Abstract
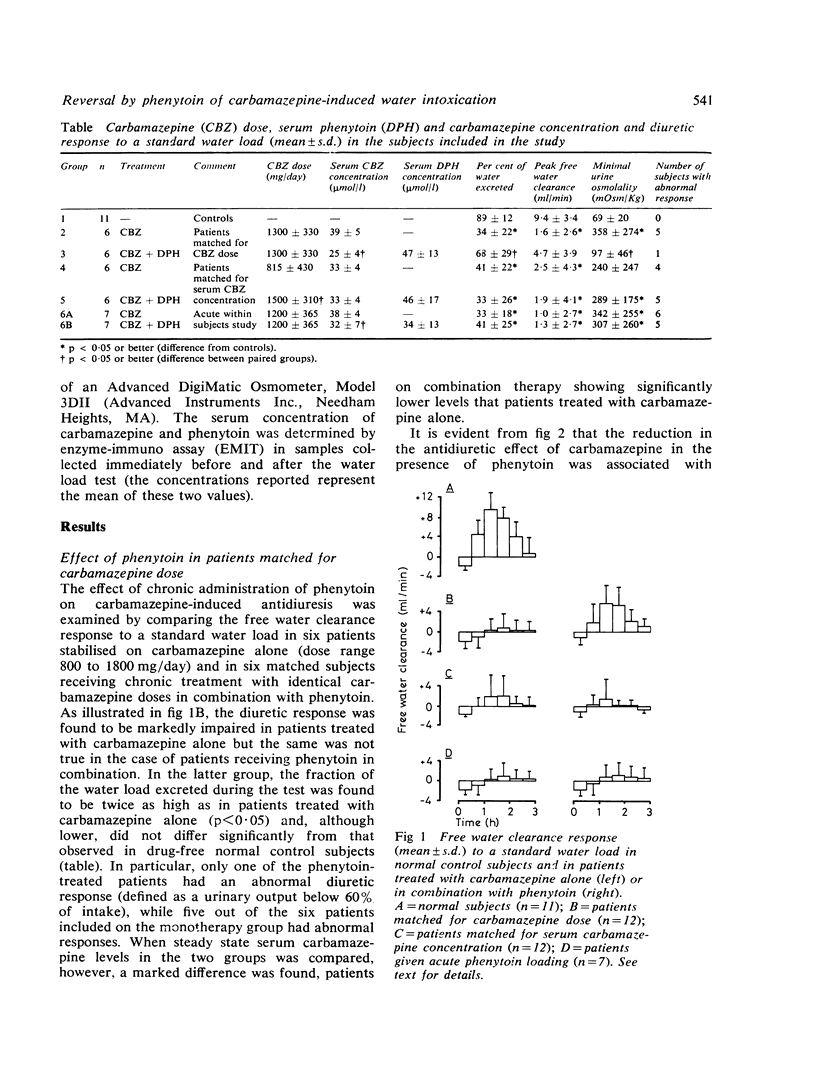
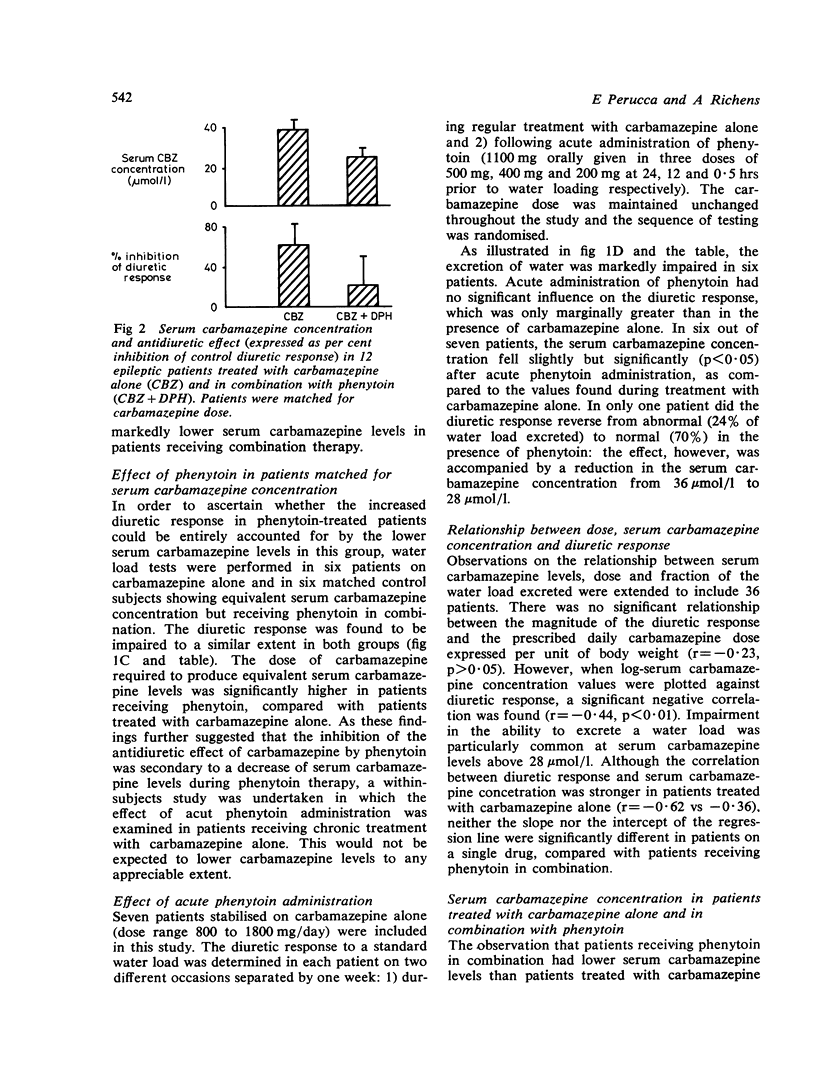
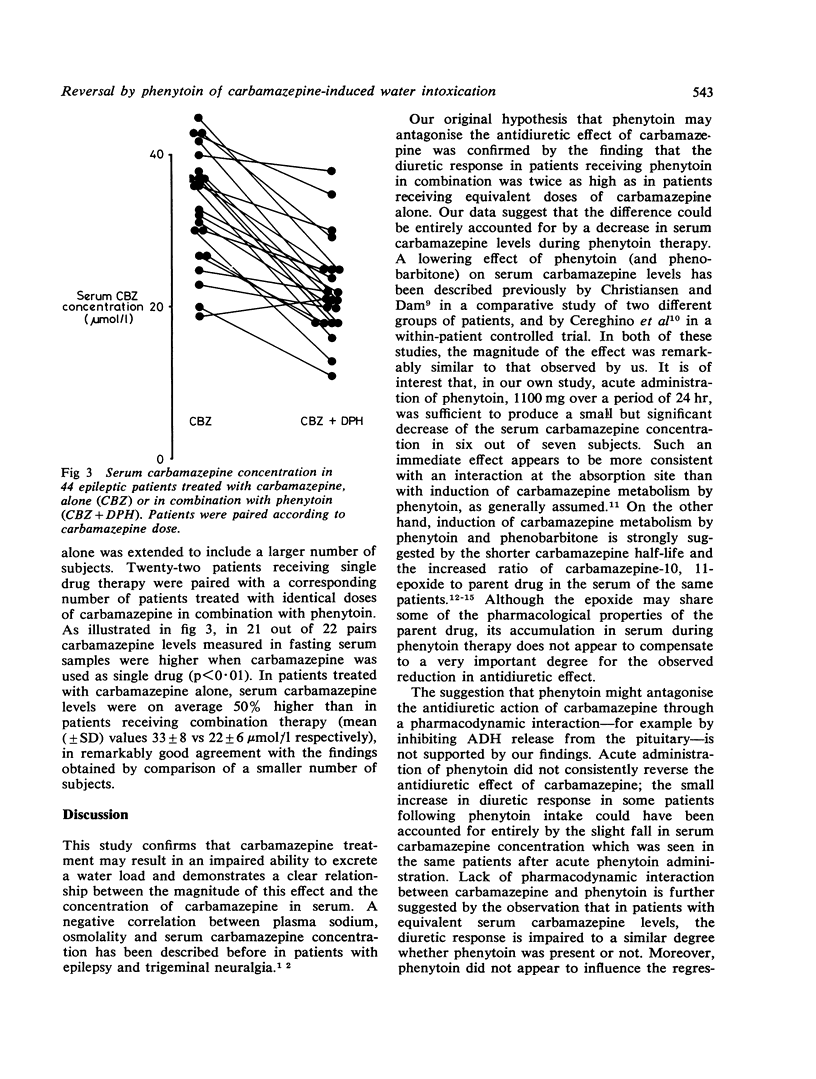
The hypothesis that phenytoin may antagonise the antidiuretic effect of carbamazepine has been examined by comparing the free water clearance response to a standard water load in 36 patients stabilised on different drug regimes. The diuretic response to the water load was significantly greater in patients receiving chronic treatment with carbamazepine and phenytoin in combination than in matched control subjects receiving carbamazepine as a single drug. Acute administration of phenytoin (1,100 mg), however, had no significant influence on carbamazepine-induced antidiuresis. Evidence is presented that reversal of the antidiuretic effect of carbamazepine by chronic phenytoin administration is secondary to a marked reduction of the serum carbamazepine concentration during combined therapy. These results suggest that the risk of developing water intoxication is greater in patients receiving carbamazepine alone than in those receiving phenytoin in combination. Since the antidiuretic effect is correlated with the serum carbamazepine concentration rather than with the prescribed daily dose, monitoring the serum level of the drug is likely to provide the best rational approach to the prevention of excessive water retention.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton M. G., Ball S. G., Thomas T. H., Lee M. R. Water intoxication associated with carbamazepine treatment. Br Med J. 1977 Apr 30;1(6069):1134–1135. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6069.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghino J. J., Brock J. T., Van Meter J. C., Penry J. K., Smith L. D., White B. G. The efficacy of carbamazepine combinations in epilepsy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Dec;18(6):733–741. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975186733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J., Dam M. Influence of phenobarbital and diphenylhydantoin on plasma carbamazepine levels in patients with epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1973;49(4):543–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1973.tb01327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam M., Jensen A., Christiansen J. Plasma level and effect of carbamazepine in grand mal and psychomotor epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1975;60:33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1975.tb01385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichelbaum M., Köthe K. W., Hoffman F., von Unruh G. E. Kinetics and metabolism of carbamazepine during combined antiepileptic drug therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Sep;26(3):366–371. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979263366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichman M. P., Bethune J. E. The role of adrenocorticoids in the inappropriate antidiuretic hormone syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Apr;68(4):806–820. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-4-806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichman M. P., Kleeman C. R., Bethune J. E. Inhibition of antidiuretic hormone secretion by diphenylhydantoin. Arch Neurol. 1970 Jan;22(1):45–53. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480190049008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry D. A., Lawson D. H., Reavey P., Renfrew S. Hyponatraemia during carbamazepine treatment. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 8;1(6053):83–84. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6053.83-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucca E., Garratt A., Hebdige S., Richens A. Water intoxication in epileptic patients receiving carbamazepine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Aug;41(8):713–718. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.8.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rane A., Höjer B., Wilson J. T. Kinetics of carbamazepine and its 10,11-epoxide metabolite in children. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Mar;19(3):276–283. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976193276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. J., Espir M. L., Baylis P. H. Raised plasma arginine vasopressin concentration in carbamazepine-induced water intoxication. Br Med J. 1977 Sep 24;2(6090):804–804. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6090.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordillo P., Sagransky D. M., Mercado R. M., Michelis M. F. Carbamazepine-induced syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Reversal by concomitant phenytoin therapy. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Feb;138(2):299–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens W. P., Coe J. Y., Baylis P. H. Plasma arginine vasopressin concentrations and antidiuretic action of carbamazepine. Br Med J. 1978 Jun 3;1(6125):1445–1447. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6125.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens W. P., Espir M. L., Tattersall R. B., Quinn N. P., Gladwell S. R., Galbraith A. W., Reynolds E. H. Water intoxication due to carbamazepine. Br Med J. 1977 Mar 19;1(6063):754–755. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6063.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanay A., Yust I., Peresecenschi G., Abramov A. L., Aviram A. Long-term treatment of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion with phenytoin. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jan;90(1):50–52. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-1-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenberg H. G., van der Kleijn E., Oei T. T., de Zeeuw R. A. Kinetics of carbamazepine and carbamazepine-epoxide, determined by use of plasma and saliva. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Mar;23(3):320–328. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978233320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



