Abstract
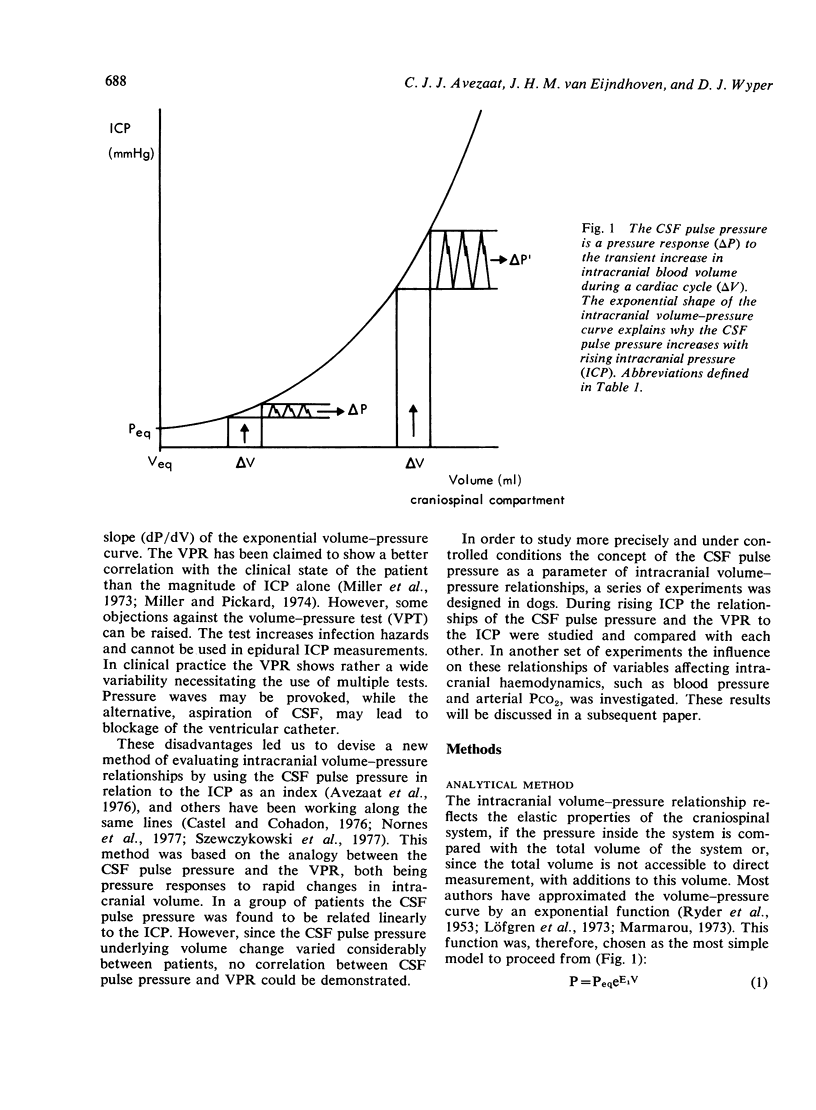
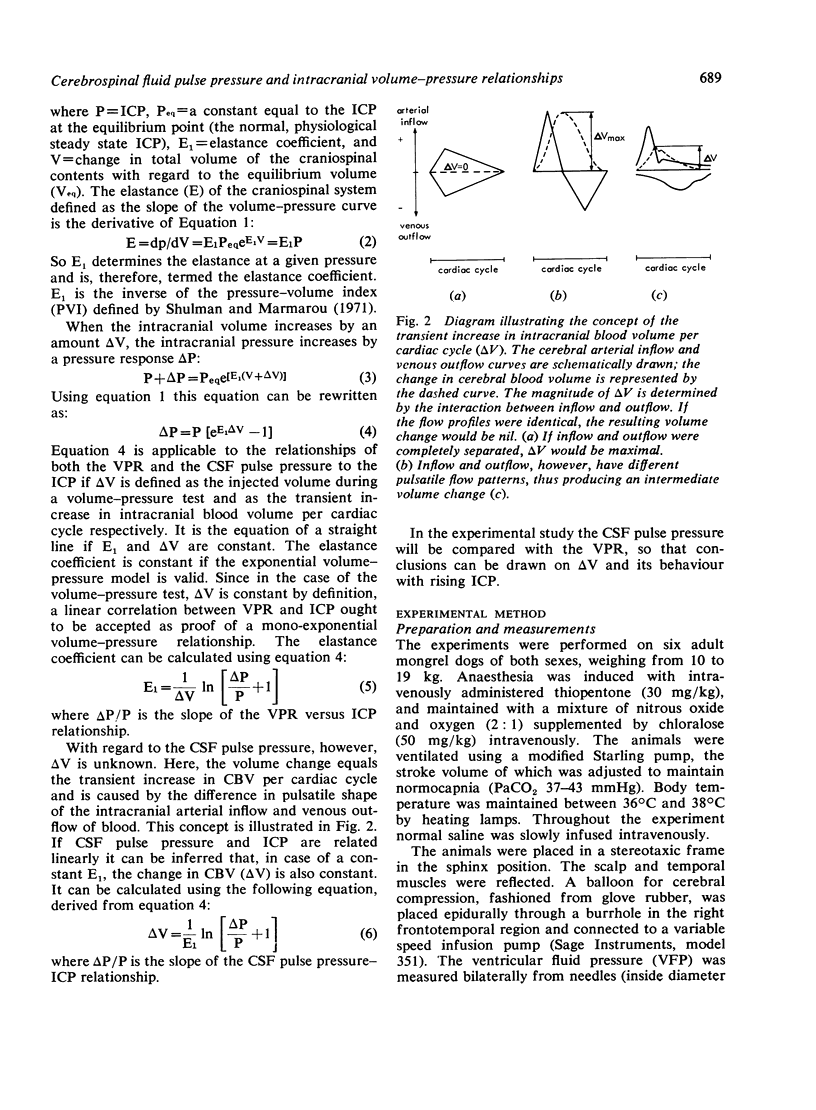
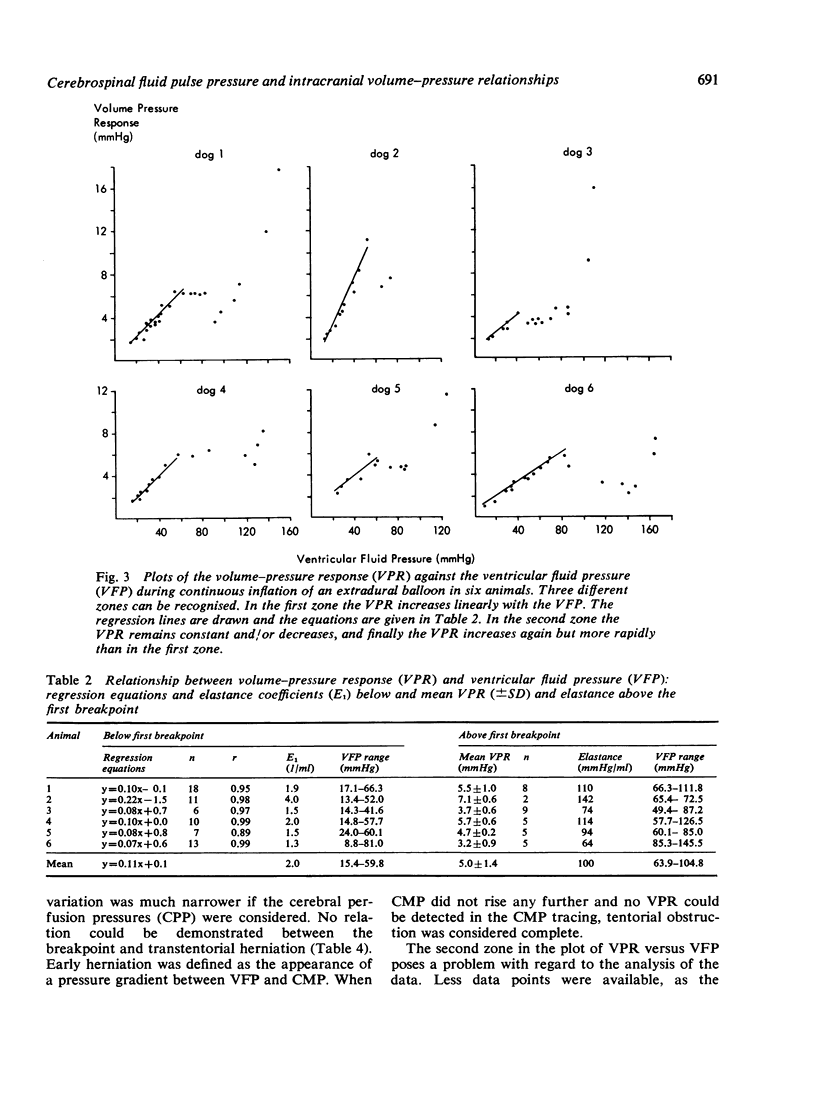
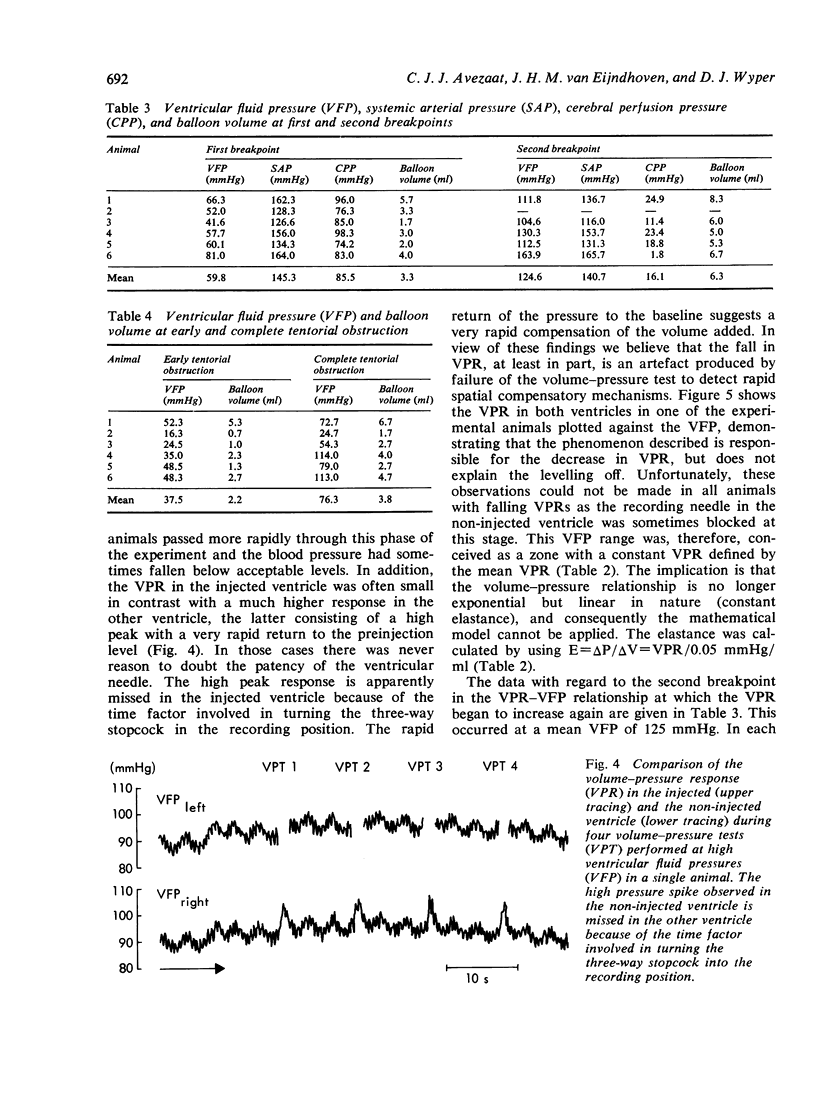
In six anaesthetised and ventilated dogs the CSF pulse pressure was compared with the volume-pressure response (VPR) during continuous inflation of an extradural balloon. Both pulse pressure and VPR increased linearly with the ventricular fluid pressure (VFP) up to a mean VFP of 60 mmHg. At this pressure a breakpoint occurred above which the CSF pulse pressure showed a steeper linear increase, while the VPR remained constant. It is suggested that the breakpoint is related to failure of autoregulation, and that in non-autoregulating patients the CSF pulse pressure is a better parameter of the clinical state than the VPR.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Guinane J. E. Cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure and brain compliance in adult cats. Neurology. 1975 Jun;25(6):559–564. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.6.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janny P. La surveillance de la pression intra-cranienne en neuro-chirurgie. Neurochirurgie. 1974 Nov;20(6):521–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston I. H., Rowan J. O., Harper A. M., Jennett W. B. Raised intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow. 2. Supratentorial and infratentorial mass lesions in primates. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Apr;36(2):161–170. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGFITT T. W., WEINSTEIN J. D., KASSELL N. F. CEREBRAL VASOMOTOR PARALYSIS PRODUCED BY INTRACRANIAL HYPERTENSION. Neurology. 1965 Jul;15:622–641. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.7.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech P., Miller J. D. Intracranial volume--pressure relationships during experimental brain compression in primates. 1. Pressure responses to changes in ventricular volume. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Oct;37(10):1093–1098. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.10.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech P., Miller J. D. Intracranial volume--pressure relationships during experimental brain compression in primates. 2. Effect of induced changes in systemic arterial pressure and cerebral blood flow. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Oct;37(10):1099–1104. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.10.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. T., Potts D. G., Deonarine V., Deck M. D. Ventricular compliance in dogs with and without aqueductal obstruction. J Neurosurg. 1973 Oct;39(4):463–473. doi: 10.3171/jns.1973.39.4.0463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg N., Cronqvist S., Kjällquist A. Clinical investigations on interrelations between intracranial pressure and intracranial hemodynamics. Prog Brain Res. 1968;30:69–75. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)61440-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfgren J. Effects of variations in arterial pressure and arterial carbon dioxide tension on the cerebrospinal fluid pressure-volume relationships. Acta Neurol Scand. 1973;49(5):586–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1973.tb01332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfgren J. Effects of variations in arterial pressure and arterial carbon dioxide tension on the cerebrospinal fluid pressure-volume relationships. Acta Neurol Scand. 1973;49(5):586–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1973.tb01332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfgren J., von Essen C., Zwetnow N. N. The pressure-volume curve of the cerebrospinal fluid space in dogs. Acta Neurol Scand. 1973;49(5):557–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1973.tb01330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmarou A., Shulman K., LaMorgese J. Compartmental analysis of compliance and outflow resistance of the cerebrospinal fluid system. J Neurosurg. 1975 Nov;43(5):523–534. doi: 10.3171/jns.1975.43.5.0523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Garibi J., Pickard J. D. Induced changes of cerebrospinal fluid volume. Effects during continuous monitoring of ventricular fluid pressure. Arch Neurol. 1973 Apr;28(4):265–269. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490220073011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Pickard J. D. Intracranial volume pressure studies in patients with head injury. Injury. 1974 Feb;5(3):265–268. doi: 10.1016/s0020-1383(74)80021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nornes H., Aaslid R., Lindegaard K. F. Intracranial pulse pressure dynamics in patients with intracranial hypertension. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1977;38(3-4):177–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01401089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYDER H. W., ESPEY F. F., KIMBELL F. D., PENKA E. J., ROSENAUER A., PODOLSKY B., EVANS J. P. The mechanism of the change in cerebrospinal fluid pressure following an induced change in the volume of the fluid space. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Mar;41(3):428–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinghaus J. W. Blood gas calculator. J Appl Physiol. 1966 May;21(3):1108–1116. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1966.21.3.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro H. M., Langfitt T. W., Weinstein J. D. Compression of cerebral vessels by intracranial hypertension. II. Morphological evidence for collapse of vessels. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1966;15(3):223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF01406784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan H. G., Miller J. D., Becker D. P., Flora R. E., Allen G. A. The physiological basis of intracranial pressure change with progressive epidural brain compression. An experimental evaluation in cats. J Neurosurg. 1977 Oct;47(4):532–550. doi: 10.3171/jns.1977.47.4.0532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symon L., Pasztor E., Branston N. M., Dorsch N. W. Effect of supratentorial space-occupying lesions on regional intracranial pressure and local cerebral blood flow: an experimental study in baboons. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Jun;37(6):617–626. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczykowski J., Sliwka S., Kunicki A., Dytko P., Korsak-Sliwka J. A fast method of estimating the elastance of the intracranial system. J Neurosurg. 1977 Jul;47(1):19–26. doi: 10.3171/jns.1977.47.1.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



