Abstract
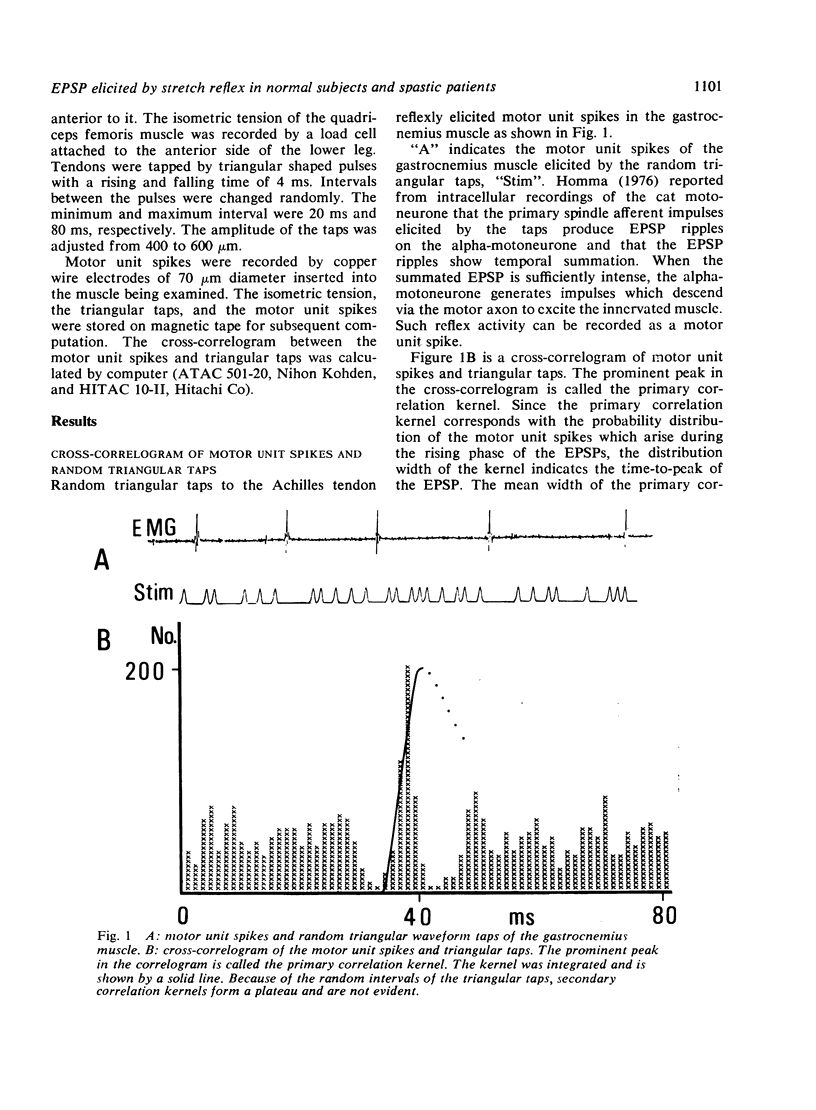
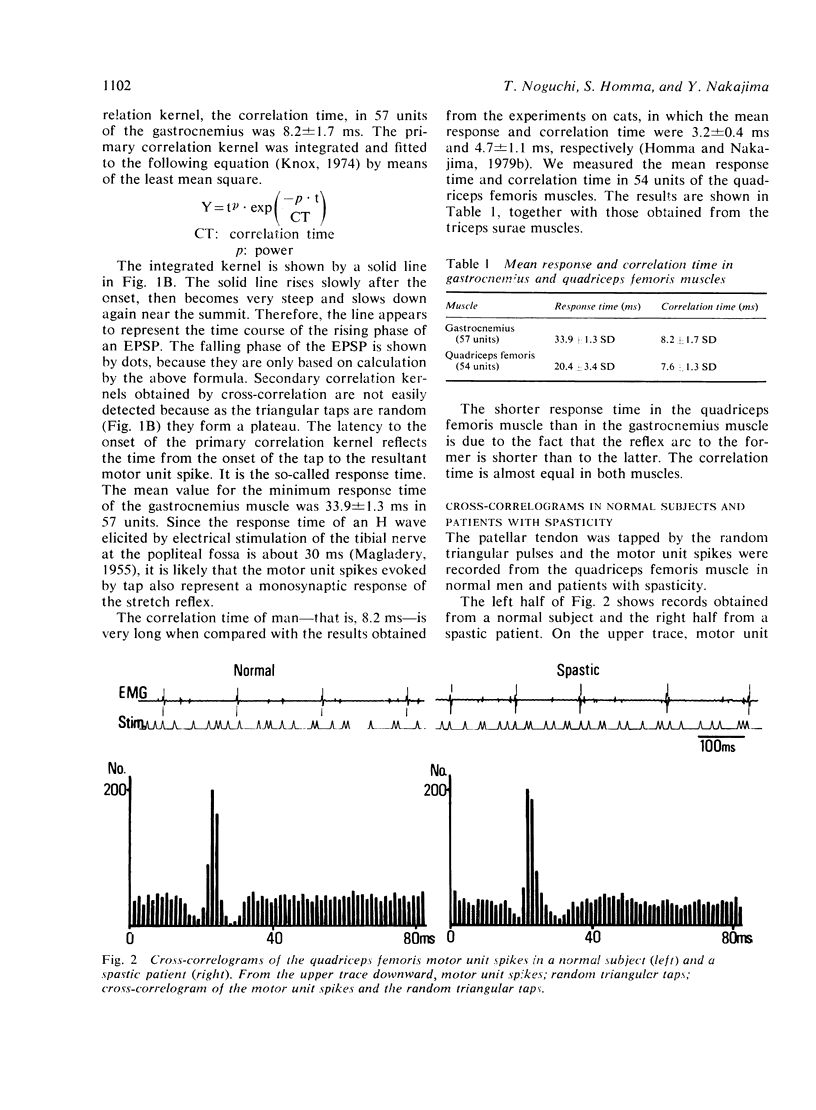
The patellar tendon was tapped by random impulses of triangular waveform and motor unit spikes were recorded from the quadriceps femoris muscle. The cross-correlogram of the taps and the motor unit spikes revealed a primary correlation kernel, the width of which was interpreted as an indicator of the mean time-to-peak of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) elicited monosynaptically in an alpha-motoneurone by the triangular taps. The mean time-to-peak was 7.6 +/- 1.3 ms in normal subjects and 9.0 +/- 1.8 ms in spastic patients (P less than 0.005). The prolonged time-to-peak of EPSP in spastic patients is consistent with the hypothesis that as a result of degeneration of the corticomotoneuronal tract the Ia axons sprout and form more synaptic contacts on distal portions of the dendrites of alpha-motoneurones.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIANCONI R., van der MEULEN J. The response to vibration of the end organs of mammalian muscle spindles. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Jan;26:177–190. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda K. [Ia, Ib and II discharges during muscle vibration]. Nihon Seirigaku Zasshi. 1973 May;35(5):242–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma S. Frequency characteristics of the impulse decoding ratio between the spinal afferents and efferents in the stretch reflex. Prog Brain Res. 1976;44:15–30. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60720-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma S., Ishikawa K., Stuart D. G. Motoneuron responses to linearly rising muscle stretch. Am J Phys Med. 1970 Oct;49(5):290–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma S., Kanda K., Watanabe S. Preferred spike intervals in the vibration reflex. Jpn J Physiol. 1972 Aug;22(4):421–432. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.22.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma S., Nakajima Y. Coding process in human stretch reflex analysed by phase-locked spikes. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Jan;11(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox C. K. Cross-correlation functions for a neuronal model. Biophys J. 1974 Aug;14(8):567–582. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85936-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W. Some observations on spinal reflexes in man. Pflugers Arch. 1955;261(4):302–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00364122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCOUCH G. P., AUSTIN G. M., LIU C. N., LIU C. Y. Sprouting as a cause of spasticity. J Neurophysiol. 1958 May;21(3):205–216. doi: 10.1152/jn.1958.21.3.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R., Hore J. Time course of minimal corticomotoneuronal excitatory postsynaptic potentials in lumbar motoneurons of the monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1969 May;32(3):443–451. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.3.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Burke R. E., Smith T. G., Nelson P. G., Frank K. Dendritic location of synapses and possible mechanisms for the monosynaptic EPSP in motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1169–1193. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASAKI K., OTANI T. Accommodation in spinal motoneurons of the cat. Jpn J Physiol. 1961 Aug 15;11:443–456. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.11.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov A. I. Neuronal organization and synaptic mechanisms of supraspinal motor control in vertebrates. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1975;72:1–54. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



