Abstract
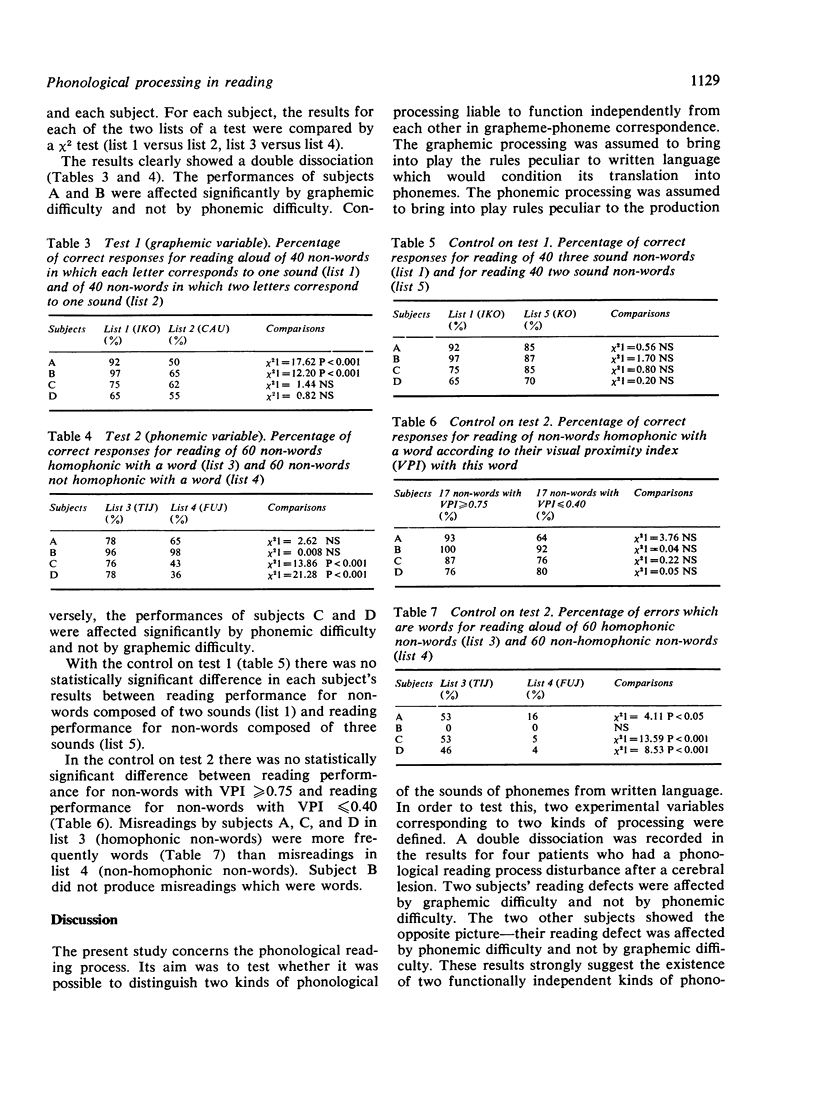
The reading of four subjects suffering from a phonological reading impairment as a result of a cerebral lesion was tested. A double dissociation observed in their results is strong evidence for the existence of two functionally independent kinds of phonological processing in reading--a graphemic and a phonetic one.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreewsky E., Seron X. Implicit processing of grammatical rules in a classical case of agrammatism. Cortex. 1975 Dec;11(4):379–390. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(75)80029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauvois M. F., Dérouesné J. Phonological alexia: three dissociations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Dec;42(12):1115–1124. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.12.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauvois M. F., Saillant B., Meininger V., Lhermitte F. Bilateral tactile aphasia: a tacto-verbal dysfunction. Brain. 1978 Sep;101(3):381–401. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.3.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. F., Brown J., Tomlinson E. B. Varieties of alexia. Word and letter blindness. Neurology. 1971 Sep;21(9):951–957. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.9.951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. F. The third alexia. Arch Neurol. 1977 Jun;34(6):327–331. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1977.00500180021004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner H., Zurif E. Bee but not be: oral reading of single words in aphasia and alexia. Neuropsychologia. 1975 Apr;13(2):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(75)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. C., Newcombe F. Patterns of paralexia: a psycholinguistic approach. J Psycholinguist Res. 1973 Jul;2(3):175–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01067101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson K. E., Marcel A. J. Aphasia, dyslexia and the phonological coding of written words. Q J Exp Psychol. 1977 May;29(2):307–318. doi: 10.1080/14640747708400606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffran E. M., Marin O. S. Reading without phonology: evidence from aphasia. Q J Exp Psychol. 1977 Aug;29(3):515–525. doi: 10.1080/14640747708400627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffran E. M., Schwartz M. F., Marin O. S. Semantic mechanisms in paralexia. Brain Lang. 1976 Apr;3(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(76)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shallice T., Warrington E. K. The possible role of selective attention in acquired dyslexia. Neuropsychologia. 1977;15(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(77)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shallice T., Warrington E. K. Word recognition in a phonemic dyslexic patient. Q J Exp Psychol. 1975 May;27(2):187–199. doi: 10.1080/14640747508400479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEUBER H. L. Physiological psychology. Annu Rev Psychol. 1955;6:267–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.06.020155.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



