0.2 |
DISCUSSION
Although it would be preferable to stop the use of aspirin preoperatively (to reduce postoperative bleeding and transfusion requirement), there are a number of situations when this may not be possible.[1,2] The latter includes patients who have recently experienced a myocardial infarction or who have had PCI as well as reported issues with withdrawal of anti-platelet medications (risk of thrombosis, risk of acute coronary events).[1,2,4]
Point-of-care testing has been reported to be associated with a reduced requirement for transfusion of blood products and can improve outcomes.[9,25] Weber et al. showed reduction in mortality with the use of POC testing though the study was not powered to test mortality reduction.[9]
The pathophysiology of bleeding after cardiac surgery is multifactorial and hence standard laboratory tests are of limited value.[1,2,9] Conventional laboratory tests for bleeding are quantitative in nature, time-consuming (with a median reported time 53–88 min) and nearly twice as expensive as POC guided coagulation management.[9,16,26] POC tests provide a functional assessment and are consequently more representative of in vivo coagulation than conventional laboratory tests.[9,25]
Several POC tests have been described to monitor platelet function in order to stratify bleeding risk and guide anti-platelet therapy.[1,2,6] TEG is a commonly performed test, and maximum amplitude is used as a surrogate for clot strength, platelet activity and fibrinogen level.[2,6,27,28] A number of platelet function tests are currently available.[2,6] Classical aggregometry otherwise known as light transmission aggregometry (LTA) takes a significant amount of time to perform, and sample processing is complex.[2,6,14] LTA assesses platelet activation by the reduction of optical density of platelet rich plasma. It requires preparation of platelet rich and platelet poor plasma.[29] PFA-100 has a high rate of false positive and false negative results and does not predict bleeding risk.[1,30] Therefore, none of the above-mentioned platelet function tests are recommended for the routine monitoring of the effects of anti-platelet therapy[18,22,28] as they are either laborious, time consuming or the predictive value of these tests in management of postoperative bleeding is as yet unclear.[2,6,17,27,28]
Multiple electrode aggregometry (MEA, Multiplate®) is an impedance aggregometry test which tests whole-blood.[17,18,25] In contrast to classical aggregometry, there is no centrifugation of plasma required or no adjustment of plasma concentration.[6,14,15,17] Multiplate® is relatively simple to perform.[6,14,15] The turnaround time for Multiplate is around 9 min, including 3 min for incubation of the blood sample.[6,9,14,15] Median turnaround time for TEG is 23–28 min if performed in a central laboratory or 18 min if performed at the bedside as a POC test.[6,9] As a result of the short turnaround time, an MEA tests based treatment algorithm has been used in an emergency room for treatment of trauma victims with improved mortality results.[1]
Moreover, the blood samples for Multiplate® are collected into tubes containing an anticoagulant that does not influence the blood calcium concentration that is, with hirudin, melagatran or heparin.[18,27,28] Different platelet agonists can be used as test reagents, e.g. arachidonic acid, ADP, collagen, TRAP, ristocetin etc.[1,19,20] It aids differential diagnosis for platelet dysfunction induced by aspirin, thienopyridines and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors (e.g. abciximab) and von Willebrand Disease (Ristotest on Multiplate®).[1,19,20]
Multiple electrode aggregometry is sensitive to platelet dysfunction resulting from anti-platelet drugs, CPB, or hypothermia and therefore allows for more targeted hemostatic therapy in post-CABG patients.[9,11,15,17,19,20,21,22] Perioperative platelet function testing during cardiac surgery using MEA or TEG analysis to guide hemostatic therapy is associated with a significant reduction in bleeding, reduced reexploration rates, reduced allogeneic blood product transfusion requirements and improved outcomes.[1,9,11,15,21,22,25] It also reduces the cost and possibly significantly reduces mortality.[9] Besides, patients on anti-platelet drugs can be hyper responders with increased risk of bleeding or poor responders at increased risk of ischemic and thrombotic events.[1,4,5] This variable response can be a risk stratified using POC platelet function analyzers: Minimal risk is associated with platelet inhibition <30%, but >60% inhibition with 2- to 6-fold increased risk.[1,5]
Hence, some institutions have started using POC platelet function testing for patients who are still on anti-platelet medications at the time of surgery.[2] Di Dedda et al. has shown that a preoperative MEA ADP test value of <31 U is associated with significant postoperative bleeding and hence surgery was deferred in such patients if possible.[2] Our study results corroborate these findings. Multiplate® results (ASPI test and ADP test) correlate well with bleeding and thrombotic complications both after cardiac surgery and PCI.[9,15,18,25] Consistent with these studies we found that in patients on anti-platelet drugs until surgery, peri-operative platelet testing (ASPI) with Multiplate® was the strongest predictor of bleeding and need for allogenic blood and platelet transfusion. TEG did not correlate well with any of these outcome measures in our study.
In contrast to the study by Rahe-Meyer et al.[14] where all types of cardiac surgery patients were included with varying CPB and cross clamp times, and probably altered platelet function in patients of aortic stenosis, in our study only CABG patients were enrolled. In addition and also in contrast, none of the patients received aprotinin (known to have protective effects on platelets). Several studies found as we did, a good correlation between Multiplate® results and total blood transfusion requirements during the intra-operative and the 24-h postoperative period.[15,21,22]
Studies suggest that routine “preoperative” (prior to hospital admission) POC measurement of coagulation does not predict bleeding during or after surgery and is not cost effective.[1] POC monitoring devices are more suitable for rapid differential diagnosis in the peri-operative period.[1,2] The benefit of peri-operative POC platelet testing is also confirmed in our study.
Platelet POC testing is more established within PCI practice. In a comparative study of various platelet function analyzers using high on-treatment platelet reactivity to predict ischemic events post-PCI the highest odds ratio was reported for Multiplate® (12) versus VASP (1.16) versus Verifynow (2.09–2.76) and LTA (3.8–5.8).[29] In this “consensus paper” (white paper) the authors concluded that Multiplate is the only platelet function test with convincing data for the prediction of bleeding in patients following PCI and patients undergoing cardiac surgery.[29]
In our study, we also demonstrated that patients who develop excessive bleeding have a higher rate of re-exploration, need more blood and blood product transfusions, and have longer CICU and in-hospital stays. Although this study was not setup to assess the cost implications, the above-mentioned issues all contribute to a significant cost. Thus, being able to predict platelet dysfunction and to treat it early could potentially benefit not only the patient but also contribute to substantial cost savings.
In summary, Multiplate® device has several advantages as a POC method for platelet function.[15] It is quick and easy to perform, uses small amounts of diluted whole blood, electronic pipetting and single-use test cells.[15,29,30] The analysis of whole blood allows assessment of platelet function in the actual physiological environment of other cellular components such as red cells, monocytes, and other white blood cells.[11,29] Adoption of Multiplate® facilitates reliable detection of patients with excessive residual effects of anti-platelet medications, therefore, nonurgent cases can be deferred.[9,11,29] This will reduce the risk postoperative bleeding, blood product transfusions and re-exploration.[9,14,29] In urgent cases, early availability of these test results showing poor platelet aggregation may prompt more targeted platelet transfusion.[1,11] These measures will lead to a better postoperative outcome, better resource utilization and cost reduction.[1,11,14,29]
CONCLUSION
Peri-operative platelet functional assessment with the Multiplate® was the strongest predictor of bleeding and the need for blood and platelet transfusions in patients exposed to anti-platelet therapy until surgery. This POC test complements the surgical team in terms of managing postoperative bleeding after CABG.
We recommend wider usage of the Multiplate® test in bleeding algorithms to risk stratify patients and guide transfusion protocols.
Limitations of the study
It is a single center nonrandomized study with its inherent limitations. Patients were managed according to the routine institutional protocol.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We sincerely acknowledge the help and assistance of all the anesthetic, surgical and perfusion staff, in particular Dr. Meraglia and Mr. S. Robins, at the Heart and Lung Center, Wolverhampton, UK.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Kozek-Langenecker SA, Afshari A, Albaladejo P, Santullano CA, De Robertis E, Filipescu DC, et al. Management of severe perioperative bleeding: Guidelines from the European Society of Anaesthesiology. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2013;30:270–382. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e32835f4d5b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Di Dedda U, Ranucci M, Baryshnikova E, Castelvecchio S Surgical and Clinical Outcome Research Group. Thienopyridines resistance and recovery of platelet function after discontinuation of thienopyridines in cardiac surgery patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014;45:165–70. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezt279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Collet JP, Montalescot G, Blanchet B, Tanguy ML, Golmard JL, Choussat R, et al. Impact of prior use or recent withdrawal of oral antiplatelet agents on acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2004;110:2361–7. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000145171.89690.B4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bachman DS. Discontinuing chronic aspirin therapy: Another risk factor for stroke? Ann Neurol. 2002;51:137–8. doi: 10.1002/ana.10023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Albaladejo P, Geeraerts T, Francis F, Castier Y, Lesèche G, Marty J. Aspirin withdrawal and acute lower limb ischemia. Anesth Analg. 2004;99:440–3. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000131965.61686.BD. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Reece MJ, Klein AA, Salviz EA, Hastings A, Ashworth A, Freeman C, et al. Near-patient platelet function testing in patients undergoing coronary artery surgery: A pilot study. Anaesthesia. 2011;66:97–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2010.06608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Harker LA, Malpass TW, Branson HE, Hessel EA, 2nd, Slichter SJ. Mechanism of abnormal bleeding in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass: Acquired transient platelet dysfunction associated with selective alpha-granule release. Blood. 1980;56:824–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Beurling-Harbury C, Galvan CA. Acquired decrease in platelet secretory ADP associated with increased postoperative bleeding in post-cardiopulmonary bypass patients and in patients with severe valvular heart disease. Blood. 1978;52:13–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weber CF, Görlinger K, Meininger D, Herrmann E, Bingold T, Moritz A, et al. Point-of-care testing: A prospective, randomized clinical trial of efficacy in coagulopathic cardiac surgery patients. Anesthesiology. 2012;117:531–47. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318264c644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Murphy GJ, Reeves BC, Rogers CA, Rizvi SI, Culliford L, Angelini GD. Increased mortality, postoperative morbidity, and cost after red blood cell transfusion in patients having cardiac surgery. Circulation. 2007;116:2544–52. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.698977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ranucci M, Baryshnikova E, Soro G, Ballotta A, De Benedetti D, Conti D, et al. Multiple electrode whole-blood aggregometry and bleeding in cardiac surgery patients receiving thienopyridines. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;91:123–9. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2010.09.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Leal-Noval SR, Rincón-Ferrari MD, García-Curiel A, Herruzo-Avilés A, Camacho-Laraña P, Garnacho-Montero J, et al. Transfusion of blood components and postoperative infection in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Chest. 2001;119:1461–8. doi: 10.1378/chest.119.5.1461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mishra PK, Chnaris A, Mohammed F, Luckraz H. A novel method for the management of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopaenia during cardiac surgery. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2014;18:850–2. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rahe-Meyer N, Winterhalter M, Boden A, Froemke C, Piepenbrock S, Calatzis A, et al. Platelet concentrates transfusion in cardiac surgery and platelet function assessment by multiple electrode aggregometry. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2009;53:168–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tóth O, Calatzis A, Penz S, Losonczy H, Siess W. Multiple electrode aggregometry: A new device to measure platelet aggregation in whole blood. Thromb Haemost. 2006;96:781–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Seyfert UT, Haubelt H, Vogt A, Hellstern P. Variables influencing Multiplate (TM) whole blood impedance platelet aggregometry and turbidimetric platelet aggregation in healthy individuals. Platelets. 2007;18:199–206. doi: 10.1080/09537100600944277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Multiplate Product Information. [Last accessed on 2014 Sep 01]. Available from: http://www.cobas.com/home/product/multiplate-analyzer.html .
- 18.Sibbing D, Braun S, Jawansky S, Vogt W, Mehilli J, Schömig A, et al. Assessment of ADP-induced platelet aggregation with light transmission aggregometry and multiple electrode platelet aggregometry before and after clopidogrel treatment. Thromb Haemost. 2008;99:121–6. doi: 10.1160/TH07-07-0478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sibbing D, Schulz S, Braun S, Morath T, Stegherr J, Mehilli J, et al. Antiplatelet effects of clopidogrel and bleeding in patients undergoing coronary stent placement. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8:250–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mengistu AM, Röhm KD, Boldt J, Mayer J, Suttner SW, Piper SN. The influence of aprotinin and tranexamic acid on platelet function and postoperative blood loss in cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2008;107:391–7. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31817b7732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mengistu AM, Wolf MW, Boldt J, Röhm KD, Lang J, Piper SN. Evaluation of a new platelet function analyzer in cardiac surgery: A comparison of modified thromboelastography and whole-blood aggregometry. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2008;22:40–6. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2007.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Calatzis A, Spannagl M, Loreth R. Multiplate® platelet function analysis – Application and interpretation. 2007. [Last accessed on 2014 Sep 01]. Available from: http://www.multiplate.net .
- 23.Rubak P, Villadsen K, Hvas AM. Reference intervals for platelet aggregation assessed by multiple electrode platelet aggregometry. Thromb Res. 2012;130:420–3. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2012.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Görlinger K, Jambor C, Hanke AA, Dirkmann D, Adamzik M, Hartmann M, et al. Perioperative coagulation management and control of platelet transfusion by point-of-care platelet function analysis. Transfus Med Hemother. 2007;34:396–411. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lordkipanidzé M, Pharand C, Schampaert E, Turgeon J, Palisaitis DA, Diodati JG. A comparison of six major platelet function tests to determine the prevalence of aspirin resistance in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:1702–8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jastrzebska M, Chelstowski K, Wódecka A, Siennicka A, Clark J, Nowacki P. Factors influencing multiplate whole blood impedance platelet aggregometry measurements, during aspirin treatment in acute ischemic stroke: A pilot study. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2013;24:830–8. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0b013e3283655640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bretschneider E, Glusa E, Schrör K. ADP-, PAF- and adrenaline-induced platelet aggregation and thromboxane formation are not affected by a thromboxane receptor antagonist at physiological external Ca++ concentrations. Thromb Res. 1994;75:233–42. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(94)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Belcher PR, Muriithi EW, Milne EM, Wanikiat P, Wheatley DJ, Armstrong RA. Heparin, platelet aggregation, neutrophils, and cardiopulmonary bypass. Thromb Res. 2000;98:249–56. doi: 10.1016/s0049-3848(99)00243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bonello L, Tantry US, Marcucci R, Blindt R, Angiolillo DJ, Becker R, et al. Consensus and future directions on the definition of high on-treatment platelet reactivity to adenosine diphosphate. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:919–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.04.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mengistu AM, Mayer J, Boldt J, Röhm KD, Suttner SW. Usefulness of monitoring platelet function by multiple electrode aggregometry in primary coronary artery bypass surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2011;25:42–7. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2010.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


