Abstract
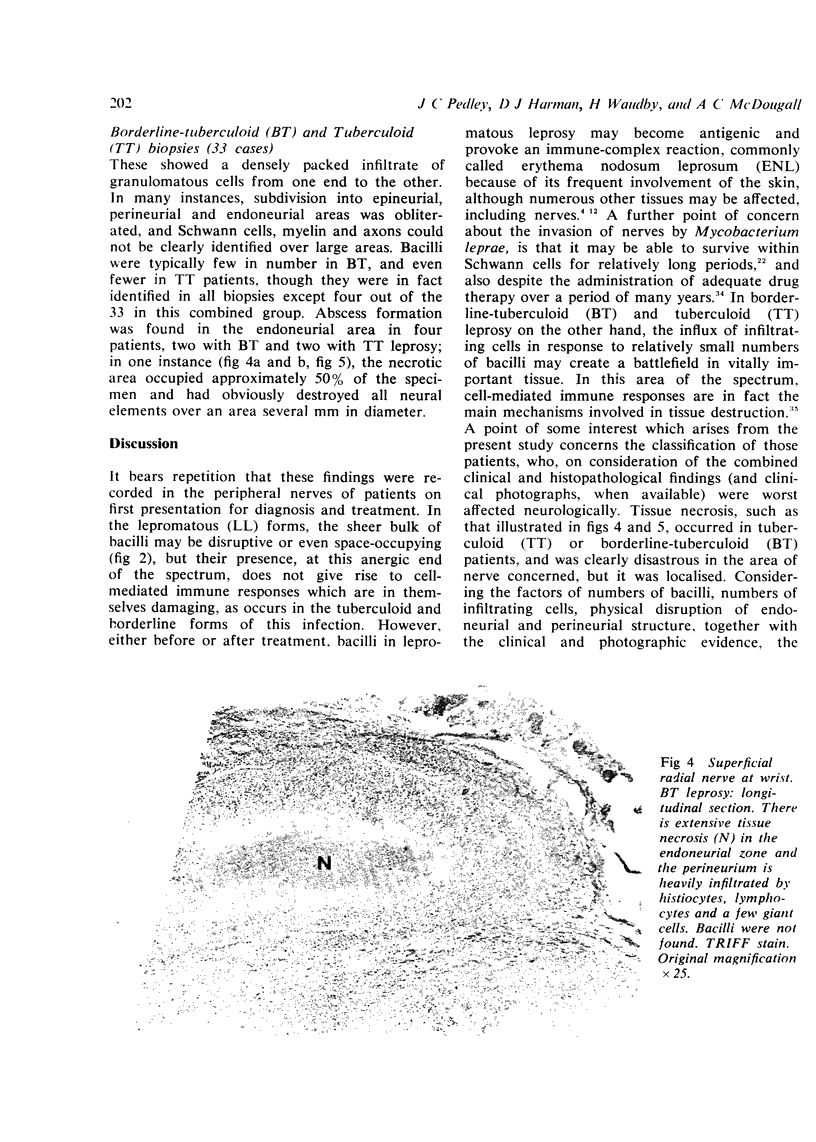
From a series of 343 nerve biopsies taken by one clinician over a period of 12 years in Nepal, this paper describes the histopathological findings in 153 biopsies from 119 patients suffering from tuberculoid, borderline (dimorphous) or lepromatous leprosy, who were untreated at the time of first presentation and diagnosis. They were taken during the course of other studies, mainly concerned with the mode of transmission of leprosy, and which included biopsies of skin, dartos muscle, nasal mucous membrane and nipple, results of which have already been published. Examination of serial sections by light microscopy revealed a density of cellular infiltration in non-lepromatous cases, or of bacilli in macrophages and Schwann cells in lepromatous cases, which was marked in degree and usually widespread from one end of the biopsy to the other. Intraneural caseation was recorded in four patients with tuberculoid or borderline-tuberculoid leprosy, and many others in this part of the spectrum showed extensive disruption of perineurial and endoneurial structure. In lepromatous patients, the numbers of bacilli in the endoneurial area not infrequently exceeded one thousand per oil immersion field. Although well known to histopathologists familiar with this disease, it is considered that the significance of these findings, in patients presenting for the first time, is not well appreciated by those working in general medicine, neurology, epidemiology, or even in leprosy control.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antia N. H. The significance of nerve involvement in leprosy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1974 Jul;54(1):55–63. doi: 10.1097/00006534-197407000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastur D. K., Pandya S. S., Antia N. H. Nerves in the arm in leprosy. 2. Pathology, pathogenesis and clinical correlations. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1970 Jan-Mar;38(1):30–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dastur D. K., Ramamohan Y., Shah J. S. Ultrastructure of lepromatous nerves. Neural pathogenesis in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1973 Jan-Mar;41(1):47–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness M. A., Ranney D. A. Nerve enlargement in relation to classification of leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1971 Sep;42(3):208–218. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19710025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman D. J. Field workers' forum. Biopsies in leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1975 Jun;46(2):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyer C. G. Predilection of M. leprae for nerves. Neurohistopathologic observations. Int J Lepr. 1965 Jul-Sep;33(3 Suppl):634–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job C. K., Desikan K. V. Pathologic changes and their distribution in peripheral nerves in lepromatous leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1968 Jul-Sep;36(3):257–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job C. K. Mycobacterium leprae in nerve lesions in lepromatous leprosy. An electron microscopic study. Arch Pathol. 1970 Mar;89(3):195–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Job C. K. Pathology of peripheral nerve lesions in lepromatous leprosy--a light and electron microscopic study. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1971 Apr-Jun;39(2):251–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn P., Scott T. The pathology of a radial nerve biopsy in leprosy: light and electron microscopy. J Pathol. 1974 Oct;114(2):97–100. doi: 10.1002/path.1711140209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karat A. B., Furness M. A., Karat S., Rao P. S. Patterns of neurological involvement in relation to chronic and-or recurrent erythema nodosum leprosum. Lepr Rev. 1969 Jan;40(1):49–53. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19690007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karat S., Rao P. S., Karat B. A. Prevalence of deformities and disabilities among leprosy patients in an endemic area. II. Nerve involvement in the limbs. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1972 Jul-Sep;40(3):265–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHIURA M. The electron microscopic basis of the pathology of leprosy. Int J Lepr. 1960 Oct-Dec;28:357–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naafs B., Pearson J. M., Baar A. J. A follow-up study of nerve lesions in leprosy during and after reaction using motor nerve conduction velocity. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1976 Jan-Jun;44(1-2):188–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley J. C., Geater J. G. Does droplet infection play a role in the transmission of leprosy? Lepr Rev. 1976 Jun;47(2):97–102. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19760018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley J. C. The nasal mucus in leprosy. Lepr Rev. 1973 Mar;44(1):33–35. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19730005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley J. C. The presence of M. leprae in human milk. Lepr Rev. 1967 Oct;38(4):239–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REES R. J., VALENTINE R. C. The appearance of dead leprosy bacilli by light and electron microscopy. Int J Lepr. 1962 Jan-Mar;30:1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S. Histological classification and the immunological spectrum of leprosy. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51(5):451–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Jopling W. H. Classification of leprosy according to immunity. A five-group system. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1966 Jul-Sep;34(3):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley D. S., Waters M. F. Significance of variations within the lepromatous group. Lepr Rev. 1969 Jul;40(3):143–152. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19690026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin T. D., Ebner J. D. Patterns of sensory loss in lepromatous leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1969 Jul-Sep;37(3):239–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland S. The internal anatomy of nerve trunks in relation to the neural lesions of leprosy. Observations on pathology, symptomatology and treatment. Brain. 1973 Dec;96(4):865–888. doi: 10.1093/brain/96.4.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M., Ittimani K. V., Satyanarayan K. R., Mathai R., Bhakthaviziam C. A study of the conduction velocity of the motor fibers of ulnar and median nerves in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1970 Jul-Sep;38(3):271–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELER E. A., HAMILTON E. G., HARMAN D. J. AN IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR THE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF LEPROSY. Lepr Rev. 1965 Jan;36:37–39. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19650010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. F., Rees R. J., McDougall A. C., Weddell A. G. Ten years of dapsone in lepromatous leprosy: clinical, bacteriological and histological assessment and the finding of viable leprosy bacilli. Lepr Rev. 1974 Dec;45(4):288–298. doi: 10.5935/0305-7518.19740034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







