Abstract
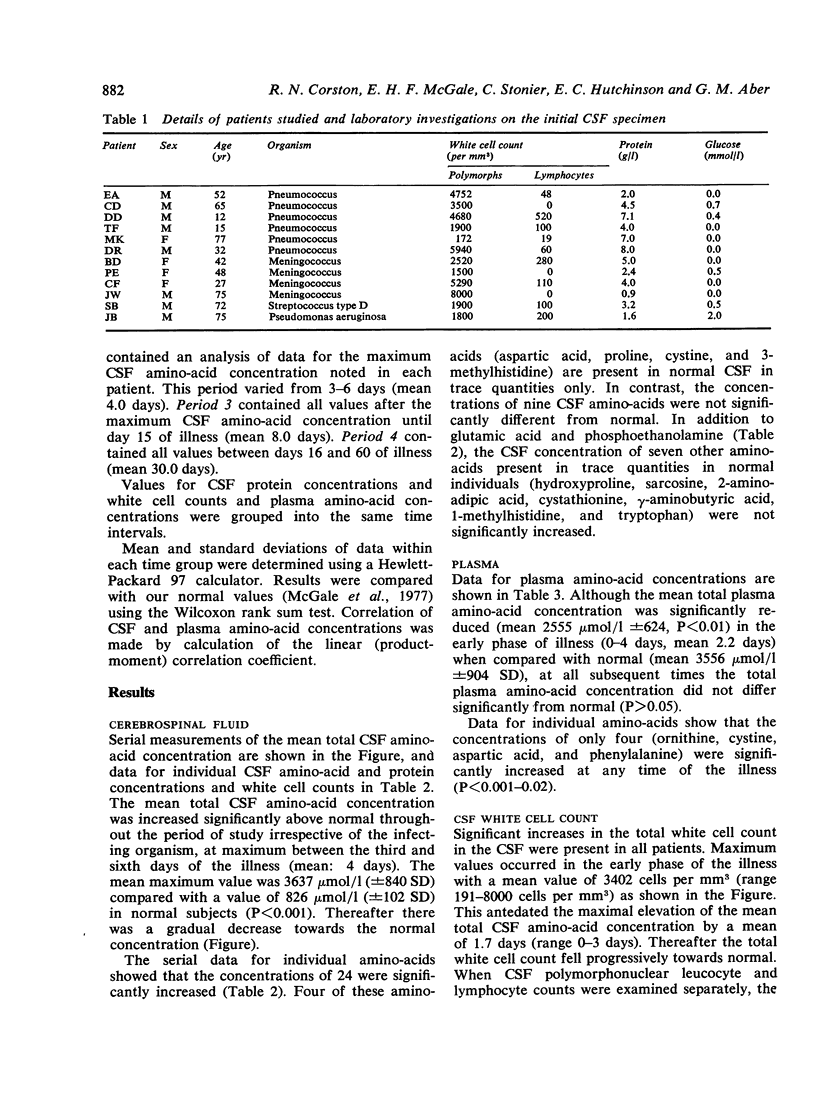
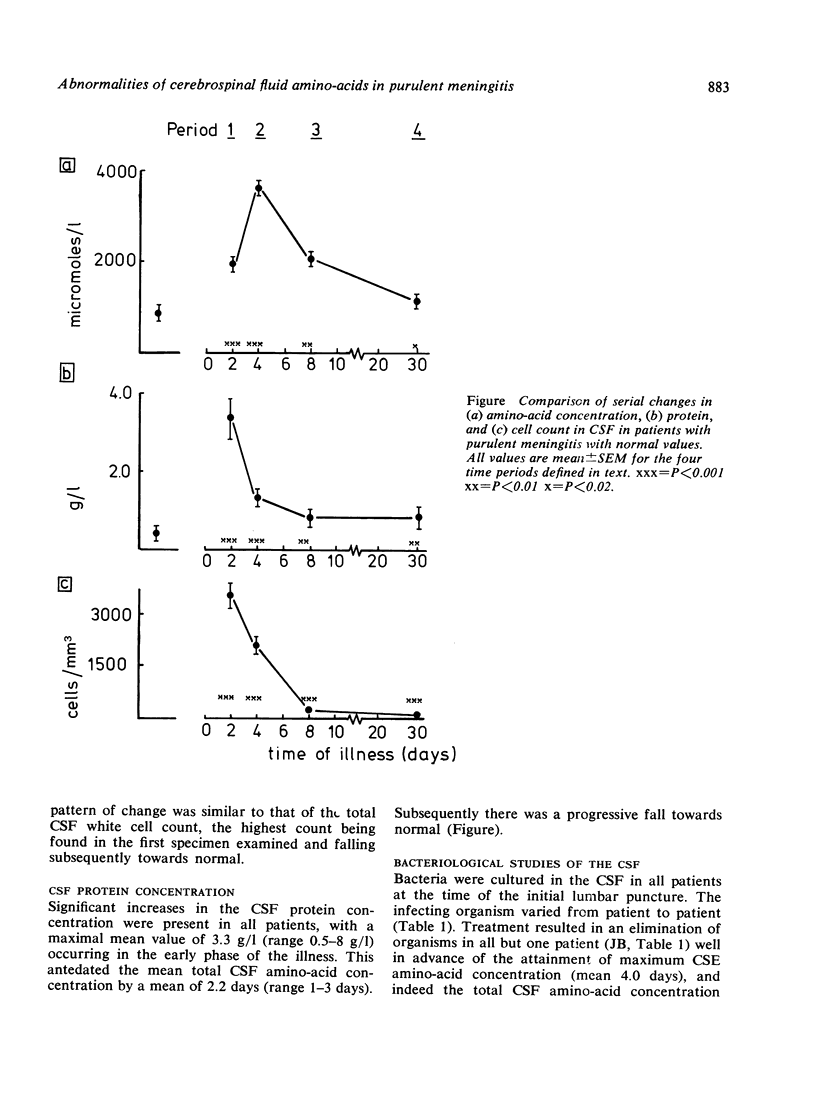
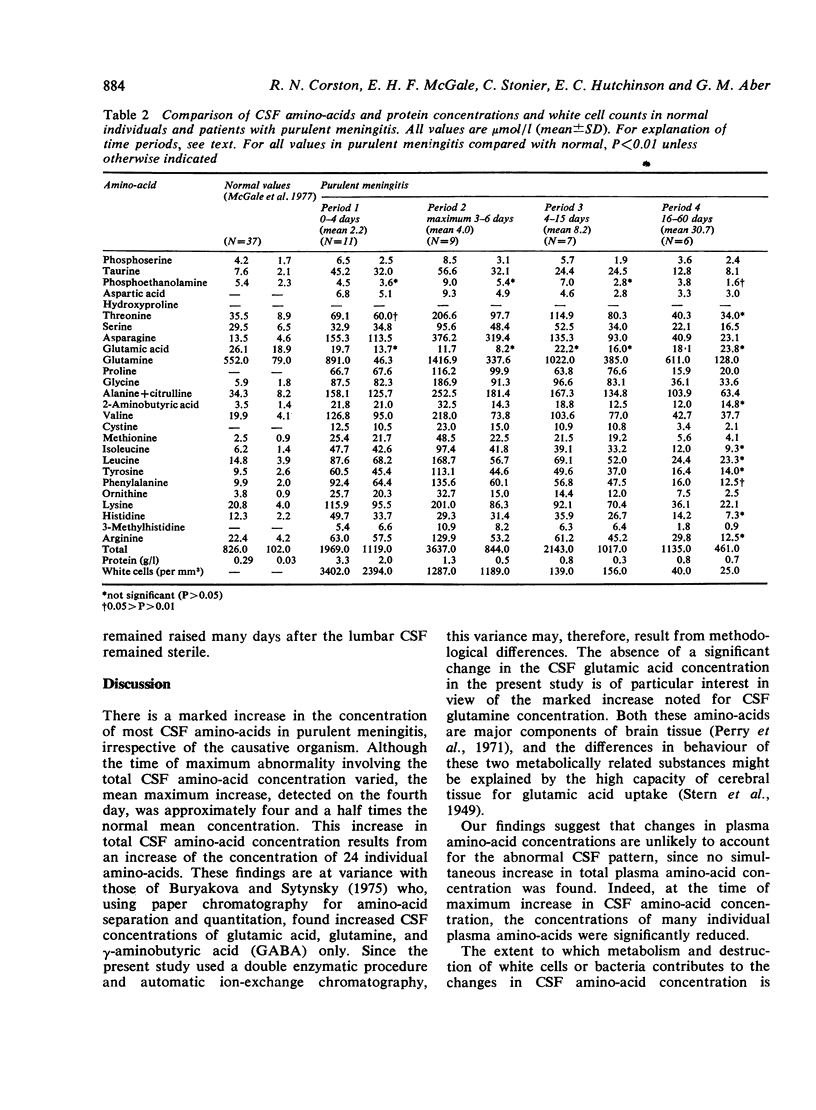
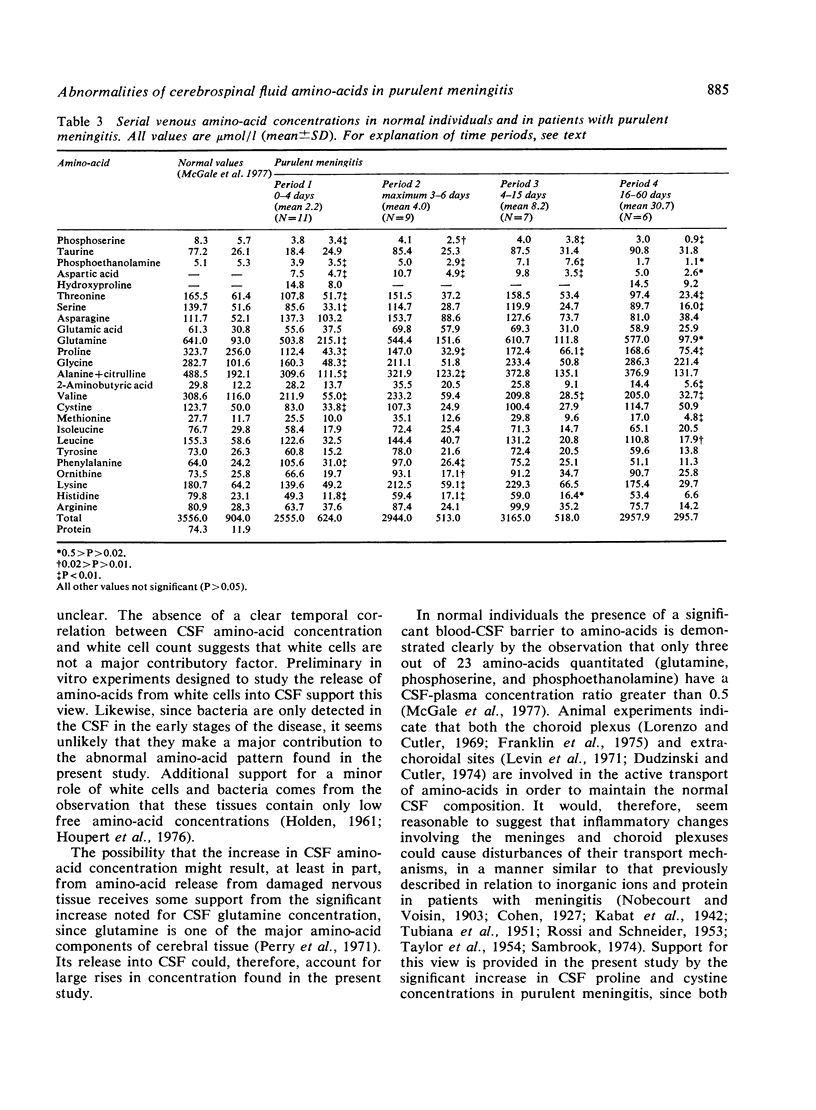
Serial measurements were made of the cerebrospinal fluid and plasma amino-acid concentrations in 12 patients with purulent meningitis. Marked increases in the concentrations of most CSF amino-acids were found, possibly caused by altered transport mechanisms in the inflamed meninges and choroid plexuses.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADBURY M. W., STUBBS J., HUGHES I. E., PARKER P. THE DISTRIBUTION OF POTASSIUM, SODIUM, CHLORIDE AND UREA BETWEEN LUMBAR CEREBROSPINAL FLUID AND BLOOD SERUM IN HUMAN SUBJECTS. Clin Sci. 1963 Aug;25:97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buryakova A. V., Sytinsky I. A. Amino acid composition of cerebrospinal fluid in actue neuroinfections in children. Arch Neurol. 1975 Jan;32(1):28–31. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490430050007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudzinski D. S., Cutler R. W. Spinal subarachnoid perfusion in the rat: glycine transport from spinal fluid. J Neurochem. 1974 Mar;22(3):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb07600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin G. M., Dudzinski D. S., Cutler R. W. Amino acid transport into the cerebrospinal fluid of the rat. J Neurochem. 1975 Feb;24(2):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb11889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houpert Y., Tarallo P., Siest G. Quantitative determination of granulocytic amino acids in healthy men and women. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jun 15;69(3):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Moore D. H., Landow H. AN ELECTROPHORETIC STUDY OF THE PROTEIN COMPONENTS IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP TO THE SERUM PROTEINS. J Clin Invest. 1942 Sep;21(5):571–577. doi: 10.1172/JCI101335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakke J. P., Teelken A. W. Amino acid abnormalities in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with parkinsonism and extrapyramidal disorders. Neurology. 1976 May;26(5):489–493. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.5.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E., Nogueira G. J., Wright P. M. Transfer of amino acids and urea to and from the subarachnoid space. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218 (Suppl):42P–43P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo A. V. Amino acid transport mechanisms of the cerebrospinal fluid. Fed Proc. 1974 Sep;33(9):2079–2085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo A. V., Cutler R. W. Amino acid transport by choroid plexus in vitro. J Neurochem. 1969 Apr;16(4):577–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGale E. H., Pye I. F., Corston R., Stonier C., Hutchinson E. C., Aber G. M. The effect of haemodialysis on cerebrospinal fluid and plasma amino acids. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Feb 15;92(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGale E. H., Pye I. F., Stonier C., Hutchinson E. C., Aber G. M. Studies of the inter-relationship between cerebrospinal fluid and plasma amino acid concentrations in normal individuals. J Neurochem. 1977 Aug;29(2):291–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb09621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutani R., Monaco F., Durelli L., Delsedime M. Free amino acids in the cerebrospinal fluid of epileptic subjects. Epilepsia. 1974 Dec;15(4):593–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1974.tb04031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry T. L., Hansen S., Berry K., Mok C., Lesk D. Free amino acids and related compounds in biopsies of human brain. J Neurochem. 1971 Mar;18(3):521–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pye I. F., McGale E. H., Stonier C., Hutchinson E. C., Aber G. M. Studies of cerebrospinal fluid and plasma amino acids in patients with steady-state chronic renal failure. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Feb 15;92(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90397-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pye I. F., Stonier C., McGale H. F. Double-enzymatic assay for determination of glutamine and glutamic acid in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma. Anal Chem. 1978 Jun;50(7):951–953. doi: 10.1021/ac50029a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI G., SCHNEIDER G. Elektrophoretische Untersuchung von pathologischem Liquor cerebrospinalis. Klin Wochenschr. 1953 Nov 1;31(41-42):969–975. doi: 10.1007/BF01533810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook M. A. The relationship between cerebrospinal fluid and plasma electrolytes in patients with meningitis. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Oct;23(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. R., Eggleston L. V., Hems R., Krebs H. A. Accumulation of glutamic acid in isolated brain tissue. Biochem J. 1949;44(4):410–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR L. M., SMITH H. V., HUNTER G. The blood-C.S.F. barrier to bromide in diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis. Lancet. 1954 Apr 3;266(6814):700–702. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)92108-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUBIANA M., BENDA P., CONSTANS J. Sodium radio-actif24 na et liquide céphalorachidien applications au diagnostic des meningites tuberculeuses et des compressions medullaries. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1951 Jul;85(1):17–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



