Abstract
One of the most powerful forms of depth perception capitalizes on the small relative displacements, or binocular disparities, in the images projected onto each eye. The brain employs these disparities to facilitate various computations, including sensori-motor transformations (reaching, grasping), scene segmentation and object recognition. In accordance with these different functions, disparity activates a large number of regions in the brain of both humans and monkeys. Here, we review how disparity processing evolves along different regions of the ventral visual pathway of macaques, emphasizing research based on both correlational and causal techniques. We will discuss the progression in the ventral pathway from a basic absolute disparity representation to a more complex three-dimensional shape code. We will show that, in the course of this evolution, the underlying neuronal activity becomes progressively more bound to the global perceptual experience. We argue that these observations most probably extend beyond disparity processing per se, and pertain to object processing in the ventral pathway in general. We conclude by posing some important unresolved questions whose answers may significantly advance the field, and broaden its scope.
This article is part of the themed issue ‘Vision in our three-dimensional world’.
Keywords: depth perception, disparity, stereovision, stereopsis, IT, ventral pathway
1. Introduction
It must be repeated here that, before stereopsis is actually experienced by the patient, there is nothing one can do or say which will adequately explain to him the actual sensation experienced. … Once the patient has experienced this new sensation, he is only too anxious to use it again and again…
—Brock [1, p. 209]
Our eyes are the interface with the vast wealth of information carried by light about our surroundings. In primates, nearly 60% of cortex is devoted to some sort of visual processing [2]. The act of vision encompasses depth perception, such as estimating the distance between objects, or determining an object's three-dimensional (3D) shape. Depth perception relies on a variety of monocular cues including perspective, occlusion, motion parallax and texture gradients, but binocular cues are employed as well. For example, one of the most powerful forms of depth perception is stereopsis, which takes advantage of the small relative displacements of the images projected onto each eye [3].
Human and non-human primates possess two adjacent, forward-facing eyes. The slightly different but overlapping views of the eyes cause some light rays to hit the retina of each eye at different positions relative to the fovea. These small binocular ‘disparities’ between corresponding points in the two retinal images allow the visual system to reconstruct depth from the two-dimensional (2D) retinal projections. Although we are often unaware of it, binocular disparity creates some of the most tangible and vivid 3D percepts. Without stereopsis, our visual experience would be akin to a normal, as opposed to a 3D movie. Note, however, that a substantial proportion of the population, 5–30% depending on the study, has moderate to poor stereovision [4]. This indicates that stereovision (like colour vision) is not crucial for survival in our society, but rather serves to enrich our perceptual experience of depth.
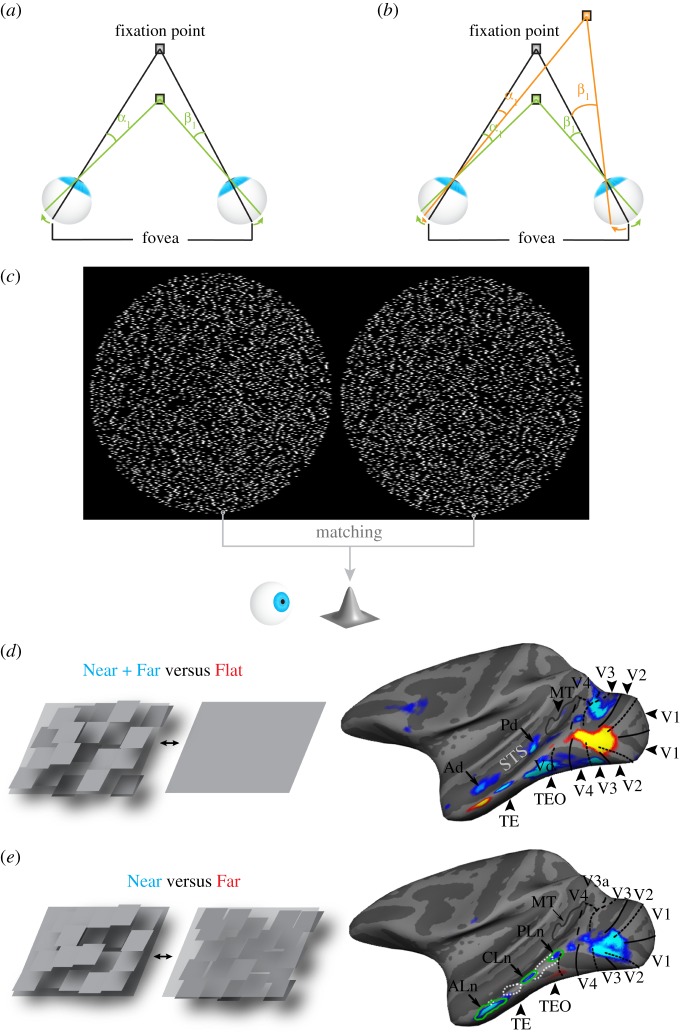
Stereopsis begins with a determination of the absolute disparity of the corresponding points in the two retinal images. The absolute disparity of a point is defined as the angular separation of a point in one eye with respect to the fovea, minus that in the other eye (figure 1a). While a point that is being fixated projects onto each eye's fovea, other points that are nearer or further relative to the plane of fixation will generally project onto different retinal locations (for a detailed discussion, see [6]). Thus, absolute disparity carries information about a point's depth relative to the point of fixation. It follows that absolute disparity directly depends on where the eyes fixate: rotating the eyes inward (convergence) or outward (divergence) changes the absolute disparity of all points.
Figure 1.
Introducing absolute and relative disparity, the correspondence problem and disparity activation in the ventral visual pathway. (a) The grey fixation point projects to the fovea in each eye. A green point, placed in front of the fixation point, projects to different retinal locations with respect to each eye's fovea: to the left of the fovea in the left eye, to the right of the fovea in the right eye. The absolute disparity of the green point is defined as the angular separation of the point in one eye with respect to the fovea, minus that in the other eye, that is, α1–β1. (b) The relative disparity between the green and orange point is defined as the difference between the absolute disparity of each point: (α1–β1)–(α2–β2). (c) In order to perceive the convex cone-like 3D shape, the visual system needs to compute the disparity of all corresponding points in the two random-dot images. To do so, it must first find the corresponding points by matching each point in the left dot pattern with the equivalent point in the right pattern. (d) Stereo activation in the ventral pathway of macaques. Blue-cyan colour indicates brain regions that responded more strongly to random-dot checkerboards containing squares that were placed either in front of (Near) or behind (Far) the fixation plane, than to similar random-dot stimuli with no disparity (Flat). The pictograms on the left illustrate the stimuli by means of monocular depth cues, though the depth patterns of the actual experimental stimuli were defined solely by binocular disparities. Regions Ad, Pd and Vd represent near/far disparity-biased regions in IT that were reproduced across experiments and monkeys. (e) Blue-cyan colour indicates brain regions that responded more strongly to random-dot checkerboards containing squares that were all placed in front of (Near) the fixation plane, than to random-dot checkerboards with all squares placed behind the fixation plane (Far). Near-biased activity stretches from early visual areas (V1, V2), to more anterior ventral-pathway areas (TE). Regions PLn, CLn and ALn represent near-disparity-biased regions in IT that were reproduced across runs and monkeys. STS, super temporal sulcus; MT, middle temporal area. (d and e adapted with permission from Verhoef et al. [5].)
However, we are generally not interested in depth differences relative to the point of fixation, so much as we are in the relative distances between objects or the relative distances between different points on an object's surface, i.e. its 3D structure [7]. The visual system can extract information about relative depth based on the relative disparities between points. The relative disparity between two points is defined as the difference in the absolute disparity of each point (figure 1b). In contrast to absolute disparity, relative disparity does not depend on the vergence angle between the two eyes: when the absolute disparities of two points are subtracted from each other, the reference to the point of fixation, i.e. the vergence angle between both eyes, is cancelled out. Relative disparities therefore offer a more stable source of depth information, allowing the brain to use relative disparities to perform actions such as reaching, grasping or 3D-shape recognition.
While computing binocular disparities for depth perception, the visual system is confronted with a daunting task: it needs to pair all points in the retinal image of one eye with the corresponding points in the other eye. This challenge, called the stereo-correspondence problem, is readily illustrated in the context of random-dot stereograms, as shown in figure 1c [8–10]. Free-fusing the stereogram in figure 1c generates the percept of a 3D cone. Yet, this percept happens only after the brain has successfully matched all corresponding dots in the two dot-patterns, a necessary condition for global depth perception. Despite the apparent complexity, the brain solves the correspondence problem effortlessly.
Binocular disparity is involved in various computations, including sensori-motor transformations (reaching, grasping), scene segmentation and object recognition [11]. Consistent with its various roles, the responses in several brain regions in both humans and monkeys are affected by disparity [5,12–19]. Although disparity processing was originally considered a specialty of the dorsal visual pathway [20], recent studies employing microelectrode recordings or functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) have discovered large swaths of cortex in the ventral visual pathway of macaques and humans that are sensitive to disparity (figure 1d,e; [5,15]).
Regions in the dorsal visual pathway are thought to underlie visually guided actions such as reaching and grasping [21]. The ventral pathway, on the other hand, is implicated in object identification and categorization, and extends from V1 through a series of visual areas, such as V2, V4 and TEO, to the anterior inferior temporal (IT) cortex (area TE) [21–23]. The functional specialization of the dorsal and the ventral pathways suggest that disparity-related activity in the dorsal pathway is mainly used to improve visually guided actions, while the ventral pathway may use its disparity information predominantly to facilitate object recognition. In the following sections, we review the progress in our understanding of disparity-related depth processing in the macaque ventral pathway. We will examine how depth representations that rely on binocular disparity evolve along the different stages of the ventral pathway, and conclude with some important unresolved questions in the field.
2. Disparity processing in the early visual areas of the ventral visual pathway
Primary visual cortex (V1) contains neurons that are tuned to the disparity of stimuli within their receptive field [18,24,25]. Disparity-selective V1 neurons are binocular neurons whose inputs originate from both the left and right eyes [26,27]. These neurons can be of the simple- or complex-cell type [28,29]. Simple cells are able to detect disparity, because their receptive field in the left and right eyes can have different shapes (i.e. different location and strength of the ON- and OFF-subfields) [30,31] or slightly different overall positions [31]. An influential computational model of V1 disparity selectivity, the disparity-energy model, explains disparity selectivity of complex cells using the summed inputs from simple cell-like neurons [32,33]. This basic model structure has been successfully applied to describe disparity selectivity in primary visual cortex of cats [29], monkeys [34] and rodents [35], and explains certain human psychophysical data [36,37]. These findings therefore suggest a similar cortical origin of stereopsis across different mammals.
Different versions of the disparity-energy model rely on either monocular [38] or binocular [32] simple cell-like inputs. Importantly, in either model the inputs are simple cell-like, and such inputs can potentially be constructed from direct thalamo-cortical inputs to complex cells [29,38]. Hence, if and how simple cells contribute to the disparity selectivity of complex cells is still unclear. Finally, it has been suggested that even complex cells that are not selective for disparity may play a role in stereopsis. This is because the output from a disparity non-selective complex cell can be subtracted from a disparity-selective complex cell to obtain a pure disparity-sensitive signal that may be important for stereopsis [29]. Taken together, these studies indicate that the precise role of binocular and monocular cells, simple or complex, in stereopsis is still unknown.
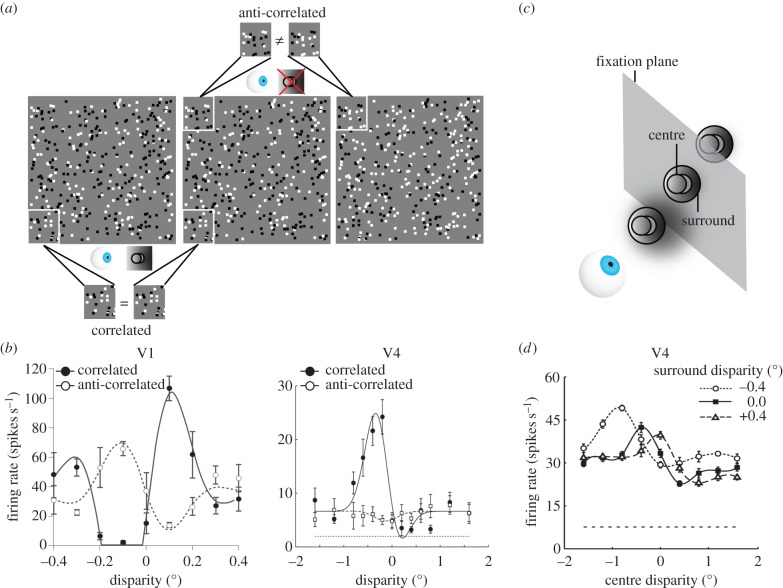
V1 neurons can be tuned to far (uncrossed), zero or near (crossed) disparities, with a variety of tuning profiles [18,28,39]. Crucially, disparity tuning in V1 corresponds to absolute disparity tuning, but not relative disparity tuning. For example, when a stimulus with constant relative disparity between two parts of a stimulus (e.g. a disc surrounded by an annulus at different depth; figure 2a,c) is positioned at different distances in depth by adding various amounts of absolute disparity to all parts of the stimulus, V1 neurons ignore the constant relative disparity between the stimulus parts and respond based on the absolute disparity of the stimulus component that falls within their classical receptive field [43]. Thus, neurons in V1 are sensitive to absolute, but not relative disparity.
Figure 2.
Responses to anti-correlated random-dot stereograms and to relative disparity. (a) The leftmost two random-dot stereograms are correlated, i.e. corresponding dots in the left and middle image have the same colour. Free-fusing these images led to the percept of a circular patch protruding from a background. The rightmost two random-dot stereograms are anti-correlated: the dots in both images are located at exactly the same positions, and thus have exactly the same disparities with the leftmost dot pattern, but the contrast polarity of the corresponding dots in each figure has been reversed: white dots in the middle figure are black in the right figure, and vice versa. In contrast to correlated random-dot stereograms, free-fusing the leftmost and rightmost dot pattern does not elicit the percept of a circular patch protruding from a background. (b) Average responses of a V1 neuron (left panel) and a V4 neuron (right panel) to correlated (black filled symbols) and anti-correlated (white open symbols) random-dot stereograms with different disparities (x-axis). The stimuli used in these studies were similar to those shown in (a). The V1 neuron is still markedly tuned to the disparity in anti-correlated stereograms. The V4 neuron, however, is only weakly tuned to the disparity of the dots in the anti-correlated random-dot stereogram. (Figure adapted with permission from Parker and Tanabe et al. [40,41].) (c) In experiments wherein the relative disparity tunings of neurons are examined, stimuli with relative disparities are placed at different positions in depth with respect to the fixation plane. For example, a surrounding annulus can be placed in front of, behind or at the fixation plane. One can then manipulate the disparity of the circular centre stimulus, which brings the centre stimulus to the front or the back of the fixation plane. If neurons are tuned to the relative disparity between the centre and surrounding stimulus, their tuning curves should shift by the same amount as that of the applied surround disparity. (d) This V4 neuron preferred a nearby centre (negative/crossed disparities) when the surround was placed at the plane of fixation (filled rectangular symbols). When the surround was moved to a position −0.4° in front of the fixation plane (open circular symbols), the tuning curve to the centre stimulus moved by approximately the same amount to the left. Positioning the surround +0.4° behind the fixation plane, moves the tuning curve to the right by a similar amount. Hence, regardless of the surround disparity, this neuron preferred a centre that was positioned in front of the surround. This tuning behaviour reflects selectivity to a relative disparity between the centre and surround stimuli. (Figure adapted with permission from Umeda et al. [42].)
Although V1 neurons display a high degree of selectivity for absolute disparity, converging evidence suggests that they do not represent globally perceived depth. Here, the term global depth percept refers to the coherent percept of a spatially continuous shape derived from integrating disparity across the spatial extent of the stimulus [10], e.g. the percept of a cone in figure 1c or a protruding disc in figure 2a. In contrast to such global stereopsis, local stereopsis processes disparity locally, which may result in the percept of an incoherent cloud of dots wherein each dot is perceived as having its own position in depth [37]. Psychophysical [37] and neurophysiological evidence indicates that V1 is mainly involved in local, not global, stereopsis. For instance, disparity-selective V1 neurons respond selectively to the disparities of dots in random-dot stimuli in which the luminance contrasts of corresponding dots in the left and right eyes are reversed (figure 2b, left panel). In these anti-correlated random-dot stereograms, black dots in one eye appear as white dots in the other eye, and vice versa [34] (figure 2a). Crucially, and in contrast to correlated stereograms, the anti-correlated random-dot stereograms for which V1 neurons have been shown to respond selectively induce no global percept of depth in either humans or macaques [34,41,44–46]. Furthermore, one study used sine-wave grating stimuli, chosen to be larger than the neuron's receptive field [47]. Displacing the stimuli by one spatial period of the grating left the portion of the image inside the receptive field unchanged, but changed the disparity and perceived depth of the stimulus. Again, V1 neurons signalled the disparity of the local image inside the receptive field, i.e. they did not change their response following this stimulus manipulation, but did not signal the globally perceived depth of the whole stimulus. These findings indicate that V1 neurons respond to local disparities but not to global matches: V1 neurons detect disparity even when the parts of the stimuli that cover their classical receptive fields do not match. The responsiveness of V1 neurons to ‘false matches’ indicates that the stereo-correspondence problem is not yet solved at this initial stage of the visual system.
The view that V1 neurons act as local absolute disparity filters that convey information that is still too far-removed from global depth perception is further supported by the fact that the activity of V1 neurons does not correlate with monkeys’ perceptual reports during a depth-discrimination task [48] (but see [49] for an alternative explanation and [50] for a discussion). Nevertheless, and as expected from the resulting cortical blindness, lesioning V1 in macaques dramatically impairs stereoacuity [51]. Thus, although disparity representations in V1 are still rudimentary and distant from the global perceptual end product, they are nonetheless vital for depth perception, in that V1 provides disparity information that subsequent cortical regions use for further processing.
The disparity tuning characteristics of V1 neurons indicate that the initial disparity representation requires further disambiguation for it to be useful for global depth perception. Some of the transformations required to realize this goal are already performed at the next stage of the ventral pathway, area V2. For example, some V2 neurons are tuned to relative disparity, but in general the activity of V2 neurons reflects a mixture of absolute and relative disparity selectivities [52]. Interestingly, a model with a structure akin to the V1 disparity-energy model can generate relative disparity tuning curves similar to those observed in V2 [52]. This suggests that analogous computations, like those in the energy model (i.e. involving a sequence of linear and nonlinear operations), are repeated along the ventral pathway to produce neuronal tuning to increasingly complex 3D objects. Comparable designs have been proposed to explain the increasingly complex 2D-feature tuning in the ventral pathway [53].
V2 neurons additionally respond to stimulus borders defined by relative disparity [54,55]. Although these responses to disparity borders cannot be explained by pure absolute disparity selectivity, as seen in V1, they are dependent on the location within the receptive field and the edge sign, as well as sensitive to the disparities that define the edge [55]. V2 neurons can also respond to illusory depth percepts [56], and their activity correlates with monkeys' perceptual reports during a depth-discrimination task [48]. Finally, and similar to V1, lesioning V2 strongly impairs stereoacuity [51]. However, despite V2's link to perception, some evidence indicates that the stereo-correspondence problem still has not been solved at this stage [57].
These findings indicate that early visual transformations, in V1 and V2, lead to rudimentary relative disparity representations that, to a certain extent, tie in with depth perception.
3. Disparity processing in the mid-stages of the ventral visual pathway
Several neurons in area V4 respond selectively to stimuli in which absolute disparity varies [58]. Early analyses showed that tuning for absolute disparity in V4 does not differ substantially from the tuning for absolute disparity seen in early visual areas V1 and V2 [58–60]. However, other findings indicate that disparity computations in V4 extend significantly beyond those observed in earlier visual areas.
For example, V4 appears to be the first ventral-pathway area in which the stereo-correspondence problem has been partially solved: most disparity-selective V4 neurons are only weakly tuned to disparity in anti-correlated random-dot stereograms [41] (figure 2b, right panel). This finding indicates that V4 neurons are much less sensitive to the disparity of false matches within their receptive field, and respond mostly according to the global depth percept induced by the stimulus. Correspondingly, one study found that performance in a global stereopsis task, in which monkeys judged the relative depth of noisy random-dot stereograms, is impaired after bilateral removal of a part of posterior prestriate cortex that included area V4 [61].
Another distinction from early visual areas is V4's increased sensitivity to relative disparity (figure 2c,d). It has been shown that the responses of V4 neurons contain considerably more information about relative disparity compared with the responses of neurons in V2 [42]. Although relative disparity is still not fully encoded by all V4 neurons, i.e. most neurons' responses to relative disparity remain affected by the position in depth of the stimulus, the combined data from V1, V2 and V4 indicate a progressive transformation along the ventral visual pathway from encoding absolute disparity to representations of relative disparity.
One study offered a clue as to how V4's relative disparity information could lead to behaviorally relevant depth representations. Hinkle & Connor [62] showed that a significant proportion of V4 neurons are not only tuned to the orientation of bar-like stimuli in the fronto-parallel plane (i.e. the 2D image plane), but are also tuned to the orientation in depth of stimuli (defined by horizontal disparity or orientation disparity; [62]). This selectivity, for 3D orientation or slant, was often maintained across different positions in depth of the stimulus.
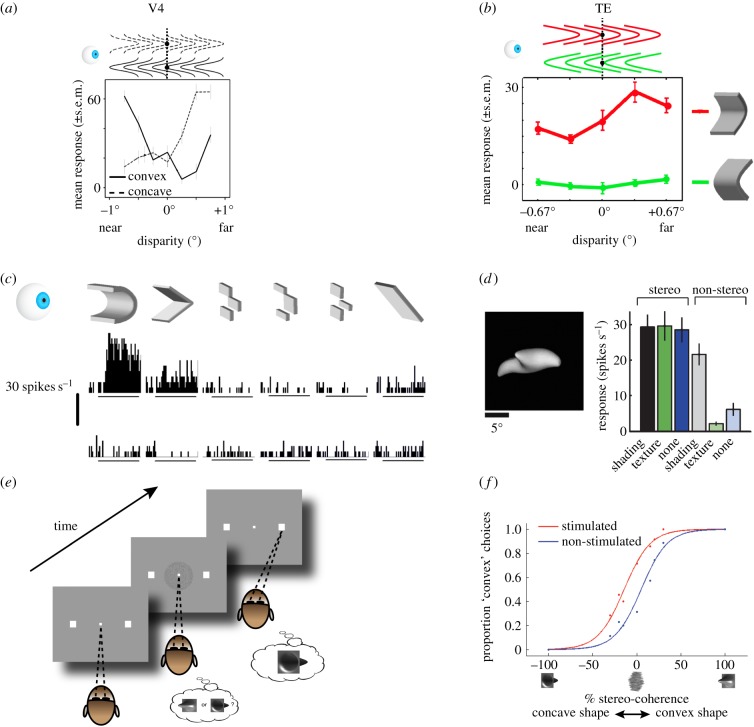
Nonetheless, depth encoding in V4 still appears to be relatively basic. For instance, one study suggested that V4 neurons show little evidence of depth-invariant 3D-shape selectivity: the preference of V4 neurons for convex or concave 3D structures varies with the position in depth of the stimulus, suggesting that it is not the 3D shape of these stimuli driving the neuronal responses [63] (figure 3a). Hence, V4 neurons can discriminate the orientation of small linear surfaces in depth, which can inform observers about the orientation in depth of real-world objects.
Figure 3.
3D-shape representations in the anterior ventral pathway. (a) Average response of a V4 neuron to convex (solid line) and concave (dashed line) stimuli at different positions in depth relative to the fixation plane (x-axis; see pictograms above). This neuron changed its stimulus preference depending on the position-in-depth of the stimulus. Its tuning curve was similar to that obtained when a flat stimulus was varied across positions in depth (not shown), indicating that 3D shape was not driving this neuron's response. (Figure adapted with permission from Hegdé & Van Essen [63].) (b) Average response of a TE neuron to concave stimuli (top row; red) or convex stimuli (bottom row; green) placed at different positions in depth relative to the fixation plane (dotted line). Left: in front of the fixation plane. Right: behind the fixation plane. This neuron retained its concave-shape preference across different positions in depth. (Figure adapted with permission from Orban et al. [11].) (c) Average response of a TE neuron to concave (top row) and convex (bottom row) stimuli. The different columns indicate different approximations to the smoothly curved stimulus on the left (see pictograms above). This neuron preferred smoothly-curved concave 3D shapes. (Figure adapted with permission from Janssen et al. [64].) (d) Yamane et al. [65] used a genetic algorithm to optimize stimuli to individual TE neurons. They found that neurons in TE prefer fairly complex 3D shapes (see example on left). The labels below or above the bar plots show which depth cues (disparity, shading or texture) were present in the stimulus. Removing disparity significantly reduced this neuron's response (compare left three and right three bars), illustrating the importance of depth for shape representations in TE. (Figure adapted with permission from [65].) (e) 3D-shape categorization task. See figure 1c for an example stimulus. Monkeys were trained to categorize disparity-defined 3D shapes as either convex or concave by making an eye movement to the left (convex) or right (concave) response target to indicate the perceived shape. (f) Example microstimulation session in TE. Proportion ‘convex’ choices is plotted as a function of the stimulus (right x-axis: convex shape, left: concave shape) and the noise applied to the stimulus (% stereo-coherence). Blue colour shows performance on trials without stimulation, red colour on trials with stimulation. Stimulation was applied on 50% of randomly chosen trials, and only during stimulus presentation. When clusters of TE neurons with a convex 3D-shape preference were electrically stimulated while the monkey performed the 3D-shape categorization task, the monkey more often reported perceiving a convex shape. (Figure adapted with permission from Verhoef et al. [66].)
The findings thus far suggest that activity in V4 is closely related to relative-depth perception. This was further evidenced by the findings from a study by Shiozaki et al. [67], in which the authors examined how V4 activity relates to behaviour in a fine disparity discrimination task, which was based on relative rather than absolute disparity signals. They found that the information encoded by V4 neurons was nearly sufficient to support behaviour during relative-depth discrimination. V4 activity also correlated with the behavioural choices of the monkeys during task performance, and microstimulation of disparity-selective V4 neurons influenced depth-discrimination behaviour in accordance with the disparity preference of the stimulated neurons [67].
Taken together, these findings implicate V4 as an important processing stage involved in basic relative-depth perception.
Little is known about disparity processing in area TEO, the next stage of the ventral pathway. Uka et al. [68] recorded from a population of inferotemporal neurons, which included neurons from area TEO, but also from more anterior IT regions (TE) [68]. They found that in their population of neurons, more than half of the visually responsive neurons were disparity selective. One study found that monkeys performed more poorly on a global stereopsis task after bilateral removal of TEO [61]. Another study showed that lesioning parts of the temporal lobe, including area TEO, led to reduced stereoacuity [51]. However, the lesions in this study also included large parts of anterior IT, so it is unclear to what extent TEO was responsible for these visual impairments.
Although neurons in TEO are likely to be involved in some disparity-related depth computations, no study thus far has clearly demonstrated what these computations consist of, and what sets TEO apart from other ventral-pathway areas. One fMRI study hinted at some of the disparity computations in which TEO might be involved. Verhoef et al. [5] observed disparity-related activity in a posterior IT region, which overlapped with parts of ventral TEO (figure 1d). This region was preferentially activated by images of scenes or places, which suggests that scene perception may be facilitated by disparity-related depth information, and that ventral TEO has a role in this.
4. Disparity processing in the end-stages of the ventral visual pathway
Neurons near the final stage of the ventral pathway, area TE, respond to stimuli that are defined by horizontal disparity [12,68,69]. The activity of some of these neurons correlates with perceptual choices during a fine depth-discrimination task in which monkeys judge whether a stimulus is presented in front of (near) or behind (far) the plane of fixation [70]. TE neurons can also signal the orientation in depth of planar stimuli [64,71]. However, what is novel in TE neurons is that they encode gradients of relative disparities such as 3D curvature [64].
When different disparity-defined 3D shapes are presented to neurons in TE, neurons often respond selectively and retain their preferences when the stimuli are presented at different positions in depth [12] (figure 3b). Note that, although IT neurons frequently preserve their 3D-shape preference across different positions in depth, the magnitude of the differential response to the preferred and the non-preferred 3D shape may vary depending on the exact position-in-depth of the stimulus (figure 3b). This is similar to the ‘imperfect’ invariance for position-in-depth that has been observed for the relative disparity tuning or 3D-orientation tuning of V4 neurons [42,62]. Moreover, tolerance of feature tuning to identity-preserving transformations (such as varying the position in depth of a stimulus) rather than complete invariance is a common property of feature tuning in (ventral) visual cortex [72,73].
Importantly, some position-in-depth tolerant IT neurons are sensitive to curvature in depth. This means that close, but non-curved, approximations of curved stimuli elicit markedly reduced responses [64] (figure 3c). Apart from the position-in-depth of the stimulus, the 3D-structure preference of these neurons is tolerant to other identity-preserving transformations, such as positional changes of the stimulus within the neuron's receptive field, and changes in the total variation in depth of the stimulus (e.g. the amplitude of a convex shape). Finally, neurons in TE are extremely sensitive to the direction of disparity gradients. For example, convex and concave shapes of very small amplitude are easily discriminated by TE neurons.
Apart from selectivity for relatively simple 3D shapes, Yamane et al. [65] presented evidence that TE neurons encode specific spatial configurations of elementary 3D shapes. As a whole, these spatial configurations form more complex 3D shapes (figure 3d). This study also showed that the majority of TE neurons represent 3D shapes: presenting the same stimuli without 3D cues, including disparity, reduces the responses of many TE neurons (figure 3d). Thus, most TE neurons represent 3D shapes and rely, at least partly, on disparity to build this representation.
The sensitivity to 3D structure and the tolerance to various transformations that preserve the qualitative distinctions between 3D shapes, makes populations of TE neurons suitable for representing the 3D shape of real-world objects. If TE neurons contribute to representing real-world objects, their activity should be closely related to depth perception. Several lines of evidence support this view. First, the correspondence problem has been fully solved in TE: TE neurons respond to the globally perceived 3D shapes as depicted by (correlated) disparity-defined stimuli, but not to anti-correlated random-dot stereograms in which no global depth is perceived [46]. Second, the activity of 3D-shape-selective TE neurons predicts the choices made by monkeys when categorizing 3D shapes as either convex or concave [74]. Third, lesioning IT, including large parts of TE, causes serious impairments in disparity-related depth perception, such as deficits in judgements of the position in depth (near or far) of a stimulus and deficits in global stereopsis [51,61]. Finally, when monkeys are trained to categorize disparity-defined 3D shapes as either convex or concave (figure 3e), electrical microstimulation of clusters of TE neurons having convex preferences sharply increases the number of convex choices (figure 3f). Conversely, microstimulation of clusters of TE neurons possessing concave preferences greatly increases the number of concave choices. Thus, when TE neurons with a specific 3D-shape preference are electrically activated, monkeys report perceiving that specific 3D shape [66]. Taken together, these findings indicate that TE occupies a position in the hierarchy of visual areas that is close to areas where 3D-shape processing gives rise to 3D-shape perception.
It is important to note that TE might not represent 3D shape based on disparity per se. Rather, it seems likely that TE neurons often represent 3D shapes regardless of the particular cues (disparity, texture, shading) defining them. Such a convergence of disparity and other depth cues has been shown in TE for flat shapes [69], for planar surfaces tilted in depth [71], and to some degree for curved surfaces [65,75]. Thus, TE neurons derive their 3D-shape representations from multiple depth cues, of which binocular disparity is but one.
Although we have treated TE as a single entity, this area is actually large and probably comprises multiple regions with distinct functional specializations [23]. Consistent with this view, several studies have shown that disparity-sensitive neurons are mostly concentrated in the ventral bank of the superior temporal sulcus (STSv; figure 4) [5,65,76]. By contrast, the temporal convexity (TEd) contains far fewer disparity-sensitive neurons. The different functional specializations of STSv and TEd are consistent with a modular organization of IT, as has been suggested previously in relation to IT's specialized representations for faces, places, colour, bodies and disparity [5,23,77–80].
Figure 4.
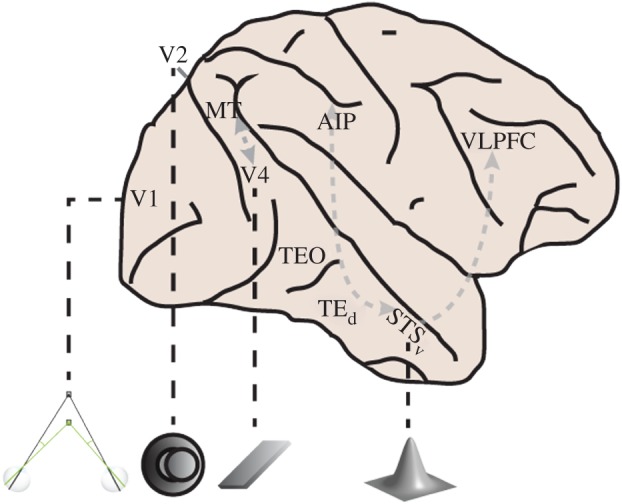
Disparity processing in the ventral visual pathway of macaques. The information represented by disparity-sensitive neurons in the ventral pathway becomes progressively more complex. Disparity processing originates in V1 where neurons signal absolute disparity. As early as V2, some neurons encode the relative disparity between a centre stimulus and a surrounding annulus (see pictogram below). Apart from relative disparities, neurons in V4 can be tuned to the orientation in depth of a planar stimulus. Neurons in STSv provide information about relative disparity (position in depth) or surface orientation, but also about which smoothly curved 3D shape is presented. Several regions in the ventral pathway may interact (dashed arrows) with regions outside the ventral pathway, such as MT, AIP or VLPFC, to facilitate depth perception. AIP, anterior intraparietal area; VLPFC, ventro-lateral prefrontal cortex.
5. Conclusion and open questions
Binocular disparity activates many regions along the posterior–anterior axis of the ventral visual pathway [5] (figure 1d,e). Disparity processing starts in V1, where absolute disparities are computed from the local images that fall within the receptive fields of binocular neurons. The absolute disparity information computed by V1 neurons is subsequently transmitted to regions in both the ventral and the dorsal pathway. For example, it is assumed that regions in the dorsal pathway control vergence eye movements—the purpose of which is to bring left and right eye images into registration—using the absolute disparity information conveyed by V1 neurons [40,81]. Hence, the V1 absolute disparity representation is a multipurpose and flexible representation that feeds into both the ventral and the dorsal visual pathways, wherein disparity is used for somewhat different purposes.
Further down the ventral pathway, however, disparity representations become increasingly based on relative, compared to absolute, disparity (figure 4). The relative disparity information initially appears in an elementary form (V2), but supplies the basis for complex 3D-shape representations once the disparity information enters IT. Neurons in IT, likely aided by their larger receptive fields, can integrate relative disparity information across larger regions of the visual field, thereby providing the degree of integration necessary for selectivity for curved 3D shapes, which consist of smooth gradients of disparity [12,65].
Along the ventral pathway, the disparity information is combined with depth information from other cues (e.g. texture, shading), eventually producing reasonably cue-invariant 3D-shape representations in IT. One should bear in mind, however, that depth-cue convergence could occur in ventral-pathway regions prior to IT. This can happen in different ways [82]. First, an area might contain neurons that are tuned to depth such that each neuron uses a different depth cue. Second, neurons within an area may encode depth through various depth cues, but with a different tuning for each depth cue. For example, neurons in dorsal-pathway area MT can be selective to 3D-surface orientation (tilt) as defined by velocity, disparity and texture gradients, but their tilt preference across these different depth cues is not correlated [83]. Third, neurons within an area may have a similar depth tuning for different depth cues. This type of depth-cue convergence has been observed in IT (see above) and, to a certain degree, for 3D-orientation tuning in the caudal intraparietal area in the dorsal pathway [84,85]. Importantly, little is known about depth-cue convergence in ventral-pathway areas prior to IT. Findings from one fMRI study suggest that V4 may encode depth from texture or shading in addition to depth from disparity [86], but to our knowledge no study has examined simultaneous tuning for different depth cues at the single-neuron level in V4. Note, however, that depth-cue convergence may not be necessary to achieve a multi-cue depth representation. For instance, it is conceivable that the activity of different neurons (in different areas), each encoding depth using a different depth cue, is combined in a distributed code to represent depth in all its aspects. Hence, more studies are needed to elucidate where and how different depth cues are combined in the ventral pathway and if this convergence facilitates depth encoding.
Another important unresolved question is the degree to which disparity contributes to well-studied inferotemporal representations such as those for faces [77] or body parts [87]. It has been shown that the face patches strongly overlap with regions activated by near (crossed) disparities [5], but the functional consequences of this overlap for face encoding by IT neurons have not yet been studied. Furthermore, disparity-activated regions are found throughout IT, even in some posterior scene patches [5], suggesting that disparity contributes to a variety of visual representations in IT.
Concurrent with the increasingly complex depth representations, disparity-related activity in the ventral pathway becomes progressively tied to global depth perception. This is evidenced by the observation that manipulating the activity of disparity-selective neurons in the ventral pathway can strongly influence behaviour during perceptual tasks [66,67]. Moreover, whereas neurons in area V1 respond selectively to the disparity of non-corresponding images inside their receptive fields, neurons in more anterior areas of the ventral pathway gradually become unresponsive to these false matches, such that neurons in IT respond only according to global percepts. Note, however, that even V1 neurons attenuate their responses to anti-correlated random-dot stereograms [34]. This attenuation becomes more and more pronounced further along the ventral pathway, until anti-correlated random-dot stereograms stop modulating responses entirely in IT [46]. This could mean that more anterior areas assist in reducing responses to false matches in earlier visual areas through the numerous feedback connections that exist between the different areas of the ventral pathway. The weakened responses to false matches in the early visual areas will in turn attenuate some of the incorrect solutions in later areas. Eventually the global solution, which matches throughout the visual field, will emerge and be perceived. In this view, solving the stereo-correspondence problem goes hand-in-hand with the formation of depth representations. It has also been suggested that the highly recurrent processing that is required for this purpose underlies other visual computations in the ventral visual pathway [23]. However, there is evidence against such a view, favouring a feed-forward solution to the stereo-correspondence problem. For example, not all disparity tuning to false matches is attenuated in V1 [47] and the disparity tuning of V4 responses to anti-correlated random-dot stereograms is already reduced at response onset [41]. These findings suggest that no feedback is necessary to attenuate disparity tuning to false matches. Furthermore, models with no feedback requirements have been proposed that can account for the reduced disparity selectivity of V1 responses to anti-correlated random-dot stereograms [38] (see also [88,33]). Hence, an important remaining question is how the stereo-correspondence problem is solved in the ventral pathway.
We have reviewed how disparity-based depth representations evolve along the ventral pathway, and have focused on the areas that comprise the ventral pathway. Nonetheless, other areas are likely to play a role in the way the ventral pathway achieves its depth representations. For example, the middle temporal area MT is reciprocally connected to area V4, and MT has been implicated in coarse depth perception [89]. In addition, the anterior intraparietal area, which is anatomically and functionally connected to STSv [90–92], encodes disparity-defined 3D shapes and has been linked to 3D-shape perception [93–95]. This does not mean that disparity-selective dorsal-pathway activity originates from ventral-pathway activity (disparity selectivity in the dorsal pathway likely originates from area V1, V2 [20,96,97] and from V3a [98]), or vice versa. Indeed, both pathways appear to process disparity in parallel. Instead, the anatomical and functional connections between disparity-sensitive areas in both the ventral and the dorsal visual pathways suggest that under certain circumstances these areas interact with each other to facilitate depth perception. Finally, anterior IT regions, such as STSv, project to the ventro-lateral prefrontal cortex (VLPFC), which is known to be activated by disparity-defined stimuli [5,99]. However, the role of VLPFC in depth perception is still unknown. Further research is needed to understand how and when other areas interact with those in the ventral pathway.
Acknowledgements
We thank Steve Raiguel for comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Competing interests
We have no competing interests.
Funding
B.-E.V. is a postdoctoral research fellow of the Flemish fund for scientific research (FWO).
References
- 1.Brock F. 1939. Anomalous projection in squint. Its cause and effect. New methods of correction. Report of cases. Am. J. Optom. 16, 201–221. ( 10.1097/00006324-193906000-00001) [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Van Essen D. 2004. Organization of visual areas in macaque and human cerebral cortex. In The visual neurosciences (eds Chalupa LM, Werner JS), pp. 507–521. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wheatstone C. 1962. On some remarkable and hitherto unobserved phenomena of binocular vision. Optom. Wkly 53, 2311–2315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hess RF, To L, Zhou J, Wang G, Cooperstock JR. 2015. Stereo vision: the haves and have-nots. Iperception 6, 1–5. ( 10.1177/2041669515593028) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Verhoef B-E, Bohon KS, Conway BR. 2015. Functional architecture for disparity in macaque inferior temporal cortex and its relationship to the architecture for faces, color, scenes, and visual field. J. Neurosci. 35, 6952–6968. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5079-14.2015) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Howard IP, Rogers BJ. 1995. Binocular vision and stereopsis. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Westheimer G. 1979. Brain involved in stereoscopic acuity. Exp. Brain Res. 36, 585–597. ( 10.1007/BF00238525) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Julesz B. 1964. Binocular depth perception without familiarity cues. Science 145, 356–362. ( 10.1126/science.145.3630.356) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Marr D, Poggio T. 1979. A computational theory of human stereo vision. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 204, 301–328. ( 10.1098/rspb.1979.0029) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Julesz B. 1971. Foundation of cyclopean perception. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Orban GA, Janssen P, Vogels R. 2006. Extracting 3D structure from disparity. Trends Neurosci. 29, 466–473. ( 10.1016/j.tins.2006.06.012) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Janssen P, Vogels R, Orban GA. 1999. Macaque inferior temporal neurons are selective for disparity-defined three-dimensional shapes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 8217–8222. ( 10.1073/pnas.96.14.8217) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ferraina S, Paré M, Wurtz RH. 2000. Disparity sensitivity of frontal eye field neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 83, 625–629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Preston TJ, Li S, Kourtzi Z, Welchman AE. 2008. Multivoxel pattern selectivity for perceptually relevant binocular disparities in the human brain. J. Neurosci. 28, 11 315–11 327. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2728-08.2008) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Georgieva S, Peeters R, Kolster H, Todd JT, Orban GA. 2009. The processing of three-dimensional shape from disparity in the human brain. J. Neurosci. 29, 727–742. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4753-08.2009) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Maunsell JH, Van Essen DC. 1983. Functional properties of neurons in middle temporal visual area of the macaque monkey. II. Binocular interactions and sensitivity to binocular disparity. J. Neurophysiol. 49, 1148–1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tsao DY. et al. . 2003. Stereopsis activates V3A and caudal intraparietal areas in macaques and humans. Neuron 39, 555–568. ( 10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00459-8) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Poggio GF, Fischer B. 1977. Binocular interaction and depth sensitivity in striate and prestriate cortex of behaving rhesus monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 40, 1392–1405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hubel DH, Wiesel TN. 1970. Stereoscopic vision in macaque monkey. Cells sensitive to binocular depth in area 18 of the macaque monkey cortex. Nature 225, 41–42. ( 10.1038/225041a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hubel DH, Livingstone MS. 1987. Segregation of form, color, and stereopsis in primate area 18. J. Neurosci. 7, 3378–3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goodale MA, Milner AD. 1992. Separate visual pathways for perception and action. Trends Neurosci. 15, 20–25. ( 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90344-8) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. 1991. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb. Cortex 1, 1–47. ( 10.1093/cercor/1.1.1) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kravitz DJ, Saleem KS, Baker CI, Ungerleider LG, Mishkin M. 2013. The ventral visual pathway: an expanded neural framework for the processing of object quality. Trends Cogn. Sci. 17, 26–49. ( 10.1016/j.tics.2012.10.011) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Barlow HB, Blakemore C, Pettigrew JD. 1967. The neural mechanism of binocular depth discrimination. J. Physiol. 193, 327–342. ( 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008360) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pettigrew JD, Nikara T, Bishop PO. 1968. Binocular interaction on single units in cat striate cortex: simultaneous stimulation by single moving slit with receptive fields in correspondence. Exp. Brain Res. 6, 391–410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ohzawa I, Freeman RD. 1986. The binocular organization of simple cells in the cat's visual cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 56, 221–242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ohzawa I, Freeman RD. 1986. The binocular organization of complex cells in the cat's visual cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 56, 243–259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ohzawa I, DeAngelis GC, Freeman RD. 1996. Encoding of binocular disparity by simple cells in the cat's visual cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 75, 1779–1805. ( 10.1007/bf00233186) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ohzawa I, DeAngelis GC, Freeman RD. 1997. Encoding of binocular disparity by complex cells in the cat's visual cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 77, 2879–2909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.DeAngelis GC, Ohzawa I, Freeman RD. 1991. Depth is encoded in the visual cortex by a specialized receptive field structure. Nature 352, 156–159. ( 10.1038/352156a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Anzai A, Ohzawa I, Freeman RD. 1999. Neural mechanisms for encoding binocular disparity: receptive field position versus phase. J. Neurophysiol. 82, 874–890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ohzawa I, DeAngelis G, Freeman R. 1990. Stereoscopic depth discrimination in the visual cortex: neurons ideally suited as disparity detectors. Science 249, 1037–1041. ( 10.1126/science.2396096) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fleet DJ, Wagner H, Heeger DJ. 1996. Neural encoding of binocular disparity: energy models, position shifts and phase shifts. Vis. Res. 36, 1839–1857. ( 10.1016/0042-6989(95)00313-4) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cumming BG, Parker AJ. 1997. Responses of primary visual cortical neurons to binocular disparity without depth perception. Nature 389, 280–283. ( 10.1038/38487) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Scholl B, Burge J, Priebe NJ. 2013. Binocular integration and disparity selectivity in mouse primary visual cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 109, 3013–3024. ( 10.1152/jn.01021.2012) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Neri P, Parker AJ, Blakemore C. 1999. Probing the human stereoscopic system with reverse correlation. Nature 401, 695–698. ( 10.1038/44409) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tanabe S, Yasuoka S, Fujita I. 2008. Disparity-energy signals in perceived stereoscopic depth. J. Vis. 8, 22 ( 10.1167/8.3.22) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Read JCA, Parker AJ, Cumming BG. 2002. A simple model accounts for the response of disparity-tuned V1 neurons to anticorrelated images. Vis. Neurosci. 19, 735–753. ( 10.1017/S0952523802196052) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Prince SJD, Pointon AD, Cumming BG, Parker AJ. 2002. Quantitative analysis of the responses of V1 neurons to horizontal disparity in dynamic random-dot stereograms. J. Neurophysiol. 87, 191–208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Parker AJ. 2007. Binocular depth perception and the cerebral cortex. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 379–391. ( 10.1038/nrn2131) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tanabe S, Umeda K, Fujita I. 2004. Rejection of false matches for binocular correspondence in macaque visual cortical area V4. J. Neurosci. 24, 8170–8180. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5292-03.2004) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Umeda K, Tanabe S, Fujita I. 2007. Representation of stereoscopic depth based on relative disparity in macaque area V4. J. Neurophysiol. 98, 241–252. ( 10.1152/jn.01336.2006) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cumming BG, Parker AJ. 1999. Binocular neurons in V1 of awake monkeys are selective for absolute, not relative, disparity. J. Neurosci. 19, 5602–5618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cogan AI, Lomakin AJ, Rossi AF. 1993. Depth in anticorrelated stereograms: effects of spatial density and interocular delay. Vis. Res. 33, 1959–1975. ( 10.1016/0042-6989(93)90021-N) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cumming BG, Shapiro SE, Parker AJ. 1998. Disparity detection in anticorrelated stereograms. Perception 27, 1367–1377. ( 10.1068/p271367) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Janssen P, Vogels R, Liu Y, Orban GA. 2003. At least at the level of inferior temporal cortex, the stereo correspondence problem is solved. Neuron 37, 693–701. ( 10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00023-0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cumming BG, Parker AJ. 2000. Local disparity not perceived depth is signaled by binocular neurons in cortical area V1 of the macaque. J. Neurosci. 20, 4758–4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Nienborg H, Cumming BG. 2006. Macaque V2 neurons, but not V1 neurons, show choice-related activity. J. Neurosci. 26, 9567–9578. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2256-06.2006) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nienborg H, Cumming BG. 2014. Decision-related activity in sensory neurons may depend on the columnar architecture of cerebral cortex. J. Neurosci. 34, 3579–3585. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2340-13.2014) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mayo JP, Verhoef B-E. 2014. Feature-specific clusters of neurons and decision-related neuronal activity. J. Neurosci. 34, 8385–8386. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1493-14.2014) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Cowey A, Wllkinson F. 1991. The role of the corpus callosum and extra striate visual areas in stereoacuity in macaque monkeys. Neuropsychologia 29, 465–479. ( 10.1016/0028-3932(91)90005-S) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Thomas OM, Cumming BG, Parker AJ. 2002. A specialization for relative disparity in V2. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 472–478. ( 10.1038/nn837) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Riesenhuber M, Poggio T. 1999. Hierarchical models of object recognition in cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 1019–1025. ( 10.1038/14819) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.von der Heydt R, Zhou H, Friedman HS. 2000. Representation of sterescopic edges in monkey visual cortex. Vis. Res. 40, 1955–1967. ( 10.1016/S0042-6989(00)00044-4) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bredfeldt CE, Cumming BG. 2006. A simple account of cyclopean edge responses in macaque V2. J. Neurosci. 26, 7581–7596. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5308-05.2006) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bakin JS, Nakayama K, Gilbert CD. 2000. Visual responses in monkey areas V1 and V2 to three-dimensional surface configurations. J. Neurosci. 20, 8188–8198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Allouni AK, Thomas OM, Solomon SG, Krug K, Parker AJ.2005. Local and global binocular matching in V2 of the awake macaque. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 510.8. Washington, DC: Society for Neuroscience.
- 58.Hinkle DA, Connor CE. 2001. Disparity tuning in macaque area V4. Neuroreport 12, 365–369. ( 10.1097/00001756-200102120-00036) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Watanabe M, Tanaka H, Uka T, Fujita I. 2002. Disparity-selective neurons in area V4 of macaque monkeys. J. Neurophysiol. 87, 1960–1973. ( 10.1152/jn.00780.2000) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hinkle DA, Connor CE. 2005. Quantitative characterization of disparity tuning in ventral pathway area V4. J. Neurophysiol. 94, 2726–2737. ( 10.1152/jn.00341.2005) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Cowey A, Porter J. 1979. Brain damage and global stereopsis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 204, 399–407. ( 10.1098/rspb.1979.0035) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hinkle DA, Connor CE. 2002. Three-dimensional orientation tuning in macaque area V4. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 665–670. ( 10.1038/nn875) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hegdé J, Van Essen DC. 2005. Role of primate visual area V4 in the processing of 3-D shape characteristics defined by disparity. J. Neurophysiol. 94, 2856–2866. ( 10.1152/jn.00802.2004) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Janssen P, Vogels R, Orban GA. 2000. Three-dimensional shape coding in inferior temporal cortex. Neuron 27, 385–397. ( 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)00045-3) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yamane Y, Carlson ET, Bowman KC, Wang Z, Connor CE. 2008. A neural code for three-dimensional object shape in macaque inferotemporal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 1352–1360. ( 10.1038/nn.2202) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Verhoef BE, Vogels R, Janssen P. 2012. Inferotemporal cortex subserves three-dimensional structure categorization. Neuron 73, 171–182. ( 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.10.031) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Shiozaki HM, Tanabe S, Doi T, Fujita I. 2012. Neural activity in cortical area V4 underlies fine disparity discrimination. J. Neurosci. 32, 3830–3841. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5083-11.2012) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Uka T, Tanaka H, Yoshiyama K, Kato M, Fujita I. 2000. Disparity selectivity of neurons in monkey inferior temporal cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 84, 120–132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tanaka H, Uka T, Yoshiyama K, Kato M, Fujita I. 2001. Processing of shape defined by disparity in monkey inferior temporal cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 85, 735–744. ( 10.1016/S0168-0102(98)82671-0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Uka T, Tanabe S, Watanabe M, Fujita I. 2005. Neural correlates of fine depth discrimination in monkey inferior temporal cortex. J. Neurosci. 25, 10 796–10 802. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1637-05.2005) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Liu Y, Vogels R, Orban GA. 2004. Convergence of depth from texture and depth from disparity in macaque inferior temporal cortex. J. Neurosci. 24, 3795–3800. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0150-04.2004) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.DiCarlo JJ, Zoccolan D, Rust NC. 2012. How does the brain solve visual object recognition? Neuron 73, 415–434. ( 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.01.010) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Vogels R, Orban GA. 1996. Coding of stimulus invariances by inferior temporal neurons. Prog. Brain Res. 112, 195–211. ( 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)63330-0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Verhoef BE, Vogels R, Janssen P. 2010. Contribution of inferior temporal and posterior parietal activity to three-dimensional shape perception. Curr. Biol. 20, 909–913. ( 10.1016/j.cub.2010.03.058) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Sereno ME, Trinath T, Augath M, Logothetis NK. 2002. Three-dimensional shape representation in monkey cortex. Neuron 33, 635–652. ( 10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00598-6) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Janssen P, Vogels R, Orban GA. 2000. Selectivity for 3D shape that reveals distinct areas within macaque inferior temporal cortex. Science 288, 2054–2056. ( 10.1126/science.288.5473.2054) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Tsao DY, Freiwald WA, Tootell RBH, Livingstone MS. 2006. A cortical region consisting entirely of face-selective cells. Science 311, 670–674. ( 10.1126/science.1119983) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Vaziri S, Carlson ET, Wang Z, Connor CE. 2014. A channel for 3D environmental shape in anterior inferotemporal cortex. Neuron 84, 55–62. ( 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.08.043) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lafer-Sousa R, Conway BR. 2013. Parallel, multi-stage processing of colors, faces and shapes in macaque inferior temporal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 1870–1878. ( 10.1038/nn.3555) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Popivanov ID, Jastorff J, Vanduffel W, Vogels R. 2012. Stimulus representations in body-selective regions of the macaque cortex assessed with event-related fMRI. Neuroimage 63, 723–741. ( 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.07.013) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Takemura A, Inoue Y, Kawano K, Quaia C, Miles FA. 2001. Single-unit activity in cortical area MST associated with disparity-vergence eye movements: evidence for population coding. J. Neurophysiol. 85, 2245–2266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ban H, Preston TJ, Meeson A, Welchman AE. 2012. The integration of motion and disparity cues to depth in dorsal visual cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 636–643. ( 10.1038/nn.3046) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Sanada TM, Nguyenkim JD, DeAngelis GC. 2012. Representation of 3-D surface orientation by velocity and disparity gradient cues in area MT. J. Neurophysiol. 107, 2109–2122. ( 10.1152/jn.00578.2011) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Tsutsui K-I, Jiang M, Yara K, Sakata H, Taira M. 2001. Integration of perspective and disparity cues in surface-orientation-selective neurons of area CIP. J. Neurophysiol. 86, 2856–2867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Tsutsui K-I, Sakata H, Naganuma T, Taira M. 2002. Neural correlates for perception of 3D surface orientation from texture gradient. Science 298, 409–412. ( 10.1126/science.1074128) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Nelissen K, Joly O, Durand J-B, Todd JT, Vanduffel W, Orban GA. 2009. The extraction of depth structure from shading and texture in the macaque brain. PLoS ONE 4, e8306 ( 10.1371/journal.pone.0008306) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Popivanov ID, Jastorff J, Vanduffel W, Vogels R. 2015. Tolerance of macaque middle STS body patch neurons to shape-preserving stimulus transformations. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 27, 1001–1016. ( 10.1162/jocn_a_00762) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Tanabe S, Haefner RM, Cumming BG. 2011. Suppressive mechanisms in monkey V1 help to solve the stereo correspondence problem. J. Neurosci. 31, 8295–8305. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5000-10.2011) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.DeAngelis GC, Cumming BG, Newsome WT. 1998. Cortical area MT and the perception of stereoscopic depth. Nature 394, 677–680. ( 10.1038/29299) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Borra E, Belmalih A, Calzavara R, Gerbella M, Murata A, Rozzi S, Luppino G. 2008. Cortical connections of the macaque anterior intraparietal (AIP) area. Cereb. Cortex 18, 1094–1111. ( 10.1093/cercor/bhm146) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Verhoef BE, Vogels R, Janssen P. 2011. Synchronization between the end stages of the dorsal and the ventral visual stream. J. Neurophysiol. 105, 2030–2042. ( 10.1152/jn.00924.2010) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Premereur E, Van Dromme IC, Romero MC, Vanduffel W, Janssen P. 2015. Effective connectivity of depth-structure-selective patches in the lateral bank of the macaque intraparietal sulcus. PLoS Biol. 13, e1002072 ( 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002072) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Srivastava S, Orban GA, De Mazière PA, Janssen P. 2009. A distinct representation of three-dimensional shape in macaque anterior intraparietal area: fast, metric, and coarse. J. Neurosci. 29, 10 613–10 626. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6016-08.2009) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Verhoef B-E, Michelet P, Vogels R, Janssen P. 2015. Choice-related activity in the anterior intraparietal area during 3-D structure categorization. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 27, 1104–1115. ( 10.1162/jocn_a_00773) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Verhoef B-E, Vogels R, Janssen P. 2015. Effects of microstimulation in the anterior intraparietal area during three-dimensional shape categorization. PLoS ONE 10, e0136543 ( 10.1371/journal.pone.0136543) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ponce CR, Lomber SG, Born RT. 2008. Integrating motion and depth via parallel pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 216–223. ( 10.1038/nn2039) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Smolyanskaya A, Haefner RM, Lomber SG, Born RT. 2015. A modality-specific feedforward component of choice-related activity in MT. Neuron 87, 208–219. ( 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.06.018) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Anzai A, Chowdhury SA, DeAngelis GC. 2011. Coding of stereoscopic depth information in visual areas V3 and V3A. J. Neurosci. 31, 10 270–10 282. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5956-10.2011) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Joly O, Vanduffel W, Orban GA. 2009. The monkey ventral premotor cortex processes 3D shape from disparity. Neuroimage 47, 262–272. ( 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.04.043) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]