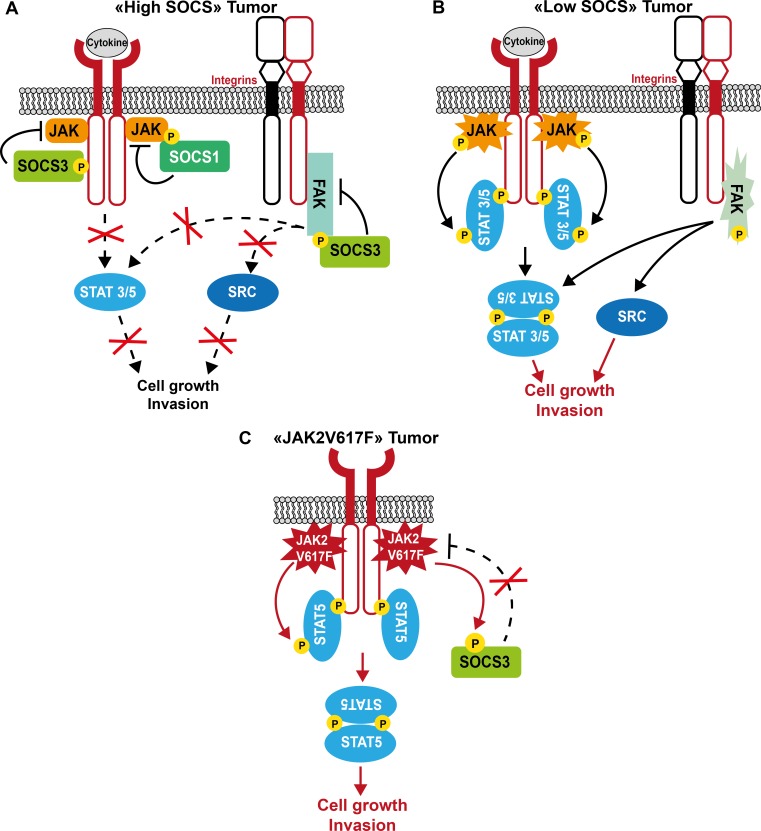
Figure 3. Model of SOCS tumor suppressor function in human cancer.
A. In tumor cells with high SOCS expression, these adaptor proteins inhibit tumor cell growth by controlling JAK/STAT-dependent cytokine signaling, and restrict integrin-dependent cell invasion by inhibiting FAK/SRC signaling. B. Upon SOCS inactivation in tumor cells, cytokine and integrin signaling are exacerbated, thus contributing to tumor progression. C. Upon expression of the JAK2V617F oncogene, SOCS inhibitory function is inactivated by tyrosine phosphorylation, which results in increased JAK2V617F oncogenic activity.