Abstract
Hoffa’s syndrome involves inflammation of the infrapatellar fat pad secondary to direct trauma or microtrauma. Alternative sources of inflammation of Hoffa’s fat pad include synovial processes such as pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS) and osteochondromatosis. Recently, a few cases of inflammation of Hoffa’s fat pad secondary to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) have been described. Our case presents an HIV patient with Hoffa’s fat-pad inflammation as well as prefemoral fat-pad edema, posterior soft-tissue inflammation, and bone infarction. Since patients with HIV now live longer due to improved treatment regimens, it is important for radiologists to recognize HIV-related musculoskeletal manifestations, such as non-neoplastic inflammation in Hoffa’s fat pad (as seen in our patient).
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging
Case report
A 44-year-old man with a 12-year history of HIV-positive status presented with a new complaint of atraumatic right knee laxity. Over the previous 10 years, the patient had reported intermittent, nonspecific right knee pain. Due to the patient's toleration of the pain, negative physical examination, and higher-priority medical issues such as seizures, he had never received imaging of the knee. The most recent physical examination of the right knee was also negative. However, due to the new laxity superimposed on chronic pain, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed.
MRI of the right knee without contrast demonstrated a large amount of high T2 signal involving Hoffa’s fat pad (Fig. 1) and replacement of normal high fat signal on proton-density-weighted images (Fig. 2). There was no discrete mass lesion or osseous component. No adjacent patellar tendon tear or fracture was seen to suggest traumatic etiology. All ligamentous structures were intact. A similar but smaller degree of high signal on fluid-sensitive sequences was also present in the prefemoral fat pad and in the posterior soft tissues (Figure 1, Figure 3). Avascular necrosis was seen in both the distal femoral shaft and proximal tibial shaft (Figure 1, Figure 4).
Figure 1.
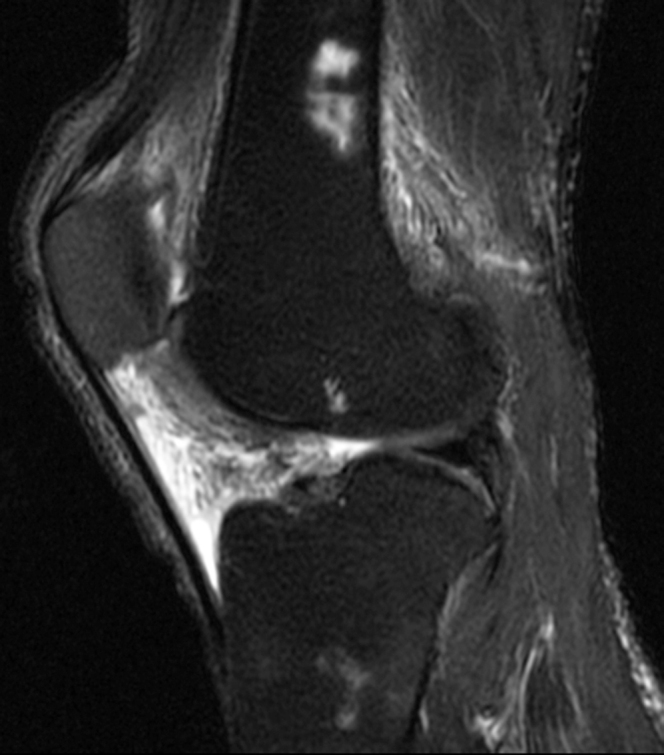
44-year-old man with Hoffa's fat-pad inflamnation. Sagittal T2 fat-suppressed image of the right knee shows high signal in Hoffa’s fat pad, prefemoral fat pad, and posterior soft tissues. High signal areas in the distal femoral diaphysis and proximal tibial diaphysis represent bone infarcts.
Figure 2.
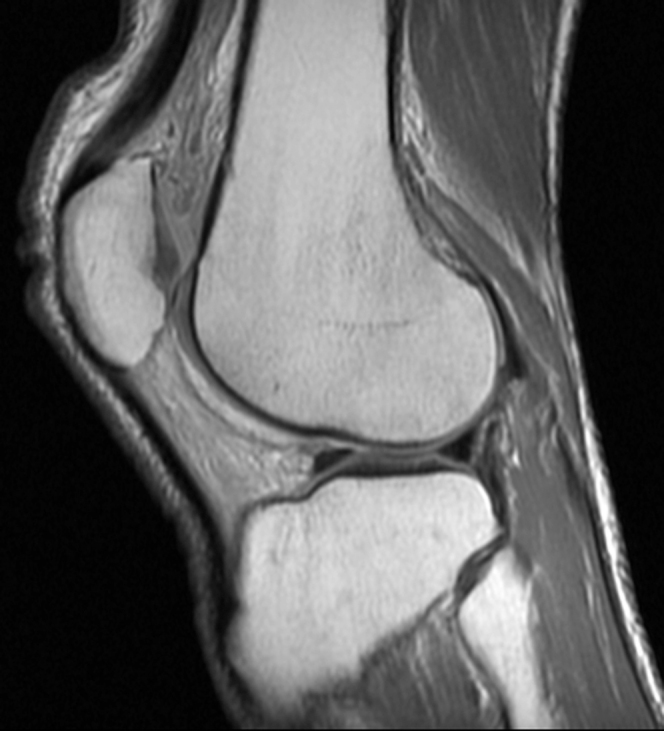
44-year-old man with Hoffa's fat-pad inflamnation. Sagittal proton-density-weighted MRI of the right knee shows intermediate signal intensity in Hoffa’s fat pad replacing normal fat signal.
Figure 3.
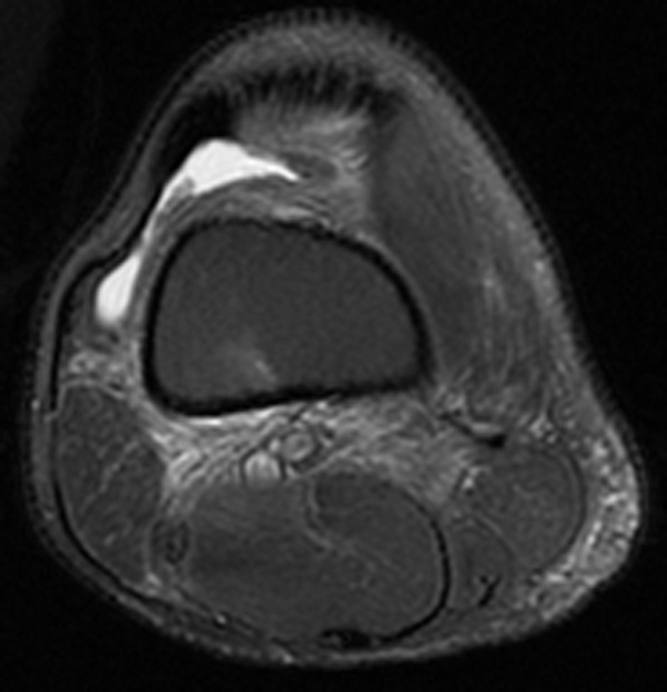
44-year-old man with Hoffa's fat-pad inflamnation. Axial T2 fat-suppressed image of the knee shows high signal involving the posterior soft tissues of the knee joint, subcutaneous fat posteromedially, and suprapatellar fat pad. A small joint effusion is also present.
Figure 4.
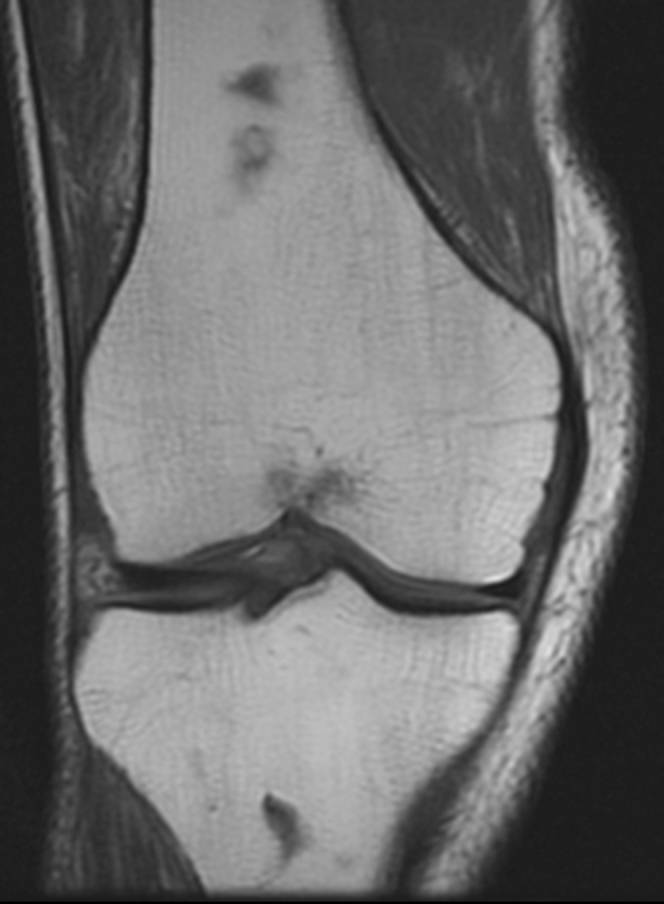
44-year-old man with Hoffa's fat-pad inflamnation. Coronal T2-weighted image of the knee shows serpiginous low-signal-intensity areas involving the distal femoral diaphysis and proximal tibial diaphysis. Findings are consistent with areas of osteonecrosis.
Due to lack of evidence suggesting trauma, lack of low T2 signal to suggest PVNS or osteochondromatosis, and lack of discrete mass, final diagnosis of inflammation of Hoffa’s fat pad related to HIV infection was made. Areas of bone infarction were attributed to HIV infection.
Discussion
The annual incidence of HIV infection in the United States is estimated at 56,300 (1). Although this incidence is believed to be stable since the 1990s, more people are being diagnosed with HIV; the 2007 estimate is that 1.6 million people are infected in the United States (2). Additionally, patients with HIV are living longer due to improvements in treatment regimens (3). Thus, physicians now encounter more patients with HIV. Potentially, more patients will present with chronic or late manifestations of disease that previously had not been seen.
Musculoskeletal manifestations of HIV are described thoroughly in the literature (4, 5). Disorders seen early in the disease, such as polymyositis, psoriatic arthritis, and Reiter’s syndrome, may actually be the presenting symptoms of HIV in a patient (5). Infectious HIV-related musculoskeletal disorders include septic arthritis, pyomyositis, and osteomyelitis, and are related to low CD4 counts and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). With increased survival rates and longer duration of medication use, musculoskeletal disorders resulting from treatment with highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) may be discovered in the coming years.
HAART is associated with fat redistribution and inflammatory modifications of adipose tissues (6, 7). HAART has been postulated as a potential cause of a few recently reported cases of inflammation involving Hoffa’s fat pad on MRI, sometimes termed “Hoffitis― by previous authors (8, 9). MRI findings of HIV-related Hoffa’s fat-pad inflammation include diffuse homogeneous increased signal intensity in Hoffa’s fat pad on fluid-sensitive sequences and low T1 signal intensity replacing the normal fat. An associated high signal on fluid-sensitive sequences in the quadriceps and prefemoral fat pads may also be present (8). Our case is nearly identical in MRI appearance to these previous cases and includes another sequelae of HIV infection, avascular necrosis.
Pathological analysis of HIV-related inflammation of Hoffa’s fat pad has shown the changes to be composed of synovial proliferation and chronic nonspecific perivascular inflammatory cell infiltrate, predominantly composed of lymphocytes without neoplasia (9). Thus, radiologists need not raise alarm that the findings represent Kaposi’s sarcoma or Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, which are known malignancies associated with HIV infection. Musculoskeletal involvement by Kaposi’s sarcoma on imaging most commonly presents as homogeneous, enhancing subcutaneous soft-tissue masses that are often contiguous with osteolytic bone lesions (10). Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma can present either as soft-tissue masses with permeative and lytic bone lesions or as nonenhancing synovial hypertophy that is intermediate to hyperintense on T2 and proton-density-weighted images (11). However, if there is marked change in imaging appearance on subsequent MRI or osseous extension, malignancy should be considered.
When encountering cases of abnormality involving Hoffa’s fat pad, radiologists must distinguish HIV-related inflammation from more common entities. Hoffa disease was described in 1904 as a syndrome of infrapatellar fat-pad impingement related to an inflamed fat pad of acute or repetitive trauma (12, 13). Acutely, edema and hemorrhage may appear similar to those in patients with HIV as high signal on fluid-sensitive MR sequences. Later, due to fibrous tissue formation and chronic hemorrhage, Hoffa disease has areas of low T2 and STIR signal (14).
Lesions such as intracapsular chondroma, PVNS, and synovial osteochondromatosis also demonstrate high signal intensity on fluid-sensitive sequences, but due to ossification, calcification, or hemosiderin, these are often more heterogeneous in signal (13). Additionally, these entities may show osseous erosion or involvement. Synovial inflammation resulting from rheumatoid arthritis or sero-negative spondyloarthropathy may be indistinguishable from HIV-related inflammation based solely on the appearance of Hoffa’s fat pad. Associated findings of these types of arthritis, such as erosions, joint space narrowing, and enthesophathy, may aid differentiation.
Ultimately, our case reinforces the presence of HIV as a cause of nonspecific pain and inflammation in Hoffa’s fat pad, prefemoral fat pad, and surrounding soft tissues.
Footnotes
Published: December xx, 2010
References
- 1.Hall HI, Ruiguang S, Rhodes P. Estimation of HIV incidence in the United States. JAMA. 2008;300:520–529. doi: 10.1001/jama.300.5.520. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vol. 19. US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; Atlanta: 2009. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV/AIDS Surveillance Report, 2007). Accessed June 15, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 3.The Antiretroviral Therapy Cohort Collaboration Life expectancy of individuals on combination antiretroviral therapy in high-income countries: a collaborative analysis of 14 cohort studies. The Lancet. 2008;372(9635):293–299. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61113-7. [PubMed] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tehranzadeh J, Ter-Oganesyan RR, Steinbach LS. Musculoskeletal disorders associated with HIV infection and AIDS. Part I: Infectious musculoskeletal conditions. Skeletal Radiology. 2004;33:249–259. doi: 10.1007/s00256-004-0764-z. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tehranzadeh J, Ter-Oganesyan RR, Steinbach LS. Musculoskeletal disorders associated with HIV infection and AIDS. Part II: Non-infectious musculoskeletal conditions. Skeletal Radiology. 2004;33:311–320. doi: 10.1007/s00256-004-0765-y. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Carr A. HIV lipodystrophy: risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Aids. 2003;17(Suppl. 1):S141–S148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Giralt M, Domingo P, Guallar JP. HIV-1 infection alters gene expression in adipose tissue, which contributes to HIV-1/HAART-associated lipodystrophy. Antivir Ther. 2006;11(6):729–740. [PubMed] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Torshizy H, Pathria MN, Chung CB. Inflammation of Hoffa’s fat pad in the setting of HIV: magnetic resonance imaging findings in six patients. Skeletal Radiology. 2007;36:35–40. doi: 10.1007/s00256-006-0201-6. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pluot E, Singh J, James SLJ, et al. Abnormality of the infrapatellar fat pad (Hoffa’s fat pad) in a patient with HIV: MR findings with histological correlation. European Journal of Radiology 2008; Extra 68:29-32.
- 10.Caponetti G, Dezube BJ, Restrepo CS, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma of the musculoskeletal system: a review of 66 patients. Cancer. 2007;109(6):1040–1052. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22500. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jamieson KA, Beggs I, Robb JE. Synovial presentation of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The British Journal of Radiology. 1998;71:980–982. doi: 10.1259/bjr.71.849.10195017. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hoffa A. The influence of the adipose tissue with regard to the pathology of the knee joint. JAMA. 1904;42:795–796. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jacobson JA, Lenchik L, Ruhoy MK, Schweitzer ME, Resnick D. MR imaging of the infrapatellar fat pad of Hoffa. Radiographics. 1997;17:675–691. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.17.3.9153705. [PubMed] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Magi M, Barca A, Bucca C, Langerance V. Hoffa disease. Ital J Orthop Traumatol. 1991;17:211–216. [PubMed] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


